| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5370974 | 1503924 | 2014 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
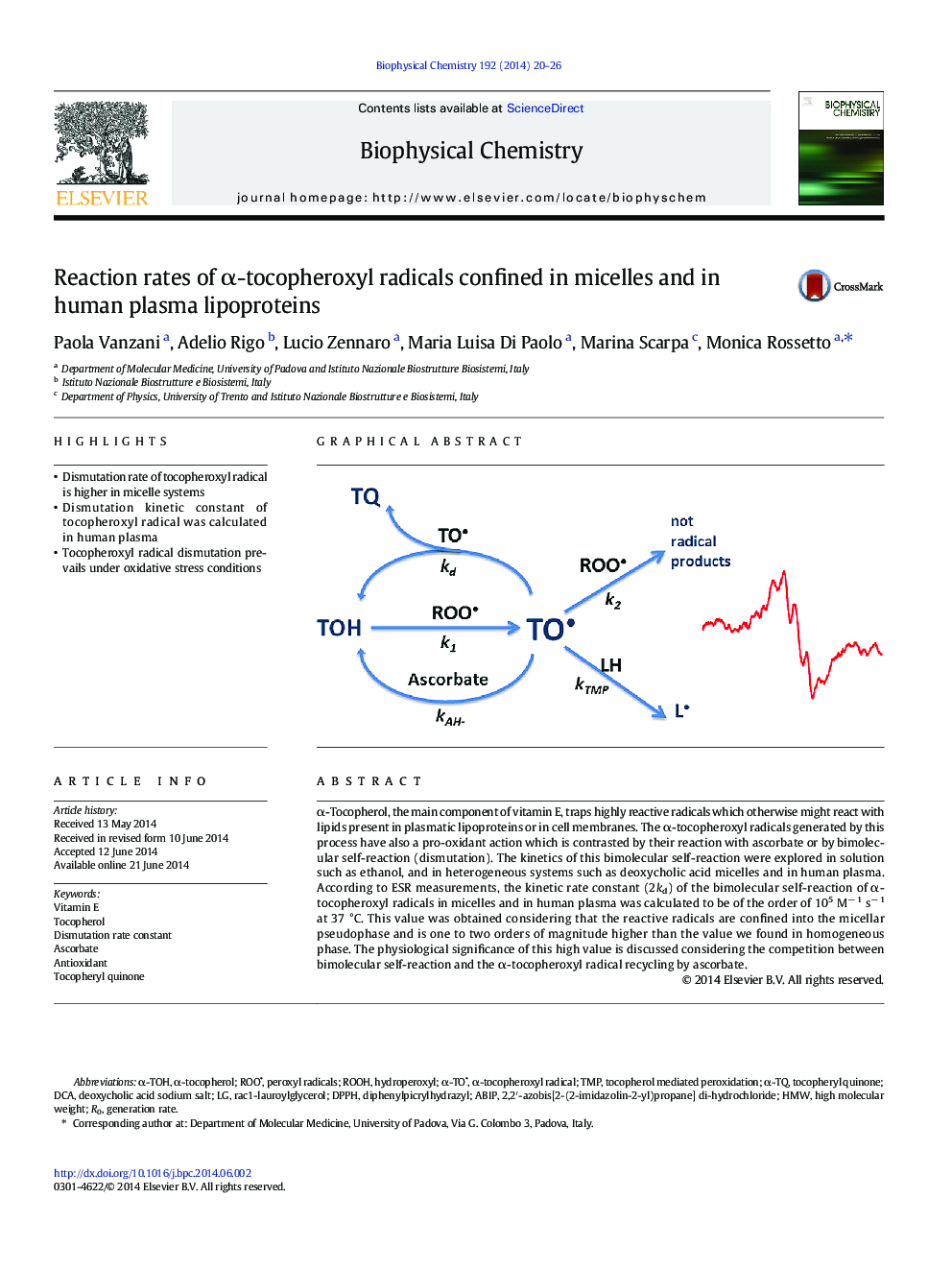
- Dismutation rate of tocopheroxyl radical is higher in micelle systems
- Dismutation kinetic constant of tocopheroxyl radical was calculated in human plasma
- Tocopheroxyl radical dismutation prevails under oxidative stress conditions
α-Tocopherol, the main component of vitamin E, traps highly reactive radicals which otherwise might react with lipids present in plasmatic lipoproteins or in cell membranes. The α-tocopheroxyl radicals generated by this process have also a pro-oxidant action which is contrasted by their reaction with ascorbate or by bimolecular self-reaction (dismutation). The kinetics of this bimolecular self-reaction were explored in solution such as ethanol, and in heterogeneous systems such as deoxycholic acid micelles and in human plasma. According to ESR measurements, the kinetic rate constant (2kd) of the bimolecular self-reaction of α-tocopheroxyl radicals in micelles and in human plasma was calculated to be of the order of 105 Mâ 1 sâ 1 at 37 °C. This value was obtained considering that the reactive radicals are confined into the micellar pseudophase and is one to two orders of magnitude higher than the value we found in homogeneous phase. The physiological significance of this high value is discussed considering the competition between bimolecular self-reaction and the α-tocopheroxyl radical recycling by ascorbate.
Journal: Biophysical Chemistry - Volume 192, August 2014, Pages 20-26