| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5131116 | 1490873 | 2017 | 23 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
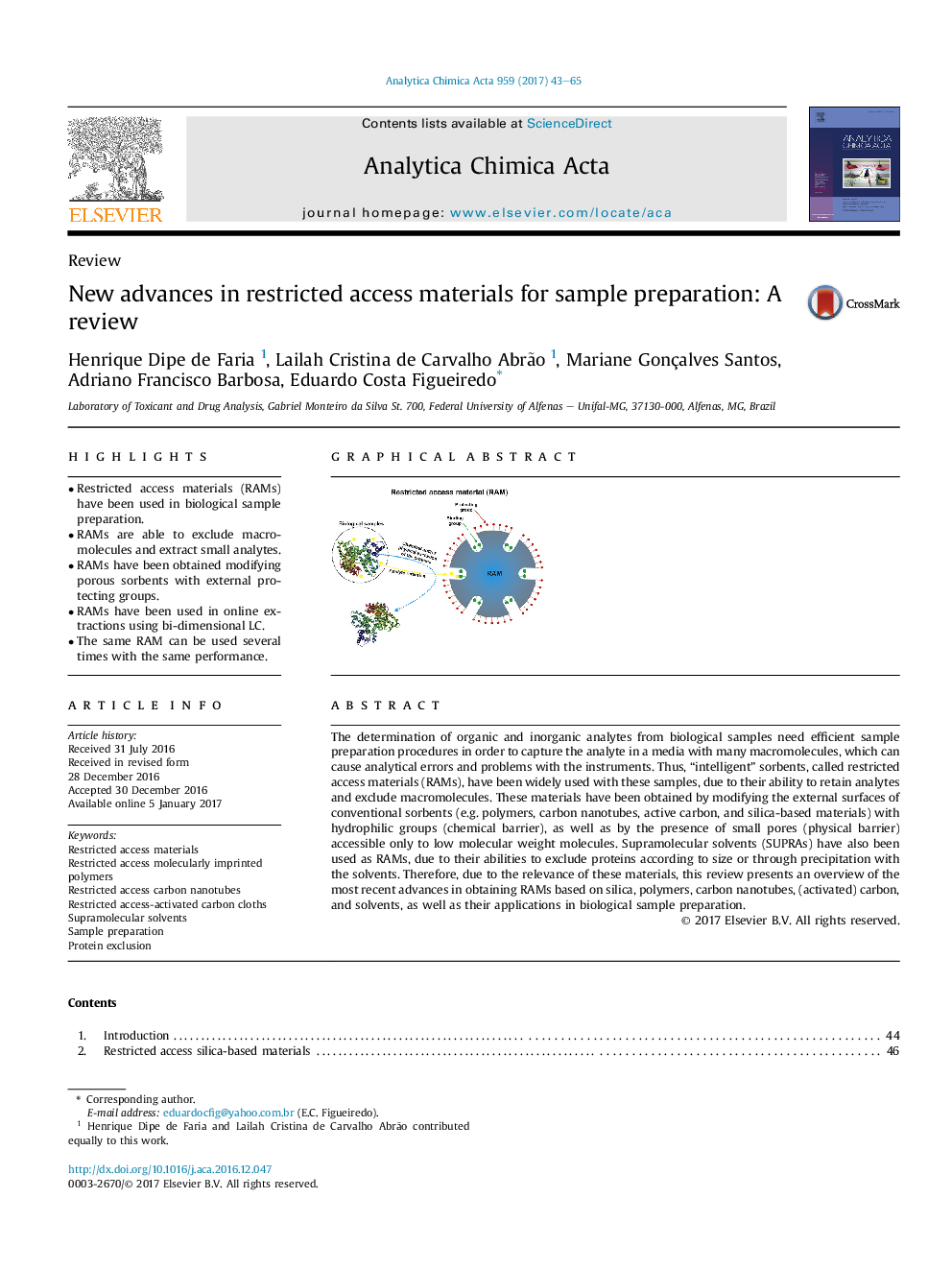
- Restricted access materials (RAMs) have been used in biological sample preparation.
- RAMs are able to exclude macromolecules and extract small analytes.
- RAMs have been obtained modifying porous sorbents with external protecting groups.
- RAMs have been used in online extractions using bi-dimensional LC.
- The same RAM can be used several times with the same performance.
The determination of organic and inorganic analytes from biological samples need efficient sample preparation procedures in order to capture the analyte in a media with many macromolecules, which can cause analytical errors and problems with the instruments. Thus, “intelligent” sorbents, called restricted access materials (RAMs), have been widely used with these samples, due to their ability to retain analytes and exclude macromolecules. These materials have been obtained by modifying the external surfaces of conventional sorbents (e.g. polymers, carbon nanotubes, active carbon, and silica-based materials) with hydrophilic groups (chemical barrier), as well as by the presence of small pores (physical barrier) accessible only to low molecular weight molecules. Supramolecular solvents (SUPRAs) have also been used as RAMs, due to their abilities to exclude proteins according to size or through precipitation with the solvents. Therefore, due to the relevance of these materials, this review presents an overview of the most recent advances in obtaining RAMs based on silica, polymers, carbon nanotubes, (activated) carbon, and solvents, as well as their applications in biological sample preparation.
231
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 959, 22 March 2017, Pages 43-65