| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4408324 | 1618841 | 2015 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• Phenolic resin-based carbon foam is a low-cost adsorbent alternative.
• Lead and copper removal from aqueous solution is possible with carbon foam.
• Key mechanism of lead and copper removal on carbon foam is surface precipitation.
• Maximum sorption capacities were 460.50 mg g−1 for lead and 212.14 mg g−1 for copper.
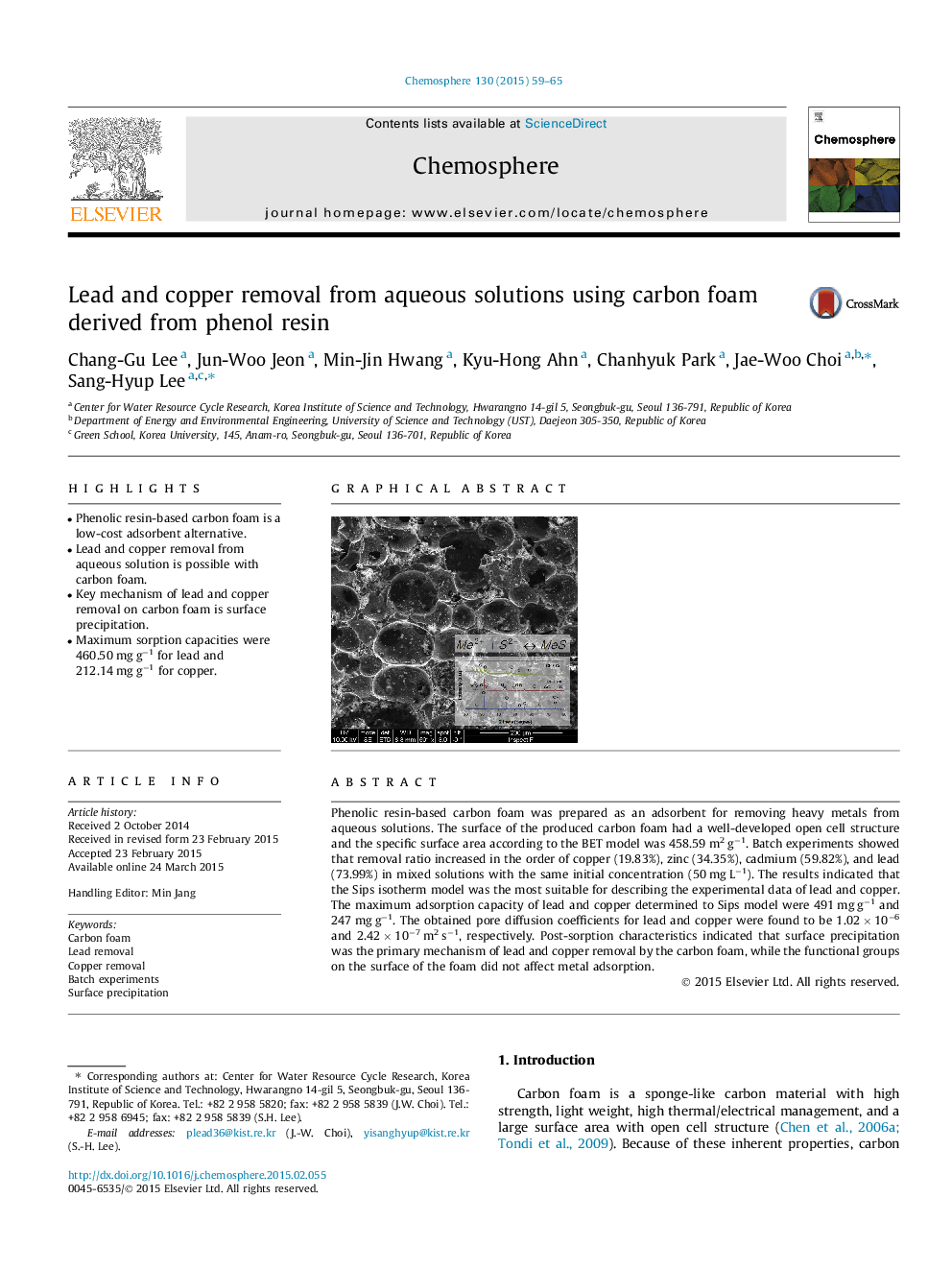
Phenolic resin-based carbon foam was prepared as an adsorbent for removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions. The surface of the produced carbon foam had a well-developed open cell structure and the specific surface area according to the BET model was 458.59 m2 g−1. Batch experiments showed that removal ratio increased in the order of copper (19.83%), zinc (34.35%), cadmium (59.82%), and lead (73.99%) in mixed solutions with the same initial concentration (50 mg L−1). The results indicated that the Sips isotherm model was the most suitable for describing the experimental data of lead and copper. The maximum adsorption capacity of lead and copper determined to Sips model were 491 mg g−1 and 247 mg g−1. The obtained pore diffusion coefficients for lead and copper were found to be 1.02 × 10−6 and 2.42 × 10−7 m2 s−1, respectively. Post-sorption characteristics indicated that surface precipitation was the primary mechanism of lead and copper removal by the carbon foam, while the functional groups on the surface of the foam did not affect metal adsorption.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 130, July 2015, Pages 59–65