| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148121 | 456406 | 2013 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
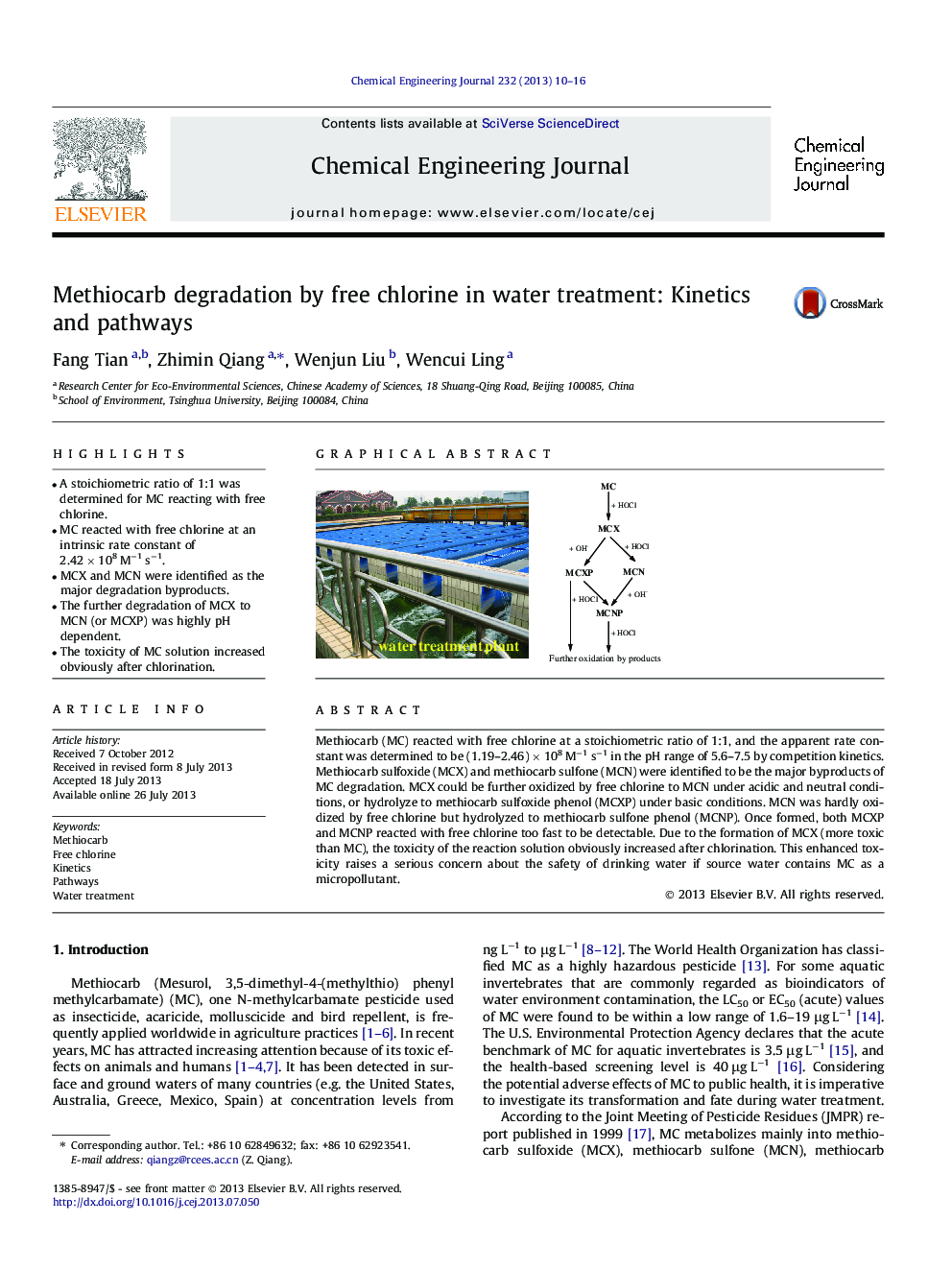
• A stoichiometric ratio of 1:1 was determined for MC reacting with free chlorine.
• MC reacted with free chlorine at an intrinsic rate constant of 2.42 × 108 M−1 s−1.
• MCX and MCN were identified as the major degradation byproducts.
• The further degradation of MCX to MCN (or MCXP) was highly pH dependent.
• The toxicity of MC solution increased obviously after chlorination.
Methiocarb (MC) reacted with free chlorine at a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1, and the apparent rate constant was determined to be (1.19–2.46) × 108 M−1 s−1 in the pH range of 5.6–7.5 by competition kinetics. Methiocarb sulfoxide (MCX) and methiocarb sulfone (MCN) were identified to be the major byproducts of MC degradation. MCX could be further oxidized by free chlorine to MCN under acidic and neutral conditions, or hydrolyze to methiocarb sulfoxide phenol (MCXP) under basic conditions. MCN was hardly oxidized by free chlorine but hydrolyzed to methiocarb sulfone phenol (MCNP). Once formed, both MCXP and MCNP reacted with free chlorine too fast to be detectable. Due to the formation of MCX (more toxic than MC), the toxicity of the reaction solution obviously increased after chlorination. This enhanced toxicity raises a serious concern about the safety of drinking water if source water contains MC as a micropollutant.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 232, October 2013, Pages 10–16