| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148988 | 456425 | 2013 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
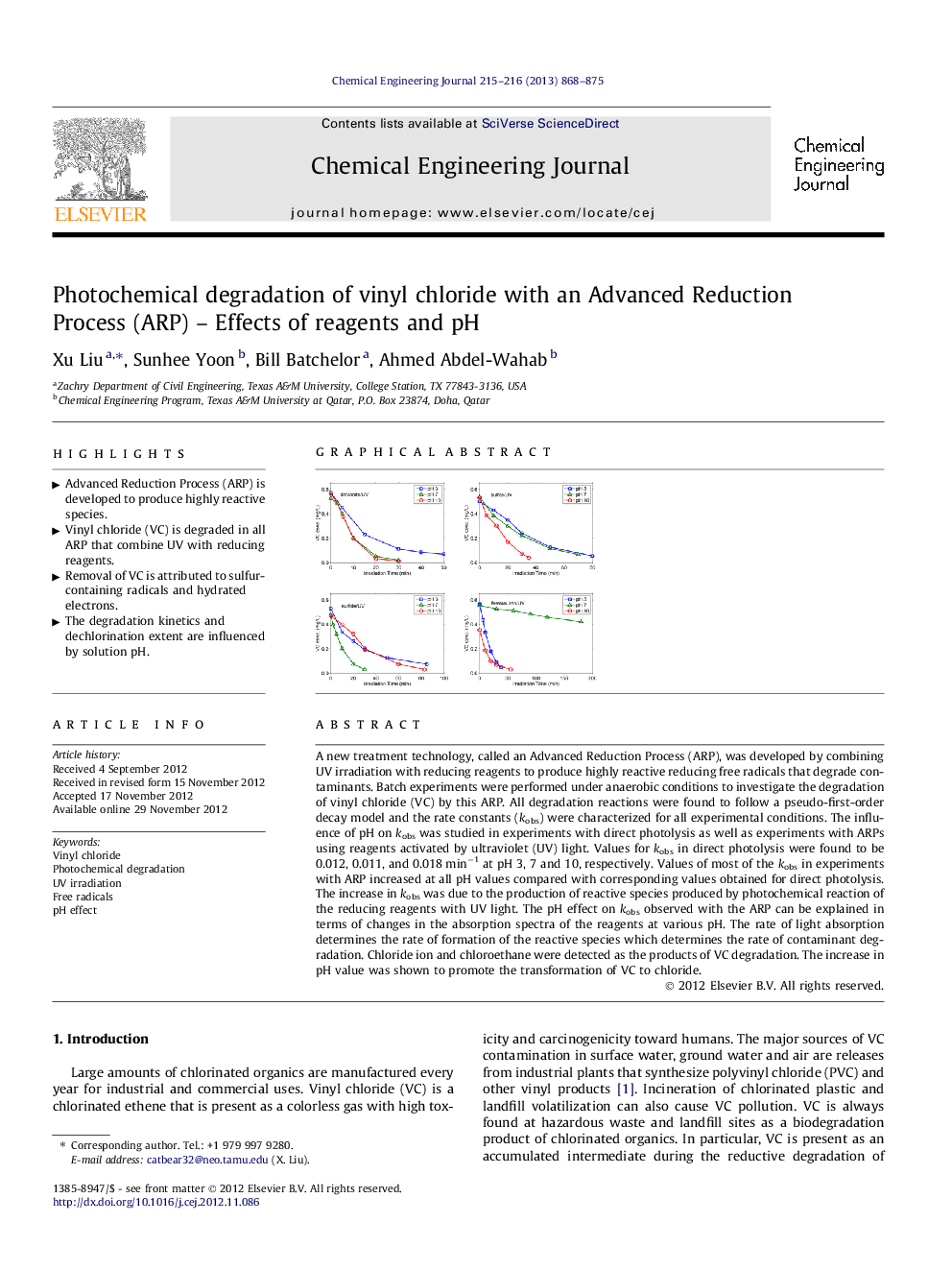
A new treatment technology, called an Advanced Reduction Process (ARP), was developed by combining UV irradiation with reducing reagents to produce highly reactive reducing free radicals that degrade contaminants. Batch experiments were performed under anaerobic conditions to investigate the degradation of vinyl chloride (VC) by this ARP. All degradation reactions were found to follow a pseudo-first-order decay model and the rate constants (kobs) were characterized for all experimental conditions. The influence of pH on kobs was studied in experiments with direct photolysis as well as experiments with ARPs using reagents activated by ultraviolet (UV) light. Values for kobs in direct photolysis were found to be 0.012, 0.011, and 0.018 min−1 at pH 3, 7 and 10, respectively. Values of most of the kobs in experiments with ARP increased at all pH values compared with corresponding values obtained for direct photolysis. The increase in kobs was due to the production of reactive species produced by photochemical reaction of the reducing reagents with UV light. The pH effect on kobs observed with the ARP can be explained in terms of changes in the absorption spectra of the reagents at various pH. The rate of light absorption determines the rate of formation of the reactive species which determines the rate of contaminant degradation. Chloride ion and chloroethane were detected as the products of VC degradation. The increase in pH value was shown to promote the transformation of VC to chloride.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
• Advanced Reduction Process (ARP) is developed to produce highly reactive species.
• Vinyl chloride (VC) is degraded in all ARP that combine UV with reducing reagents.
• Removal of VC is attributed to sulfur-containing radicals and hydrated electrons.
• The degradation kinetics and dechlorination extent are influenced by solution pH.
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volumes 215–216, 15 January 2013, Pages 868–875