| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591879 | 1453884 | 2016 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
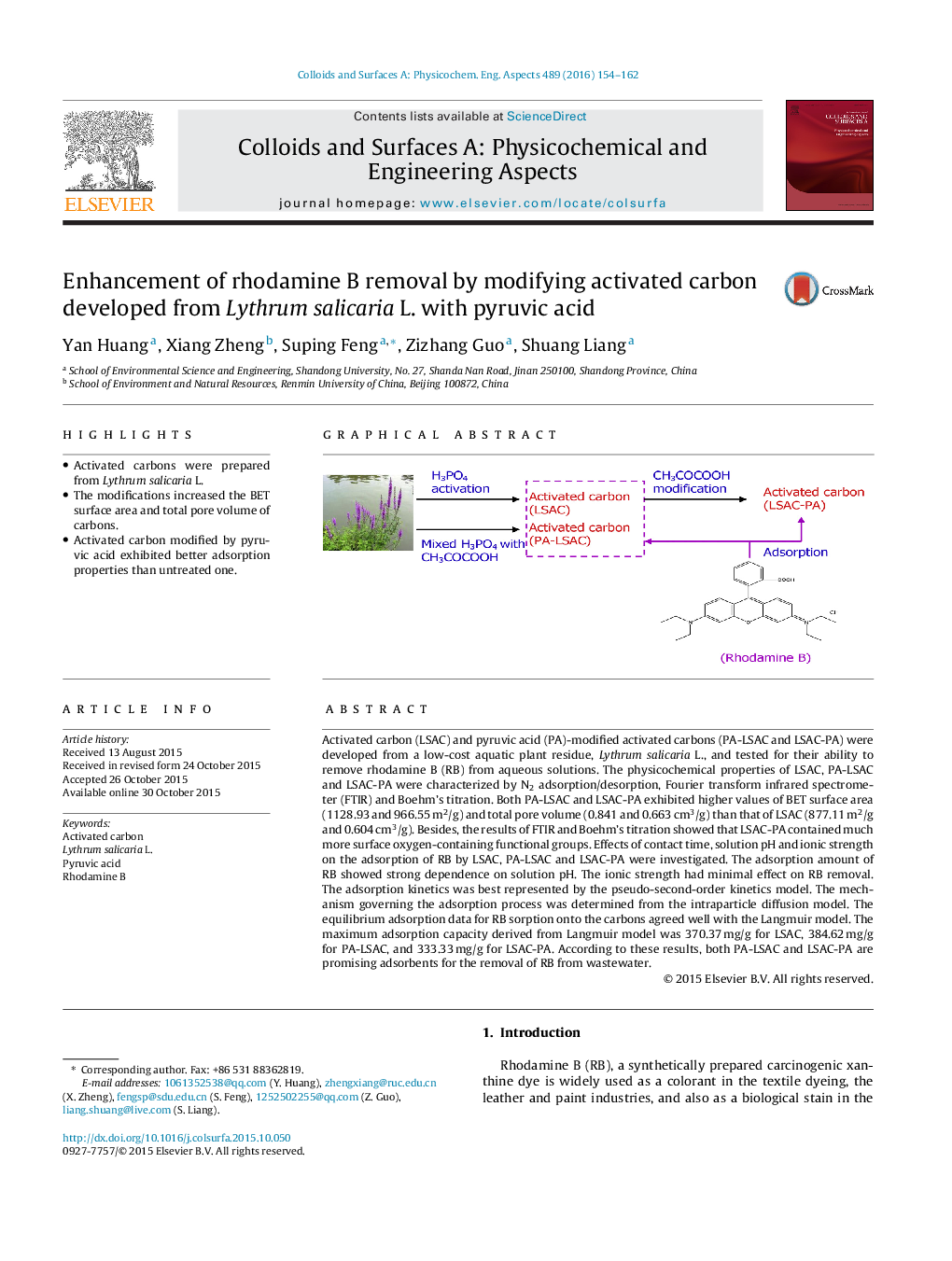
• Activated carbons were prepared from Lythrum salicaria L.
• The modifications increased the BET surface area and total pore volume of carbons.
• Activated carbon modified by pyruvic acid exhibited better adsorption properties than untreated one.
Activated carbon (LSAC) and pyruvic acid (PA)-modified activated carbons (PA-LSAC and LSAC-PA) were developed from a low-cost aquatic plant residue, Lythrum salicaria L., and tested for their ability to remove rhodamine B (RB) from aqueous solutions. The physicochemical properties of LSAC, PA-LSAC and LSAC-PA were characterized by N2 adsorption/desorption, Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) and Boehm’s titration. Both PA-LSAC and LSAC-PA exhibited higher values of BET surface area (1128.93 and 966.55 m2/g) and total pore volume (0.841 and 0.663 cm3/g) than that of LSAC (877.11 m2/g and 0.604 cm3/g). Besides, the results of FTIR and Boehm’s titration showed that LSAC-PA contained much more surface oxygen-containing functional groups. Effects of contact time, solution pH and ionic strength on the adsorption of RB by LSAC, PA-LSAC and LSAC-PA were investigated. The adsorption amount of RB showed strong dependence on solution pH. The ionic strength had minimal effect on RB removal. The adsorption kinetics was best represented by the pseudo-second-order kinetics model. The mechanism governing the adsorption process was determined from the intraparticle diffusion model. The equilibrium adsorption data for RB sorption onto the carbons agreed well with the Langmuir model. The maximum adsorption capacity derived from Langmuir model was 370.37 mg/g for LSAC, 384.62 mg/g for PA-LSAC, and 333.33 mg/g for LSAC-PA. According to these results, both PA-LSAC and LSAC-PA are promising adsorbents for the removal of RB from wastewater.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 489, 20 January 2016, Pages 154–162