| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4407954 | 1618825 | 2016 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Metabolism of BDE-47 and BDE-99 was examined using polar bear liver microsomes.
• Multiple hydroxylated metabolites of BDE-47 and BDE-99 were detected by UHPLC/MS/MS.
• The results clearly show that polar bears are capable of oxidative metabolism of PBDEs.
• Study provides insight into the fate of PBDEs in an arctic marine mammal.
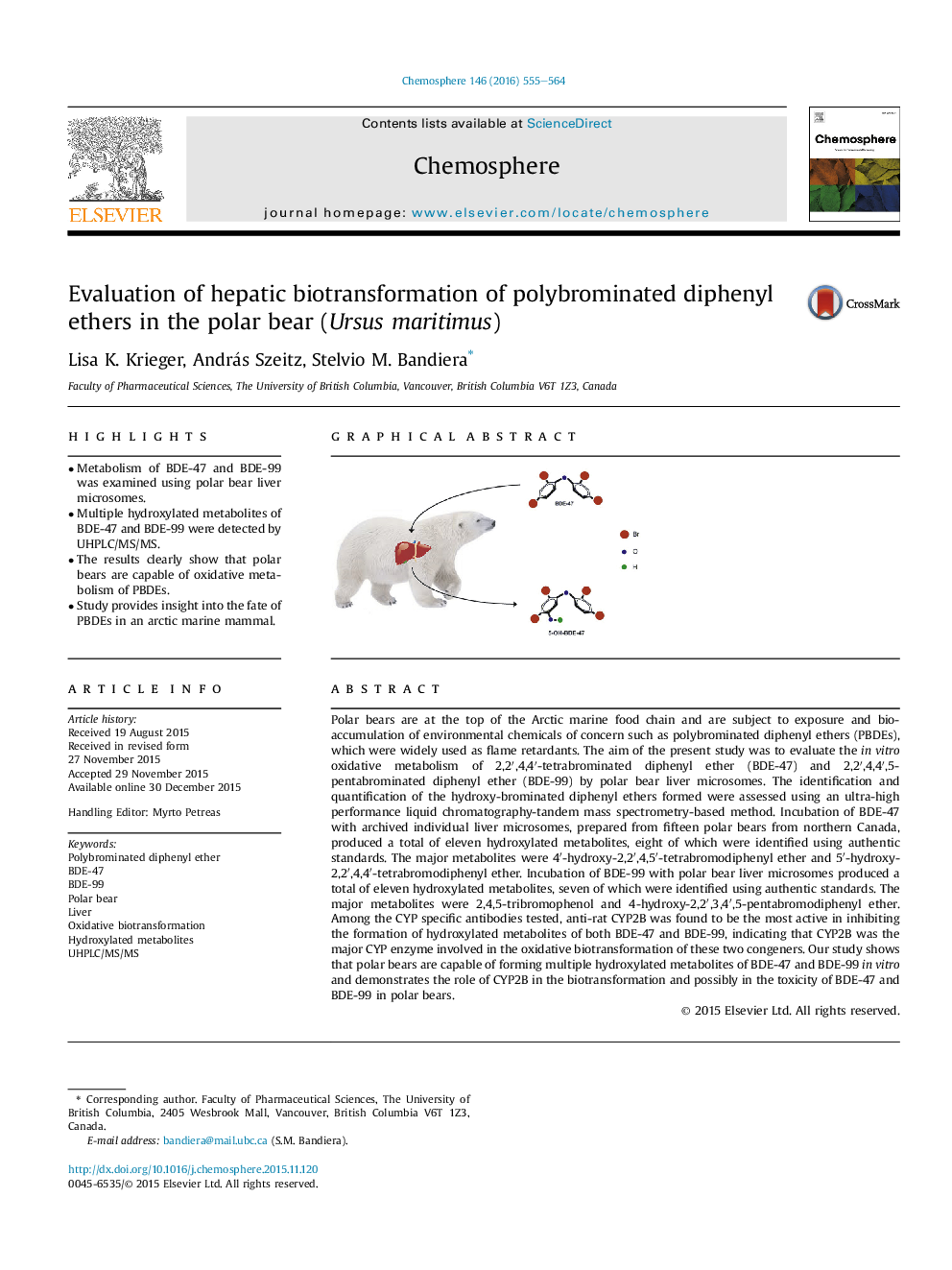
Polar bears are at the top of the Arctic marine food chain and are subject to exposure and bioaccumulation of environmental chemicals of concern such as polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), which were widely used as flame retardants. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the in vitro oxidative metabolism of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabrominated diphenyl ether (BDE-47) and 2,2′,4,4′,5-pentabrominated diphenyl ether (BDE-99) by polar bear liver microsomes. The identification and quantification of the hydroxy-brominated diphenyl ethers formed were assessed using an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based method. Incubation of BDE-47 with archived individual liver microsomes, prepared from fifteen polar bears from northern Canada, produced a total of eleven hydroxylated metabolites, eight of which were identified using authentic standards. The major metabolites were 4′-hydroxy-2,2′,4,5′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether and 5′-hydroxy-2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether. Incubation of BDE-99 with polar bear liver microsomes produced a total of eleven hydroxylated metabolites, seven of which were identified using authentic standards. The major metabolites were 2,4,5-tribromophenol and 4-hydroxy-2,2′,3,4′,5-pentabromodiphenyl ether. Among the CYP specific antibodies tested, anti-rat CYP2B was found to be the most active in inhibiting the formation of hydroxylated metabolites of both BDE-47 and BDE-99, indicating that CYP2B was the major CYP enzyme involved in the oxidative biotransformation of these two congeners. Our study shows that polar bears are capable of forming multiple hydroxylated metabolites of BDE-47 and BDE-99 in vitro and demonstrates the role of CYP2B in the biotransformation and possibly in the toxicity of BDE-47 and BDE-99 in polar bears.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 146, March 2016, Pages 555–564