| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148853 | 456423 | 2013 | 13 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
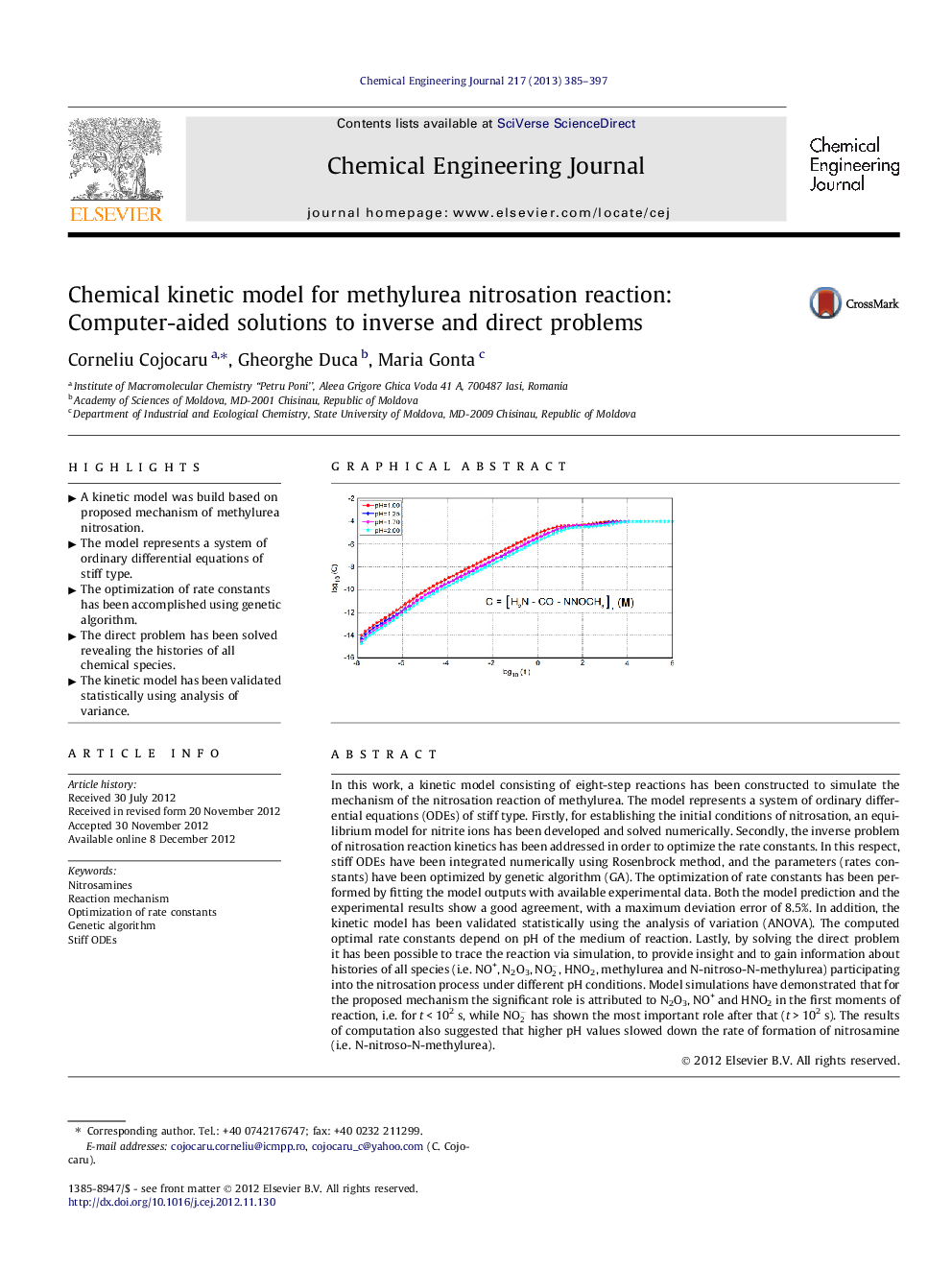
In this work, a kinetic model consisting of eight-step reactions has been constructed to simulate the mechanism of the nitrosation reaction of methylurea. The model represents a system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) of stiff type. Firstly, for establishing the initial conditions of nitrosation, an equilibrium model for nitrite ions has been developed and solved numerically. Secondly, the inverse problem of nitrosation reaction kinetics has been addressed in order to optimize the rate constants. In this respect, stiff ODEs have been integrated numerically using Rosenbrock method, and the parameters (rates constants) have been optimized by genetic algorithm (GA). The optimization of rate constants has been performed by fitting the model outputs with available experimental data. Both the model prediction and the experimental results show a good agreement, with a maximum deviation error of 8.5%. In addition, the kinetic model has been validated statistically using the analysis of variation (ANOVA). The computed optimal rate constants depend on pH of the medium of reaction. Lastly, by solving the direct problem it has been possible to trace the reaction via simulation, to provide insight and to gain information about histories of all species (i.e. NO+, N2O3, NO2-, HNO2, methylurea and N-nitroso-N-methylurea) participating into the nitrosation process under different pH conditions. Model simulations have demonstrated that for the proposed mechanism the significant role is attributed to N2O3, NO+ and HNO2 in the first moments of reaction, i.e. for t < 102 s, while NO2- has shown the most important role after that (t > 102 s). The results of computation also suggested that higher pH values slowed down the rate of formation of nitrosamine (i.e. N-nitroso-N-methylurea).
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► A kinetic model was build based on proposed mechanism of methylurea nitrosation.
► The model represents a system of ordinary differential equations of stiff type.
► The optimization of rate constants has been accomplished using genetic algorithm.
► The direct problem has been solved revealing the histories of all chemical species.
► The kinetic model has been validated statistically using analysis of variance.
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 217, 1 February 2013, Pages 385–397