| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1402184 | 1501738 | 2015 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
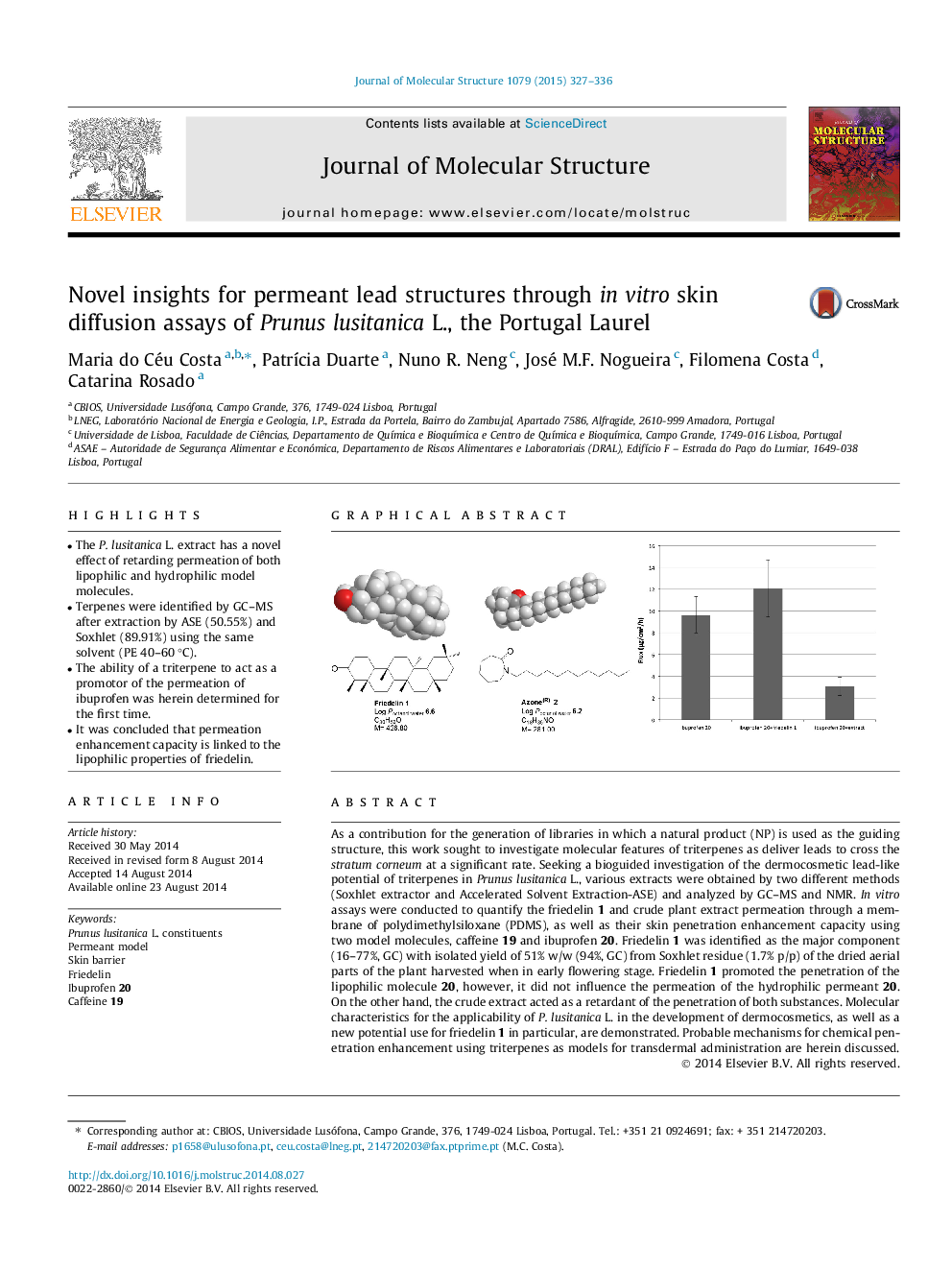
• The P. lusitanica L. extract has a novel effect of retarding permeation of both lipophilic and hydrophilic model molecules.
• Terpenes were identified by GC–MS after extraction by ASE (50.55%) and Soxhlet (89.91%) using the same solvent (PE 40–60 °C).
• The ability of a triterpene to act as a promotor of the permeation of ibuprofen was herein determined for the first time.
• It was concluded that permeation enhancement capacity is linked to the lipophilic properties of friedelin.
As a contribution for the generation of libraries in which a natural product (NP) is used as the guiding structure, this work sought to investigate molecular features of triterpenes as deliver leads to cross the stratum corneum at a significant rate. Seeking a bioguided investigation of the dermocosmetic lead-like potential of triterpenes in Prunus lusitanica L., various extracts were obtained by two different methods (Soxhlet extractor and Accelerated Solvent Extraction-ASE) and analyzed by GC–MS and NMR. In vitro assays were conducted to quantify the friedelin 1 and crude plant extract permeation through a membrane of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), as well as their skin penetration enhancement capacity using two model molecules, caffeine 19 and ibuprofen 20. Friedelin 1 was identified as the major component (16–77%, GC) with isolated yield of 51% w/w (94%, GC) from Soxhlet residue (1.7% p/p) of the dried aerial parts of the plant harvested when in early flowering stage. Friedelin 1 promoted the penetration of the lipophilic molecule 20, however, it did not influence the permeation of the hydrophilic permeant 20. On the other hand, the crude extract acted as a retardant of the penetration of both substances. Molecular characteristics for the applicability of P. lusitanica L. in the development of dermocosmetics, as well as a new potential use for friedelin 1 in particular, are demonstrated. Probable mechanisms for chemical penetration enhancement using triterpenes as models for transdermal administration are herein discussed.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Journal of Molecular Structure - Volume 1079, 5 January 2015, Pages 327–336