| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1408341 | 1501736 | 2015 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Ethylammonium nitrate helps in folding–refolding of hydrated cytochrome c.
• Ionic liquid assembly around cytochrome c stabilizes it against denaturation.
• Protein with ethyl ammonium nitrate is compacter than the native state.
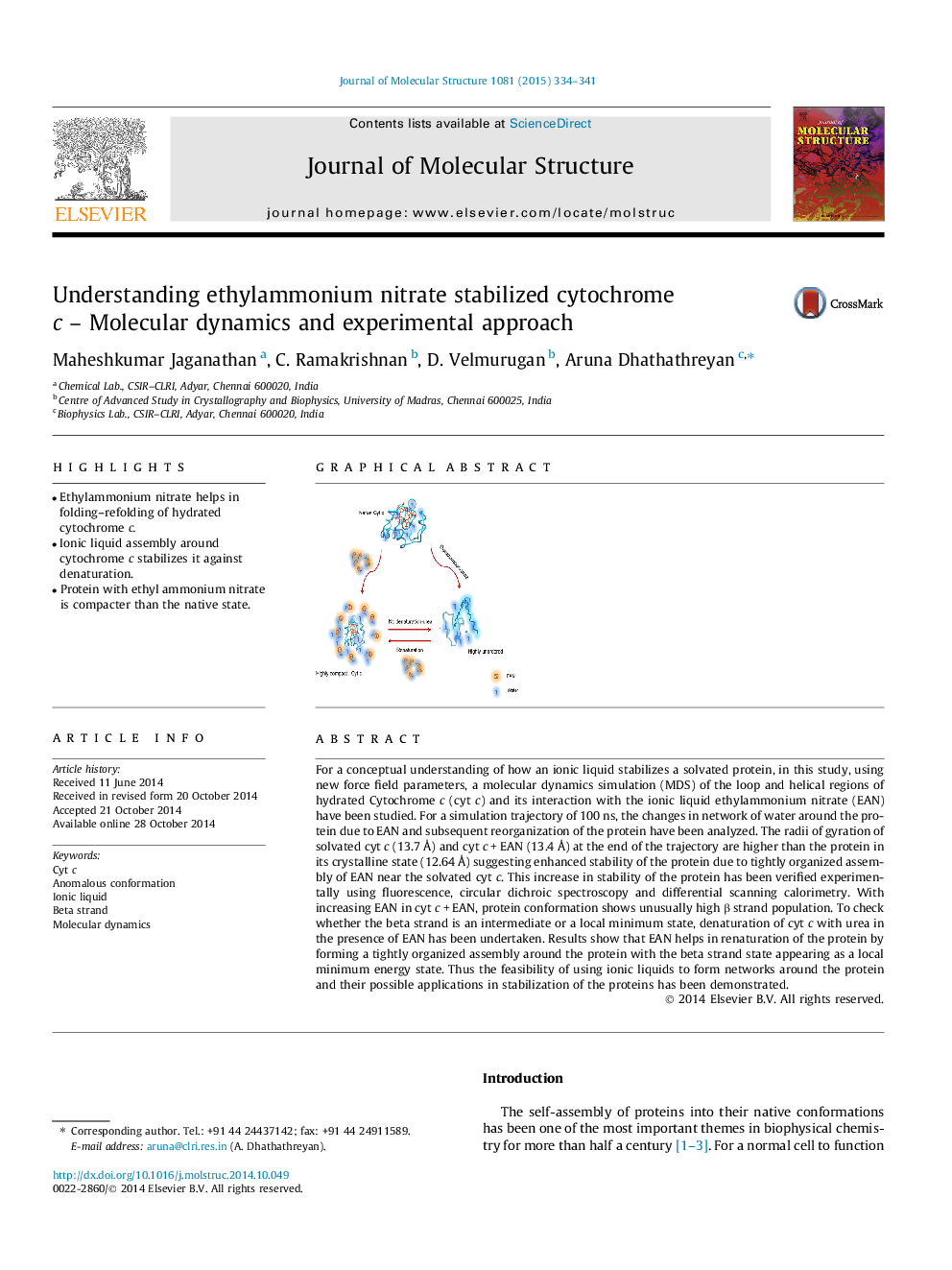
For a conceptual understanding of how an ionic liquid stabilizes a solvated protein, in this study, using new force field parameters, a molecular dynamics simulation (MDS) of the loop and helical regions of hydrated Cytochrome c (cyt c) and its interaction with the ionic liquid ethylammonium nitrate (EAN) have been studied. For a simulation trajectory of 100 ns, the changes in network of water around the protein due to EAN and subsequent reorganization of the protein have been analyzed. The radii of gyration of solvated cyt c (13.7 Å) and cyt c + EAN (13.4 Å) at the end of the trajectory are higher than the protein in its crystalline state (12.64 Å) suggesting enhanced stability of the protein due to tightly organized assembly of EAN near the solvated cyt c. This increase in stability of the protein has been verified experimentally using fluorescence, circular dichroic spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. With increasing EAN in cyt c + EAN, protein conformation shows unusually high β strand population. To check whether the beta strand is an intermediate or a local minimum state, denaturation of cyt c with urea in the presence of EAN has been undertaken. Results show that EAN helps in renaturation of the protein by forming a tightly organized assembly around the protein with the beta strand state appearing as a local minimum energy state. Thus the feasibility of using ionic liquids to form networks around the protein and their possible applications in stabilization of the proteins has been demonstrated.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Journal of Molecular Structure - Volume 1081, 5 February 2015, Pages 334–341