| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 149595 | 456434 | 2012 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
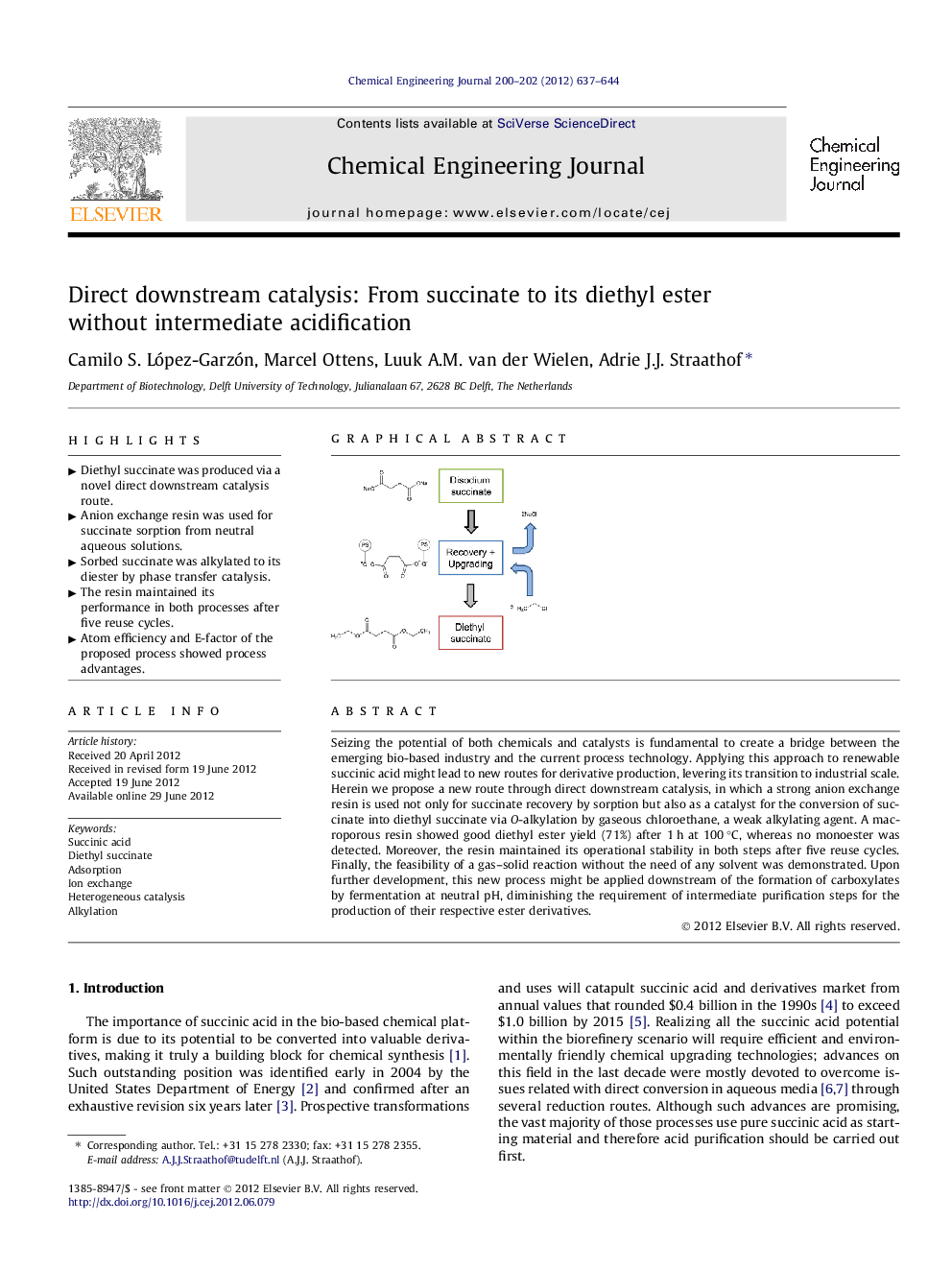
Seizing the potential of both chemicals and catalysts is fundamental to create a bridge between the emerging bio-based industry and the current process technology. Applying this approach to renewable succinic acid might lead to new routes for derivative production, levering its transition to industrial scale. Herein we propose a new route through direct downstream catalysis, in which a strong anion exchange resin is used not only for succinate recovery by sorption but also as a catalyst for the conversion of succinate into diethyl succinate via O-alkylation by gaseous chloroethane, a weak alkylating agent. A macroporous resin showed good diethyl ester yield (71%) after 1 h at 100 °C, whereas no monoester was detected. Moreover, the resin maintained its operational stability in both steps after five reuse cycles. Finally, the feasibility of a gas–solid reaction without the need of any solvent was demonstrated. Upon further development, this new process might be applied downstream of the formation of carboxylates by fermentation at neutral pH, diminishing the requirement of intermediate purification steps for the production of their respective ester derivatives.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Diethyl succinate was produced via a novel direct downstream catalysis route.
► Anion exchange resin was used for succinate sorption from neutral aqueous solutions.
► Sorbed succinate was alkylated to its diester by phase transfer catalysis.
► The resin maintained its performance in both processes after five reuse cycles.
► Atom efficiency and E-factor of the proposed process showed process advantages.
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volumes 200–202, 15 August 2012, Pages 637–644