| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5130858 | 1490850 | 2017 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
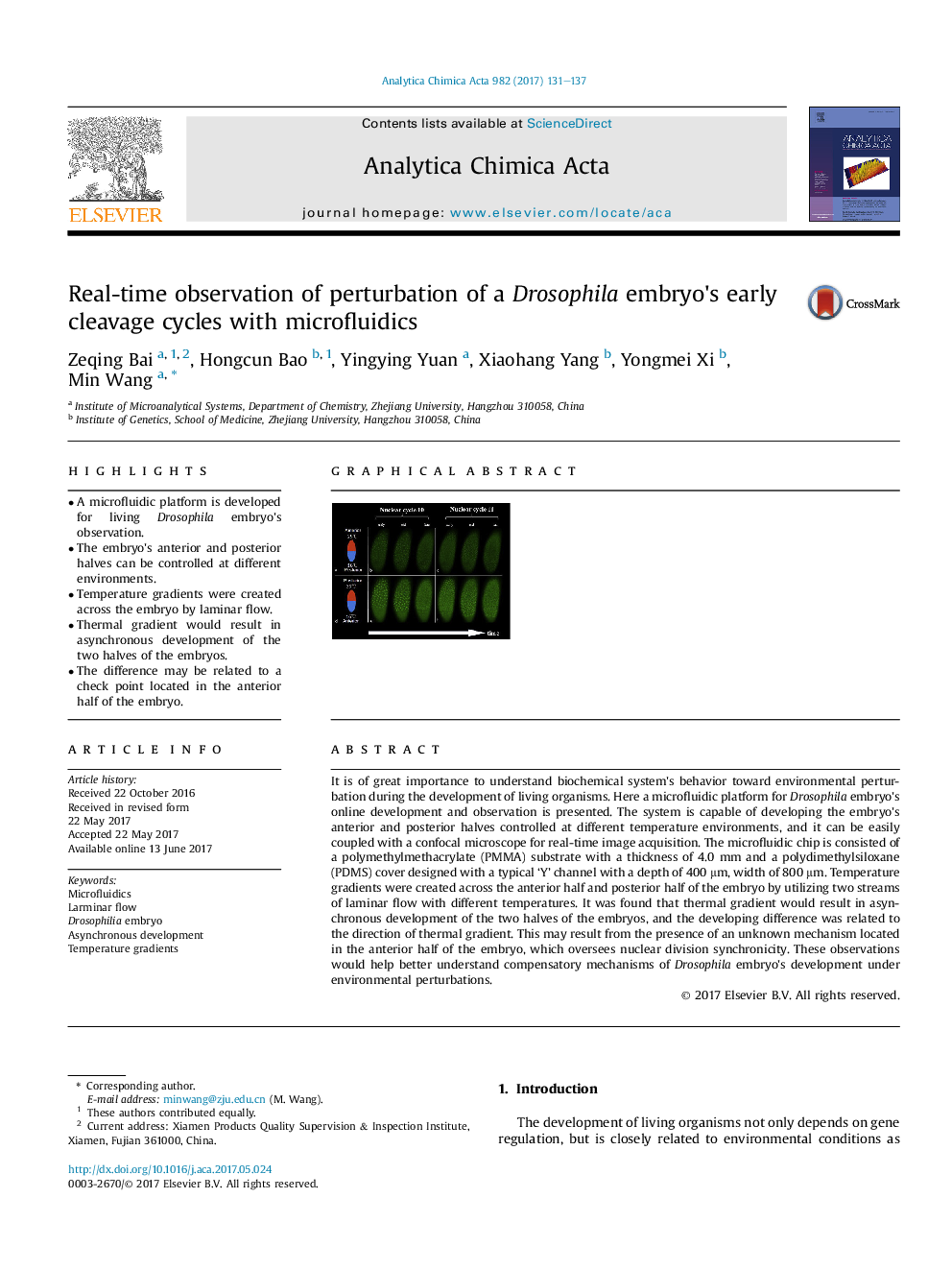
- A microfluidic platform is developed for living Drosophila embryo's observation.
- The embryo's anterior and posterior halves can be controlled at different environments.
- Temperature gradients were created across the embryo by laminar flow.
- Thermal gradient would result in asynchronous development of the two halves of the embryos.
- The difference may be related to a check point located in the anterior half of the embryo.
It is of great importance to understand biochemical system's behavior toward environmental perturbation during the development of living organisms. Here a microfluidic platform for Drosophila embryo's online development and observation is presented. The system is capable of developing the embryo's anterior and posterior halves controlled at different temperature environments, and it can be easily coupled with a confocal microscope for real-time image acquisition. The microfluidic chip is consisted of a polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) substrate with a thickness of 4.0 mm and a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) cover designed with a typical 'Y' channel with a depth of 400 μm, width of 800 μm. Temperature gradients were created across the anterior half and posterior half of the embryo by utilizing two streams of laminar flow with different temperatures. It was found that thermal gradient would result in asynchronous development of the two halves of the embryos, and the developing difference was related to the direction of thermal gradient. This may result from the presence of an unknown mechanism located in the anterior half of the embryo, which oversees nuclear division synchronicity. These observations would help better understand compensatory mechanisms of Drosophila embryo's development under environmental perturbations.
Temperature gradients would result in asynchronous development of the two halves of Drosophila embryos, and the development difference was related to the direction of thermal gradients. It implies that there may be an unknown mechanism located in the anterior half of the embryo, which oversees nuclear division synchronicity.196
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 982, 22 August 2017, Pages 131-137