| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148552 | 456419 | 2013 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
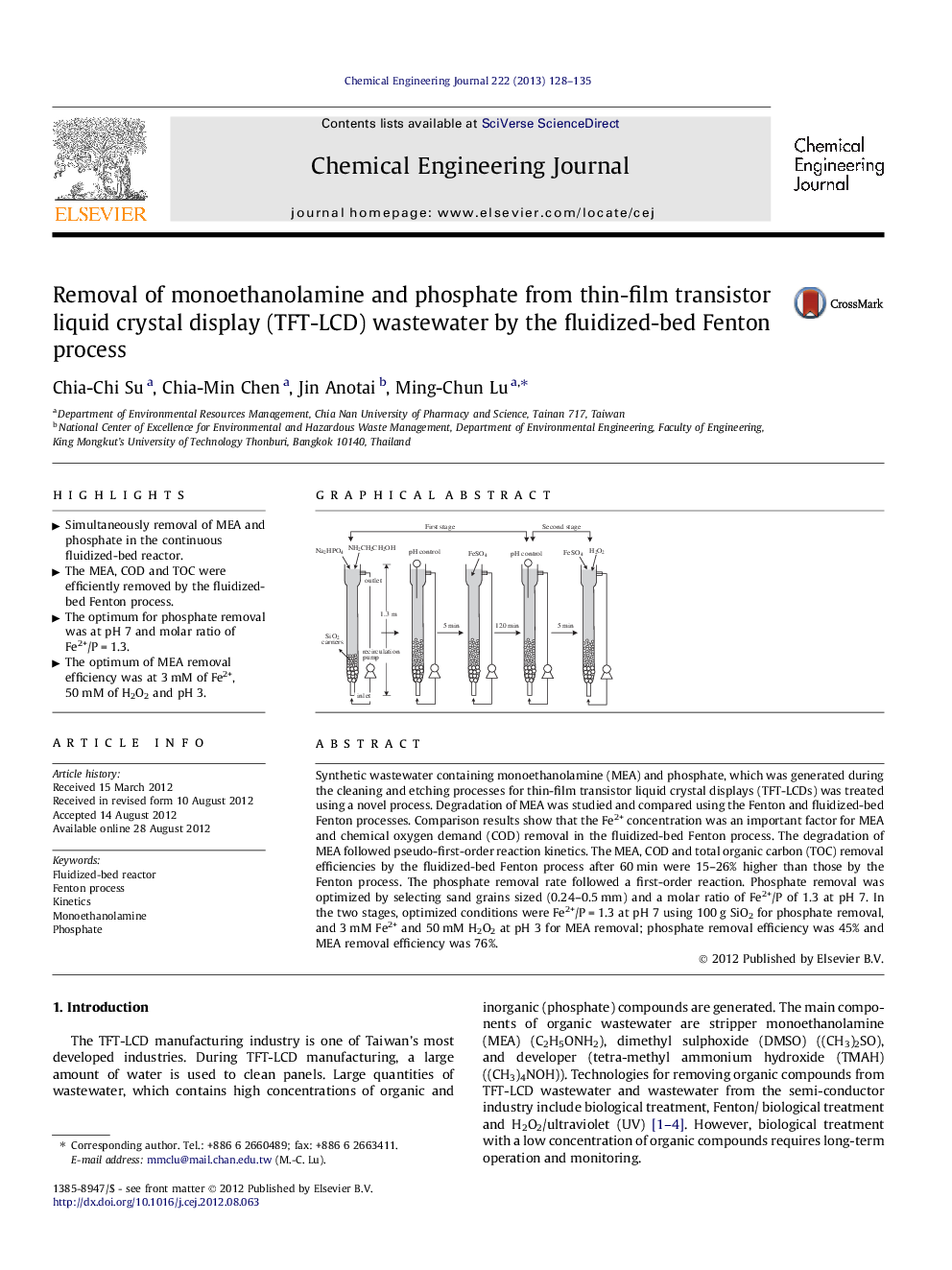
Synthetic wastewater containing monoethanolamine (MEA) and phosphate, which was generated during the cleaning and etching processes for thin-film transistor liquid crystal displays (TFT-LCDs) was treated using a novel process. Degradation of MEA was studied and compared using the Fenton and fluidized-bed Fenton processes. Comparison results show that the Fe2+ concentration was an important factor for MEA and chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal in the fluidized-bed Fenton process. The degradation of MEA followed pseudo-first-order reaction kinetics. The MEA, COD and total organic carbon (TOC) removal efficiencies by the fluidized-bed Fenton process after 60 min were 15–26% higher than those by the Fenton process. The phosphate removal rate followed a first-order reaction. Phosphate removal was optimized by selecting sand grains sized (0.24–0.5 mm) and a molar ratio of Fe2+/P of 1.3 at pH 7. In the two stages, optimized conditions were Fe2+/P = 1.3 at pH 7 using 100 g SiO2 for phosphate removal, and 3 mM Fe2+ and 50 mM H2O2 at pH 3 for MEA removal; phosphate removal efficiency was 45% and MEA removal efficiency was 76%.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Simultaneously removal of MEA and phosphate in the continuous fluidized-bed reactor.
► The MEA, COD and TOC were efficiently removed by the fluidized-bed Fenton process.
► The optimum for phosphate removal was at pH 7 and molar ratio of Fe2+/P = 1.3.
► The optimum of MEA removal efficiency was at 3 mM of Fe2+, 50 mM of H2O2 and pH 3.
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 222, 15 April 2013, Pages 128–135