| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4409686 | 1307500 | 2013 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
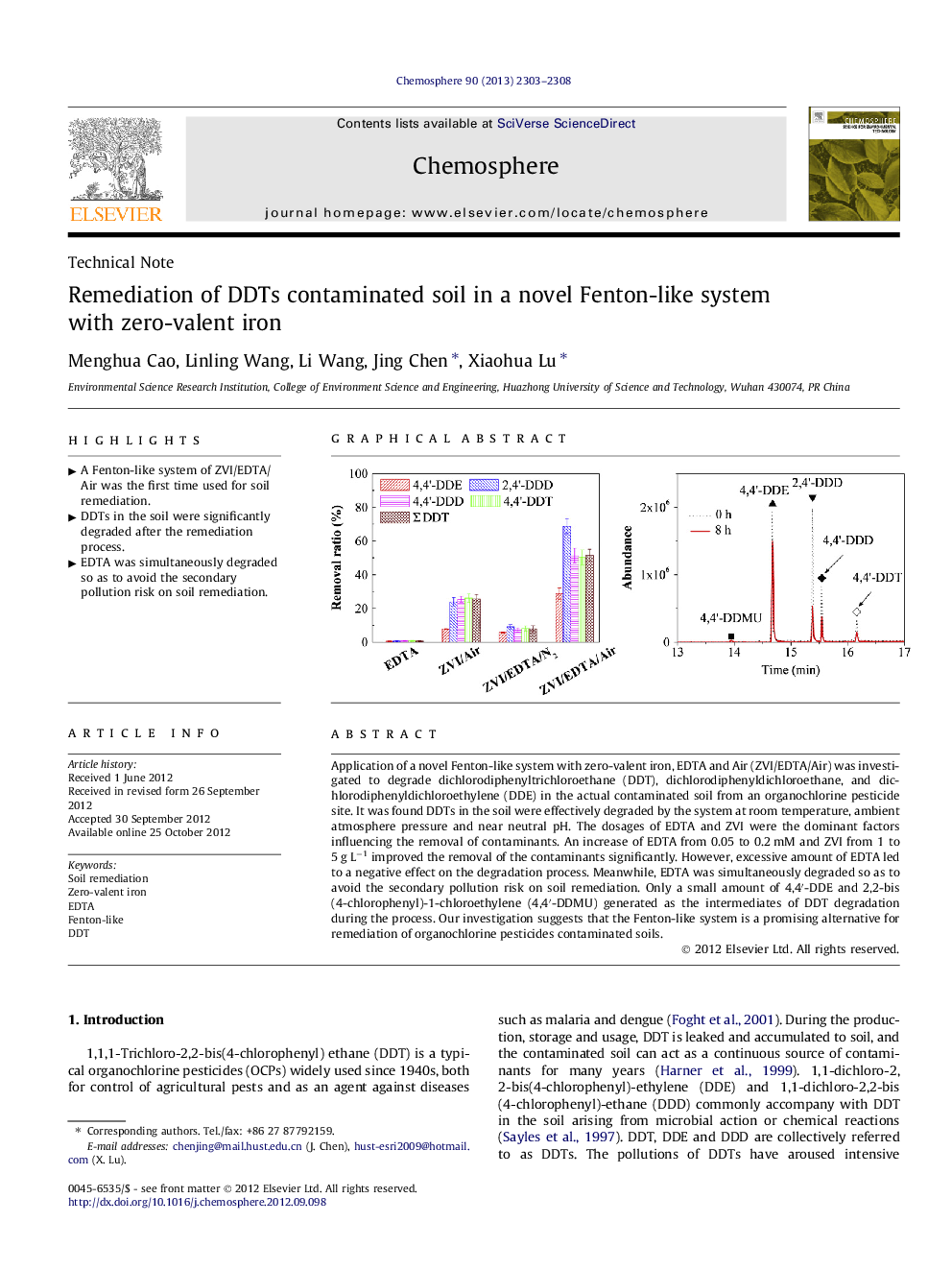
Application of a novel Fenton-like system with zero-valent iron, EDTA and Air (ZVI/EDTA/Air) was investigated to degrade dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane, and dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE) in the actual contaminated soil from an organochlorine pesticide site. It was found DDTs in the soil were effectively degraded by the system at room temperature, ambient atmosphere pressure and near neutral pH. The dosages of EDTA and ZVI were the dominant factors influencing the removal of contaminants. An increase of EDTA from 0.05 to 0.2 mM and ZVI from 1 to 5 g L−1 improved the removal of the contaminants significantly. However, excessive amount of EDTA led to a negative effect on the degradation process. Meanwhile, EDTA was simultaneously degraded so as to avoid the secondary pollution risk on soil remediation. Only a small amount of 4,4′-DDE and 2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1-chloroethylene (4,4′-DDMU) generated as the intermediates of DDT degradation during the process. Our investigation suggests that the Fenton-like system is a promising alternative for remediation of organochlorine pesticides contaminated soils.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► A Fenton-like system of ZVI/EDTA/Air was the first time used for soil remediation.
► DDTs in the soil were significantly degraded after the remediation process.
► EDTA was simultaneously degraded so as to avoid the secondary pollution risk on soil remediation.
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 90, Issue 8, February 2013, Pages 2303–2308