| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148500 | 456417 | 2013 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
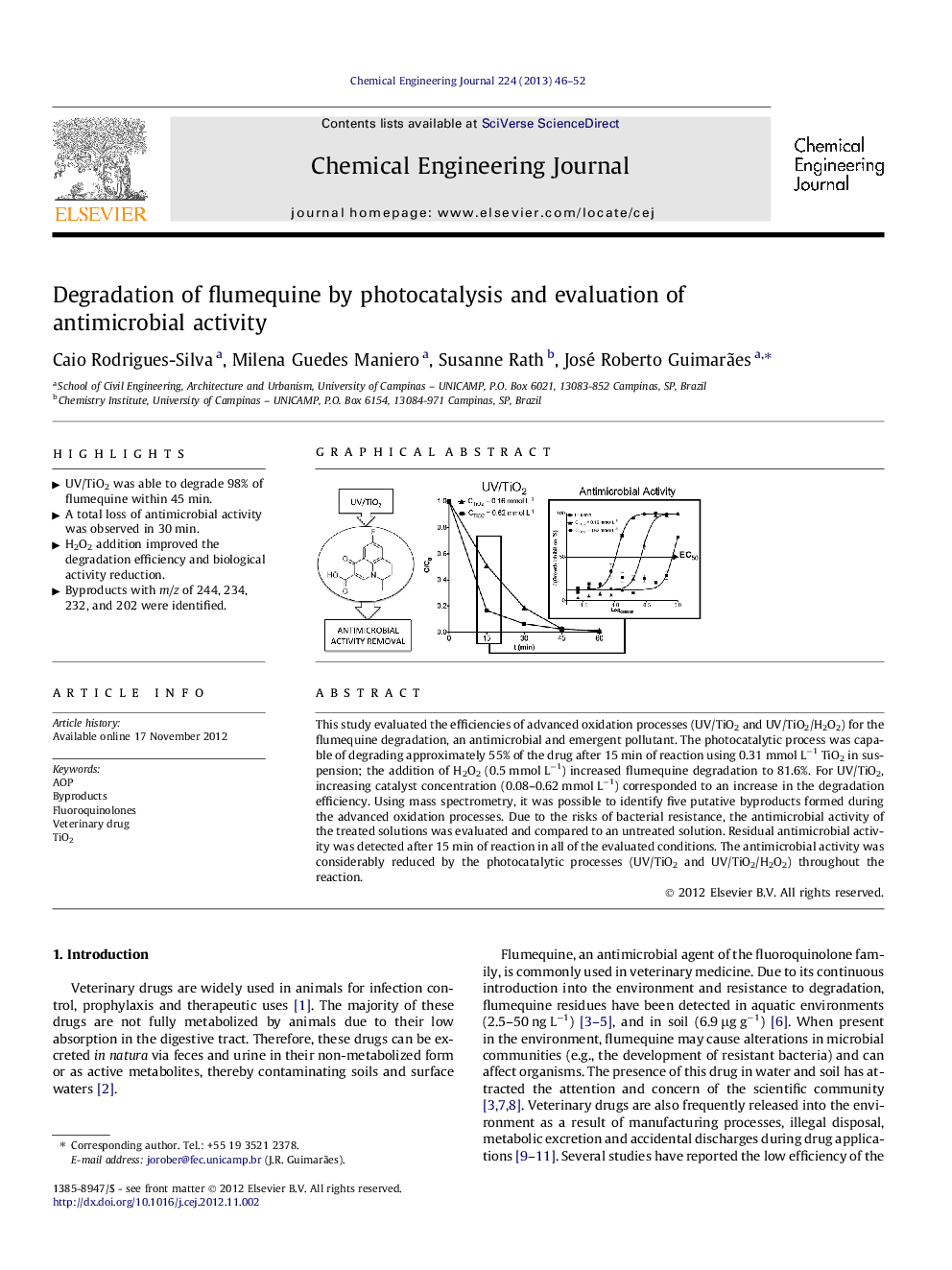
This study evaluated the efficiencies of advanced oxidation processes (UV/TiO2 and UV/TiO2/H2O2) for the flumequine degradation, an antimicrobial and emergent pollutant. The photocatalytic process was capable of degrading approximately 55% of the drug after 15 min of reaction using 0.31 mmol L−1 TiO2 in suspension; the addition of H2O2 (0.5 mmol L−1) increased flumequine degradation to 81.6%. For UV/TiO2, increasing catalyst concentration (0.08–0.62 mmol L−1) corresponded to an increase in the degradation efficiency. Using mass spectrometry, it was possible to identify five putative byproducts formed during the advanced oxidation processes. Due to the risks of bacterial resistance, the antimicrobial activity of the treated solutions was evaluated and compared to an untreated solution. Residual antimicrobial activity was detected after 15 min of reaction in all of the evaluated conditions. The antimicrobial activity was considerably reduced by the photocatalytic processes (UV/TiO2 and UV/TiO2/H2O2) throughout the reaction.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► UV/TiO2 was able to degrade 98% of flumequine within 45 min.
► A total loss of antimicrobial activity was observed in 30 min.
► H2O2 addition improved the degradation efficiency and biological activity reduction.
► Byproducts with m/z of 244, 234, 232, and 202 were identified.
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 224, 15 May 2013, Pages 46–52