| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4409685 | 1307500 | 2013 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
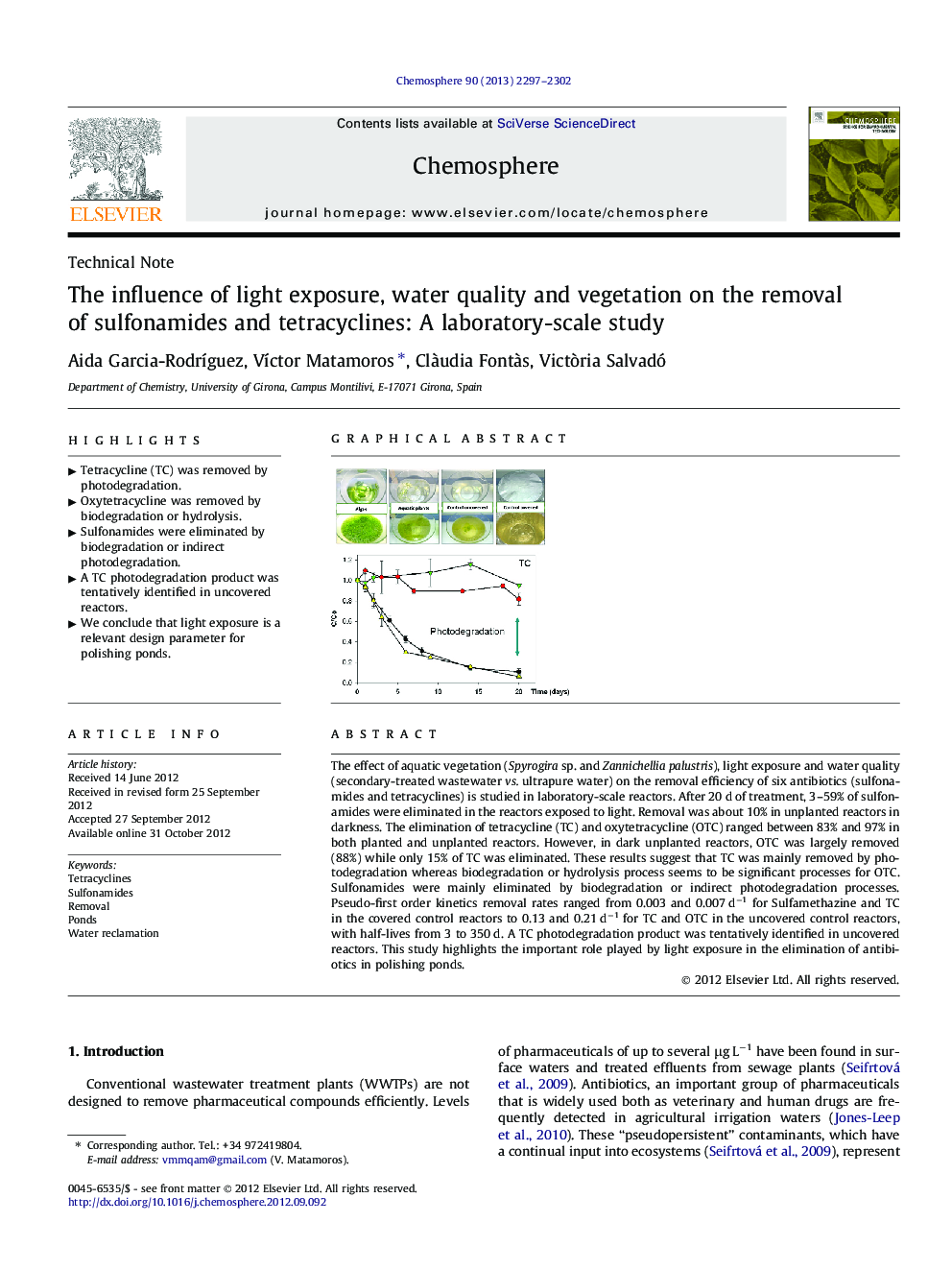
The effect of aquatic vegetation (Spyrogira sp. and Zannichellia palustris), light exposure and water quality (secondary-treated wastewater vs. ultrapure water) on the removal efficiency of six antibiotics (sulfonamides and tetracyclines) is studied in laboratory-scale reactors. After 20 d of treatment, 3–59% of sulfonamides were eliminated in the reactors exposed to light. Removal was about 10% in unplanted reactors in darkness. The elimination of tetracycline (TC) and oxytetracycline (OTC) ranged between 83% and 97% in both planted and unplanted reactors. However, in dark unplanted reactors, OTC was largely removed (88%) while only 15% of TC was eliminated. These results suggest that TC was mainly removed by photodegradation whereas biodegradation or hydrolysis process seems to be significant processes for OTC. Sulfonamides were mainly eliminated by biodegradation or indirect photodegradation processes. Pseudo-first order kinetics removal rates ranged from 0.003 and 0.007 d−1 for Sulfamethazine and TC in the covered control reactors to 0.13 and 0.21 d−1 for TC and OTC in the uncovered control reactors, with half-lives from 3 to 350 d. A TC photodegradation product was tentatively identified in uncovered reactors. This study highlights the important role played by light exposure in the elimination of antibiotics in polishing ponds.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlight
► Tetracycline (TC) was removed by photodegradation.
► Oxytetracycline was removed by biodegradation or hydrolysis.
► Sulfonamides were eliminated by biodegradation or indirect photodegradation.
► A TC photodegradation product was tentatively identified in uncovered reactors.
► We conclude that light exposure is a relevant design parameter for polishing ponds.
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 90, Issue 8, February 2013, Pages 2297–2302