| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4407331 | 1618806 | 2016 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Dimethenamid-P was rapidly biotransformed in submerged cultures of Irpex consors.
• The four main metabolites have not been reported in the literature before.
• 13C-labeled DMTA-P was used for structure elucidation of the metabolites.
• A stable thiophene S-oxide was identified.
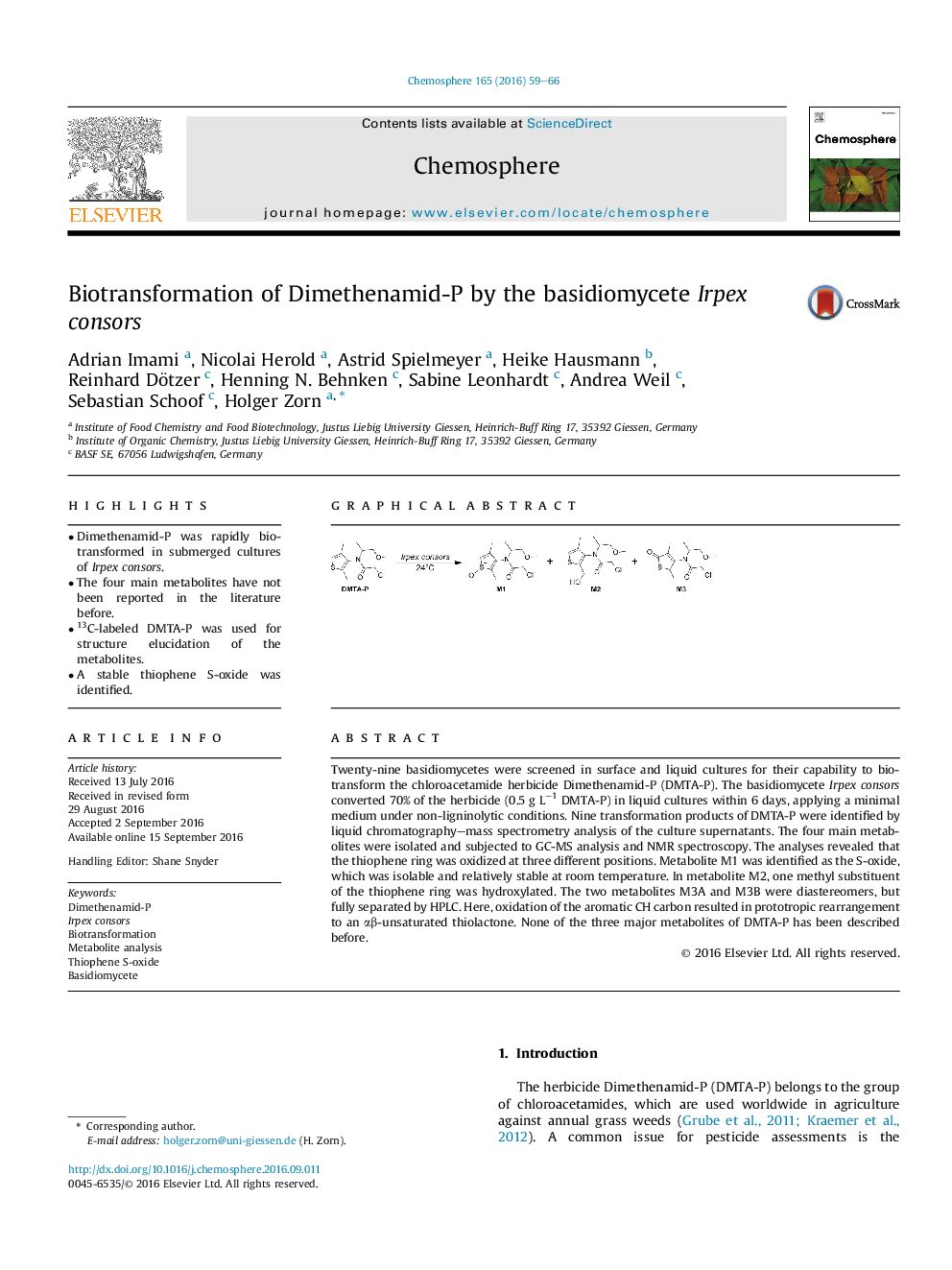
Twenty-nine basidiomycetes were screened in surface and liquid cultures for their capability to biotransform the chloroacetamide herbicide Dimethenamid-P (DMTA-P). The basidiomycete Irpex consors converted 70% of the herbicide (0.5 g L−1 DMTA-P) in liquid cultures within 6 days, applying a minimal medium under non-ligninolytic conditions. Nine transformation products of DMTA-P were identified by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of the culture supernatants. The four main metabolites were isolated and subjected to GC-MS analysis and NMR spectroscopy. The analyses revealed that the thiophene ring was oxidized at three different positions. Metabolite M1 was identified as the S-oxide, which was isolable and relatively stable at room temperature. In metabolite M2, one methyl substituent of the thiophene ring was hydroxylated. The two metabolites M3A and M3B were diastereomers, but fully separated by HPLC. Here, oxidation of the aromatic CH carbon resulted in prototropic rearrangement to an αβ-unsaturated thiolactone. None of the three major metabolites of DMTA-P has been described before.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 165, December 2016, Pages 59–66