| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5370999 | 1503930 | 2013 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
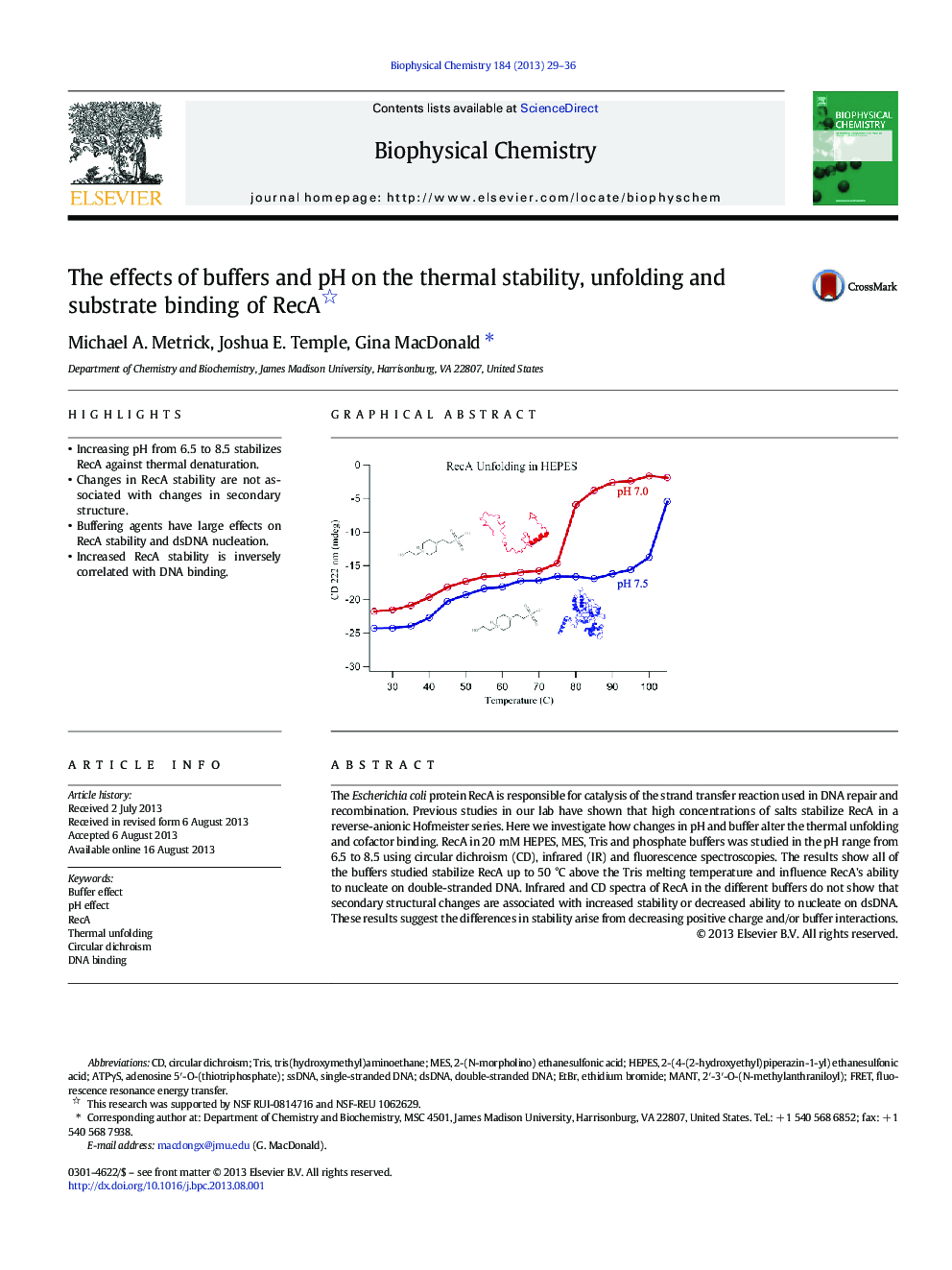
- Increasing pH from 6.5 to 8.5 stabilizes RecA against thermal denaturation.
- Changes in RecA stability are not associated with changes in secondary structure.
- Buffering agents have large effects on RecA stability and dsDNA nucleation.
- Increased RecA stability is inversely correlated with DNA binding.
The Escherichia coli protein RecA is responsible for catalysis of the strand transfer reaction used in DNA repair and recombination. Previous studies in our lab have shown that high concentrations of salts stabilize RecA in a reverse-anionic Hofmeister series. Here we investigate how changes in pH and buffer alter the thermal unfolding and cofactor binding. RecA in 20 mM HEPES, MES, Tris and phosphate buffers was studied in the pH range from 6.5 to 8.5 using circular dichroism (CD), infrared (IR) and fluorescence spectroscopies. The results show all of the buffers studied stabilize RecA up to 50 °C above the Tris melting temperature and influence RecA's ability to nucleate on double-stranded DNA. Infrared and CD spectra of RecA in the different buffers do not show that secondary structural changes are associated with increased stability or decreased ability to nucleate on dsDNA. These results suggest the differences in stability arise from decreasing positive charge and/or buffer interactions.
Journal: Biophysical Chemistry - Volume 184, 31 December 2013, Pages 29-36