| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5370789 | 1503915 | 2015 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
- IDE is present in different cellular environments experiencing different pH values.
- IDE conformation and activity have been investigated at various pH values.
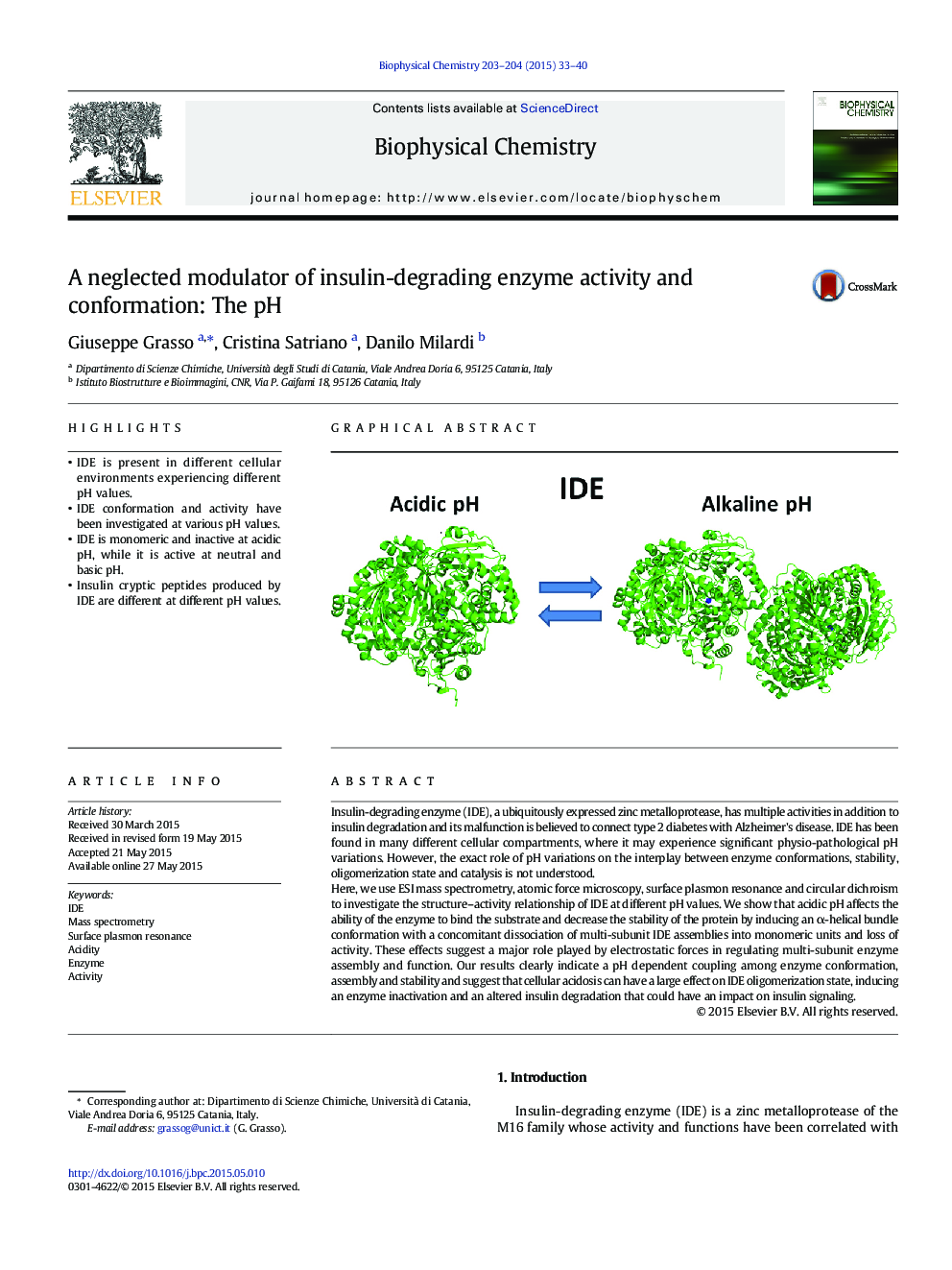
- IDE is monomeric and inactive at acidic pH, while it is active at neutral and basic pH.
- Insulin cryptic peptides produced by IDE are different at different pH values.
Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE), a ubiquitously expressed zinc metalloprotease, has multiple activities in addition to insulin degradation and its malfunction is believed to connect type 2 diabetes with Alzheimer's disease. IDE has been found in many different cellular compartments, where it may experience significant physio-pathological pH variations. However, the exact role of pH variations on the interplay between enzyme conformations, stability, oligomerization state and catalysis is not understood.Here, we use ESI mass spectrometry, atomic force microscopy, surface plasmon resonance and circular dichroism to investigate the structure-activity relationship of IDE at different pH values. We show that acidic pH affects the ability of the enzyme to bind the substrate and decrease the stability of the protein by inducing an α-helical bundle conformation with a concomitant dissociation of multi-subunit IDE assemblies into monomeric units and loss of activity. These effects suggest a major role played by electrostatic forces in regulating multi-subunit enzyme assembly and function. Our results clearly indicate a pH dependent coupling among enzyme conformation, assembly and stability and suggest that cellular acidosis can have a large effect on IDE oligomerization state, inducing an enzyme inactivation and an altered insulin degradation that could have an impact on insulin signaling.
208
Journal: Biophysical Chemistry - Volumes 203â204, AugustâSeptember 2015, Pages 33-40