| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592699 | 1453914 | 2014 | 4 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
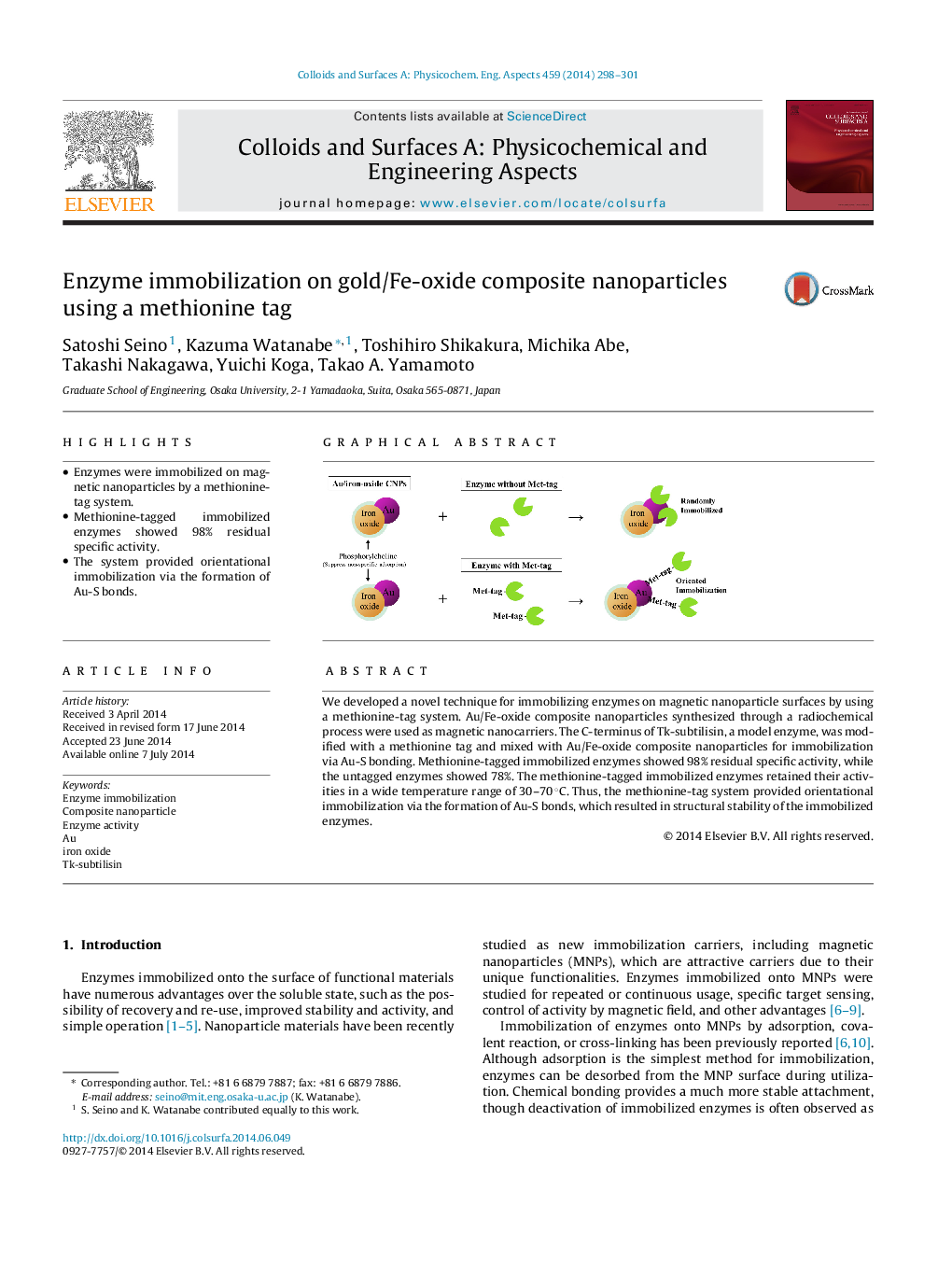
• Enzymes were immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles by a methionine-tag system.
• Methionine-tagged immobilized enzymes showed 98% residual specific activity.
• The system provided orientational immobilization via the formation of Au-S bonds.
We developed a novel technique for immobilizing enzymes on magnetic nanoparticle surfaces by using a methionine-tag system. Au/Fe-oxide composite nanoparticles synthesized through a radiochemical process were used as magnetic nanocarriers. The C-terminus of Tk-subtilisin, a model enzyme, was modified with a methionine tag and mixed with Au/Fe-oxide composite nanoparticles for immobilization via Au-S bonding. Methionine-tagged immobilized enzymes showed 98% residual specific activity, while the untagged enzymes showed 78%. The methionine-tagged immobilized enzymes retained their activities in a wide temperature range of 30–70 °C. Thus, the methionine-tag system provided orientational immobilization via the formation of Au-S bonds, which resulted in structural stability of the immobilized enzymes.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 459, 5 October 2014, Pages 298–301