| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592181 | 1453893 | 2015 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
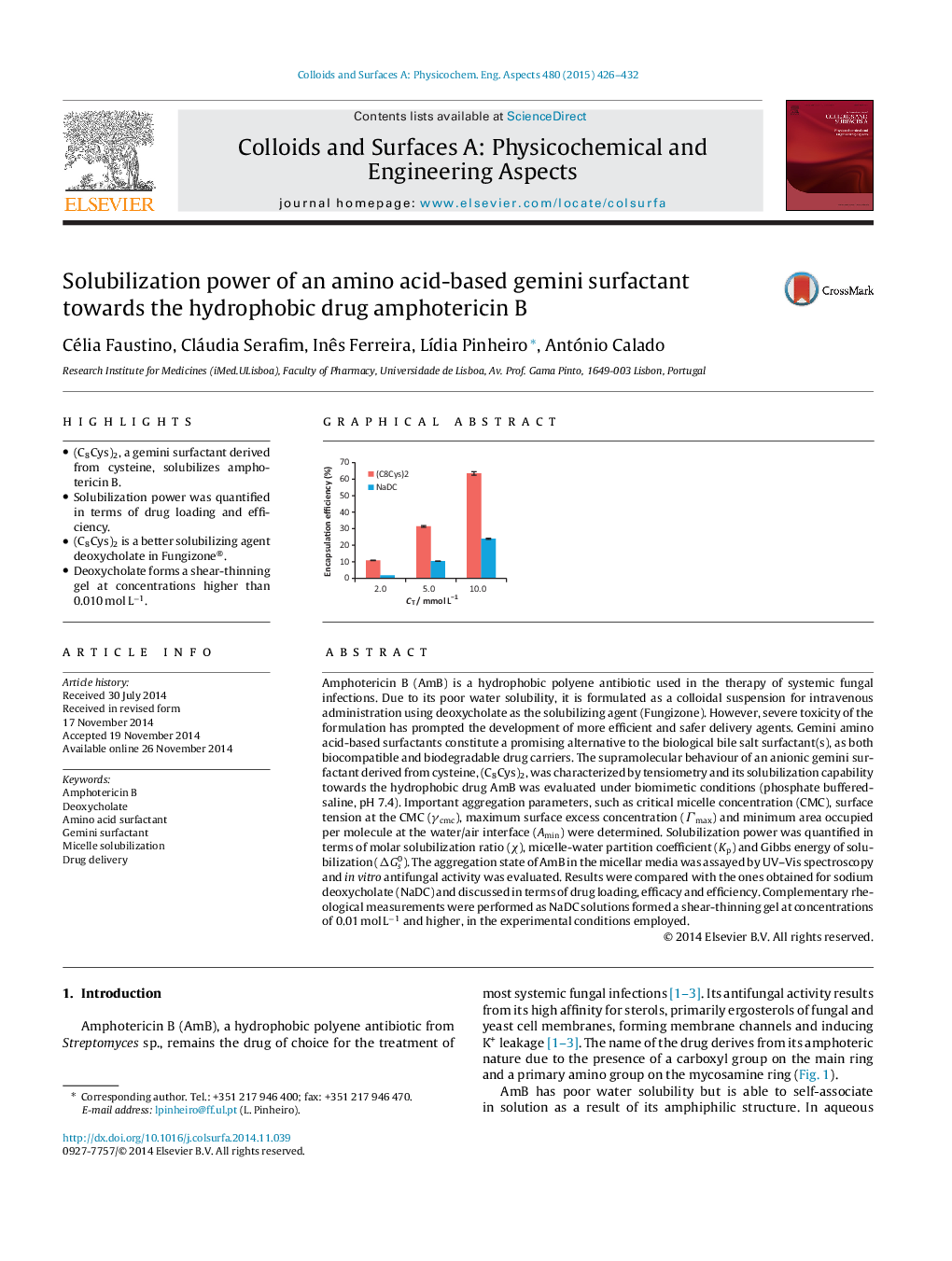
• (C8Cys)2, a gemini surfactant derived from cysteine, solubilizes amphotericin B.
• Solubilization power was quantified in terms of drug loading and efficiency.
• (C8Cys)2 is a better solubilizing agent deoxycholate in Fungizone®.
• Deoxycholate forms a shear-thinning gel at concentrations higher than 0.010 mol L−1.
Amphotericin B (AmB) is a hydrophobic polyene antibiotic used in the therapy of systemic fungal infections. Due to its poor water solubility, it is formulated as a colloidal suspension for intravenous administration using deoxycholate as the solubilizing agent (Fungizone). However, severe toxicity of the formulation has prompted the development of more efficient and safer delivery agents. Gemini amino acid-based surfactants constitute a promising alternative to the biological bile salt surfactant(s), as both biocompatible and biodegradable drug carriers. The supramolecular behaviour of an anionic gemini surfactant derived from cysteine, (C8Cys)2, was characterized by tensiometry and its solubilization capability towards the hydrophobic drug AmB was evaluated under biomimetic conditions (phosphate buffered-saline, pH 7.4). Important aggregation parameters, such as critical micelle concentration (CMC), surface tension at the CMC (γcmc), maximum surface excess concentration (Γmax) and minimum area occupied per molecule at the water/air interface (Amin) were determined. Solubilization power was quantified in terms of molar solubilization ratio (χ), micelle-water partition coefficient (Kp) and Gibbs energy of solubilization (ΔGs0). The aggregation state of AmB in the micellar media was assayed by UV–Vis spectroscopy and in vitro antifungal activity was evaluated. Results were compared with the ones obtained for sodium deoxycholate (NaDC) and discussed in terms of drug loading, efficacy and efficiency. Complementary rheological measurements were performed as NaDC solutions formed a shear-thinning gel at concentrations of 0.01 mol L−1 and higher, in the experimental conditions employed.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 480, 5 September 2015, Pages 426–432