| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 44747 | 46344 | 2016 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
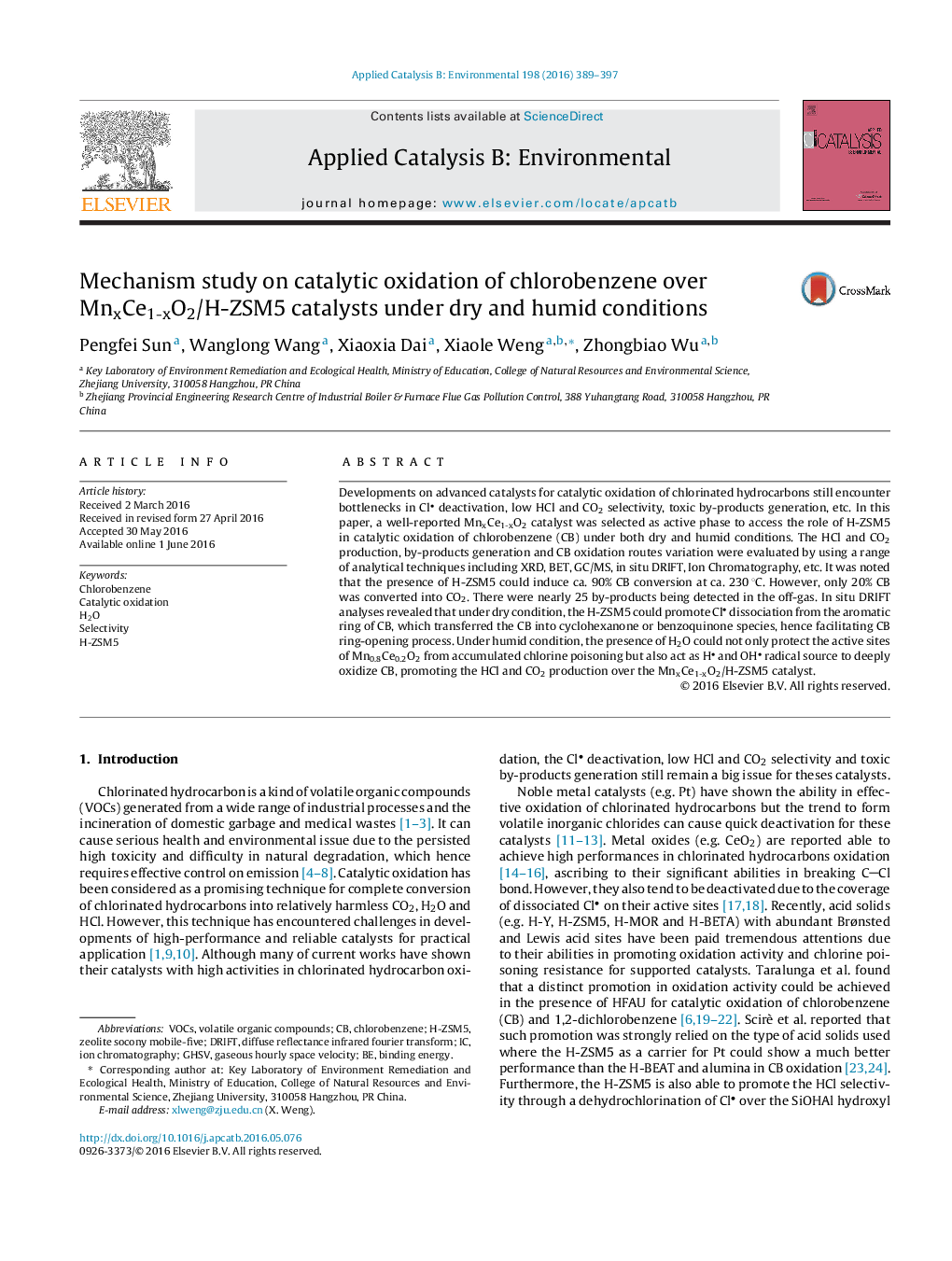
• H-ZSM5 was proven able to enhance CB conversion and HCl selectivity over Mn0.8Ce0.2O2/H-ZSM5 catalyst.
• The presence of H-ZSM5 was favorable to transfer the CB into cyclohexanone or benzoquinone species, facilitating the ring-opening process.
• Nearly 25 by-products were detected in the off-gas during CB oxidation.
• H2O could protect the active sites of Mn0.8Ce0.2O2 from the accumulated chlorine poisoning.
• The CB oxidation route has been changed from initial Cl dissociation into benzene to direct ring-opening.
Developments on advanced catalysts for catalytic oxidation of chlorinated hydrocarbons still encounter bottlenecks in Cl deactivation, low HCl and CO2 selectivity, toxic by-products generation, etc. In this paper, a well-reported MnxCe1-xO2 catalyst was selected as active phase to access the role of H-ZSM5 in catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene (CB) under both dry and humid conditions. The HCl and CO2 production, by-products generation and CB oxidation routes variation were evaluated by using a range of analytical techniques including XRD, BET, GC/MS, in situ DRIFT, Ion Chromatography, etc. It was noted that the presence of H-ZSM5 could induce ca. 90% CB conversion at ca. 230 °C. However, only 20% CB was converted into CO2. There were nearly 25 by-products being detected in the off-gas. In situ DRIFT analyses revealed that under dry condition, the H-ZSM5 could promote Cl dissociation from the aromatic ring of CB, which transferred the CB into cyclohexanone or benzoquinone species, hence facilitating CB ring-opening process. Under humid condition, the presence of H2O could not only protect the active sites of Mn0.8Ce0.2O2 from accumulated chlorine poisoning but also act as H and OH radical source to deeply oxidize CB, promoting the HCl and CO2 production over the MnxCe1-xO2/H-ZSM5 catalyst.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Applied Catalysis B: Environmental - Volume 198, 5 December 2016, Pages 389–397