| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1165828 | 1491092 | 2012 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
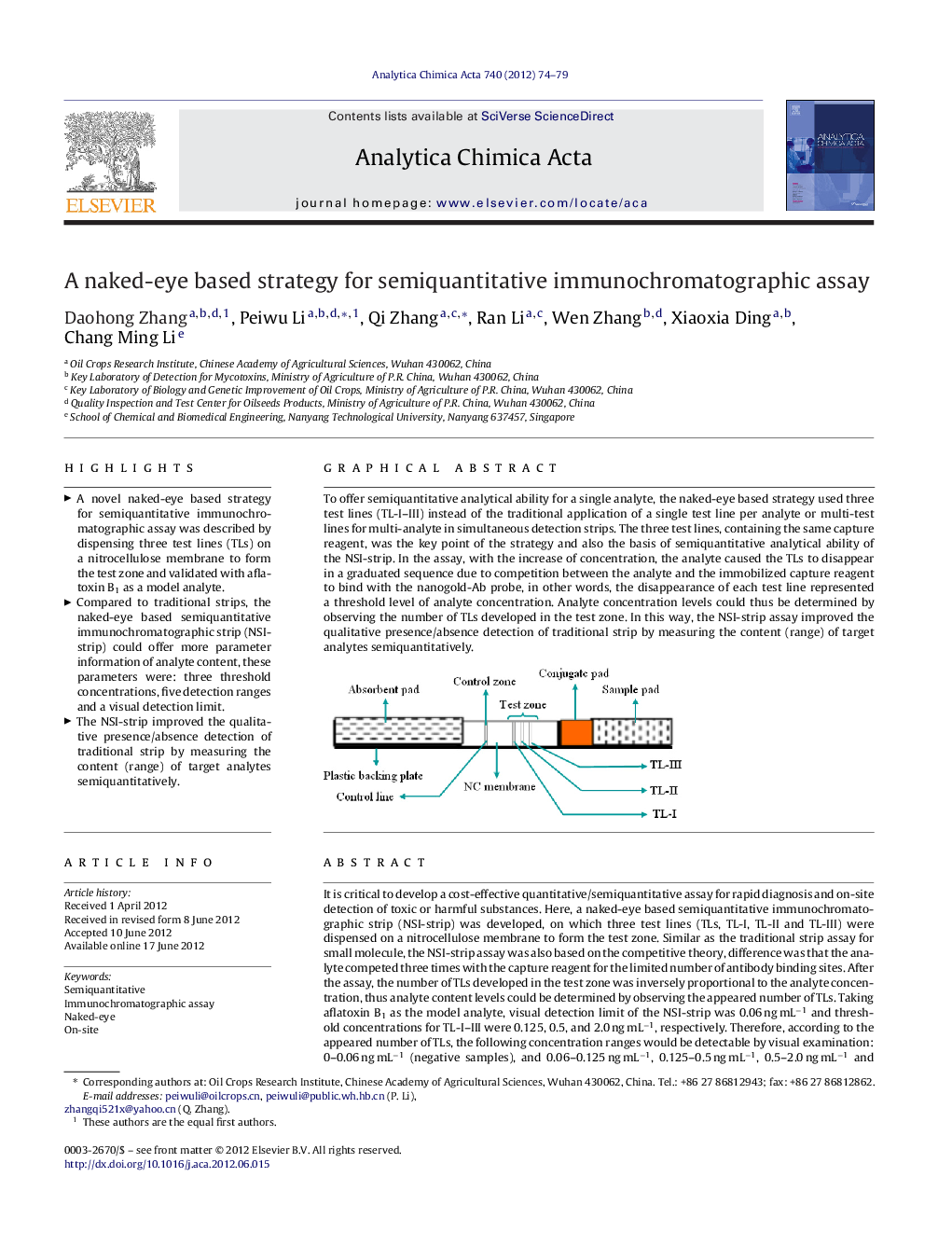
It is critical to develop a cost-effective quantitative/semiquantitative assay for rapid diagnosis and on-site detection of toxic or harmful substances. Here, a naked-eye based semiquantitative immunochromatographic strip (NSI-strip) was developed, on which three test lines (TLs, TL-I, TL-II and TL-III) were dispensed on a nitrocellulose membrane to form the test zone. Similar as the traditional strip assay for small molecule, the NSI-strip assay was also based on the competitive theory, difference was that the analyte competed three times with the capture reagent for the limited number of antibody binding sites. After the assay, the number of TLs developed in the test zone was inversely proportional to the analyte concentration, thus analyte content levels could be determined by observing the appeared number of TLs. Taking aflatoxin B1 as the model analyte, visual detection limit of the NSI-strip was 0.06 ng mL−1 and threshold concentrations for TL-I–III were 0.125, 0.5, and 2.0 ng mL−1, respectively. Therefore, according to the appeared number of TLs, the following concentration ranges would be detectable by visual examination: 0–0.06 ng mL−1 (negative samples), and 0.06–0.125 ng mL−1, 0.125–0.5 ng mL−1, 0.5–2.0 ng mL−1 and >2.0 ng mL−1 (positive samples). That was to say, compared to traditional strips the NSI-strip could offer more parameter information of the target analyte content. In this way, the NSI-strip improved the qualitative presence/absence detection of traditional strips by measuring the content (range) of target analytes semiquantitatively.
To offer semiquantitative analytical ability for a single analyte, the naked-eye based strategy used three test lines (TL-I–III) instead of the traditional application of a single test line per analyte or multi-test lines for multi-analyte in simultaneous detection strips. The three test lines, containing the same capture reagent, was the key point of the strategy and also the basis of semiquantitative analytical ability of the NSI-strip. In the assay, with the increase of concentration, the analyte caused the TLs to disappear in a graduated sequence due to competition between the analyte and the immobilized capture reagent to bind with the nanogold-Ab probe, in other words, the disappearance of each test line represented a threshold level of analyte concentration. Analyte concentration levels could thus be determined by observing the number of TLs developed in the test zone. In this way, the NSI-strip assay improved the qualitative presence/absence detection of traditional strip by measuring the content (range) of target analytes semiquantitatively.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► A novel naked-eye based strategy for semiquantitative immunochromatographic assay was described by dispensing three test lines (TLs) on a nitrocellulose membrane to form the test zone and validated with aflatoxin B1 as a model analyte.
► Compared to traditional strips, the naked-eye based semiquantitative immunochromatographic strip (NSI-strip) could offer more parameter information of analyte content, these parameters were: three threshold concentrations, five detection ranges and a visual detection limit.
► The NSI-strip improved the qualitative presence/absence detection of traditional strip by measuring the content (range) of target analytes semiquantitatively.
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 740, 31 August 2012, Pages 74–79