| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593729 | 1453952 | 2013 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
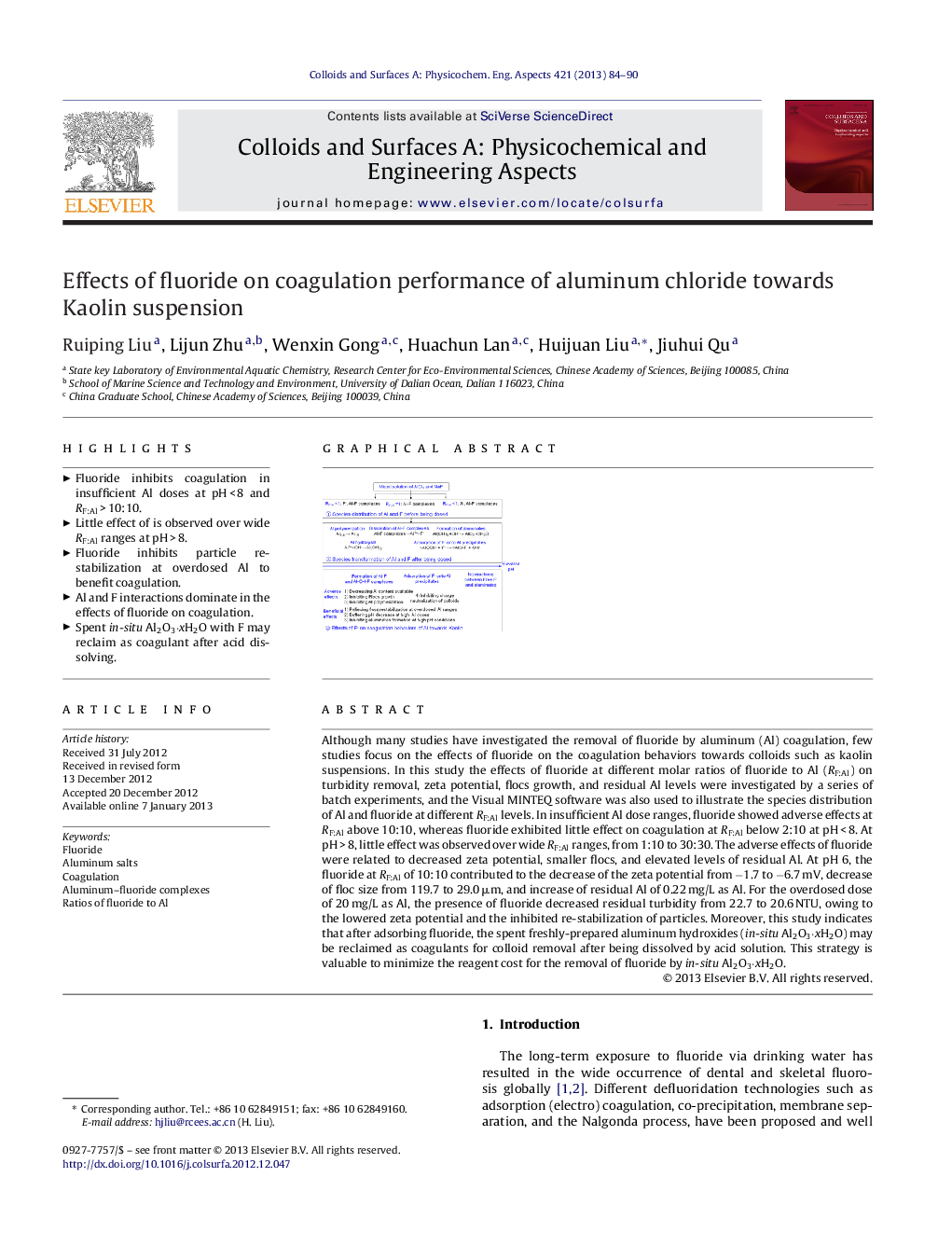
Although many studies have investigated the removal of fluoride by aluminum (Al) coagulation, few studies focus on the effects of fluoride on the coagulation behaviors towards colloids such as kaolin suspensions. In this study the effects of fluoride at different molar ratios of fluoride to Al (RF:Al) on turbidity removal, zeta potential, flocs growth, and residual Al levels were investigated by a series of batch experiments, and the Visual MINTEQ software was also used to illustrate the species distribution of Al and fluoride at different RF:Al levels. In insufficient Al dose ranges, fluoride showed adverse effects at RF:Al above 10:10, whereas fluoride exhibited little effect on coagulation at RF:Al below 2:10 at pH < 8. At pH > 8, little effect was observed over wide RF:Al ranges, from 1:10 to 30:30. The adverse effects of fluoride were related to decreased zeta potential, smaller flocs, and elevated levels of residual Al. At pH 6, the fluoride at RF:Al of 10:10 contributed to the decrease of the zeta potential from −1.7 to −6.7 mV, decrease of floc size from 119.7 to 29.0 μm, and increase of residual Al of 0.22 mg/L as Al. For the overdosed dose of 20 mg/L as Al, the presence of fluoride decreased residual turbidity from 22.7 to 20.6 NTU, owing to the lowered zeta potential and the inhibited re-stabilization of particles. Moreover, this study indicates that after adsorbing fluoride, the spent freshly-prepared aluminum hydroxides (in-situ Al2O3·xH2O) may be reclaimed as coagulants for colloid removal after being dissolved by acid solution. This strategy is valuable to minimize the reagent cost for the removal of fluoride by in-situ Al2O3·xH2O.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Fluoride inhibits coagulation in insufficient Al doses at pH < 8 and RF:Al > 10:10.
► Little effect of is observed over wide RF:Al ranges at pH > 8.
► Fluoride inhibits particle re-stabilization at overdosed Al to benefit coagulation.
► Al and F interactions dominate in the effects of fluoride on coagulation.
► Spent in-situ Al2O3·xH2O with F may reclaim as coagulant after acid dissolving.
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 421, 20 March 2013, Pages 84–90