| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6305919 | 1618804 | 2017 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
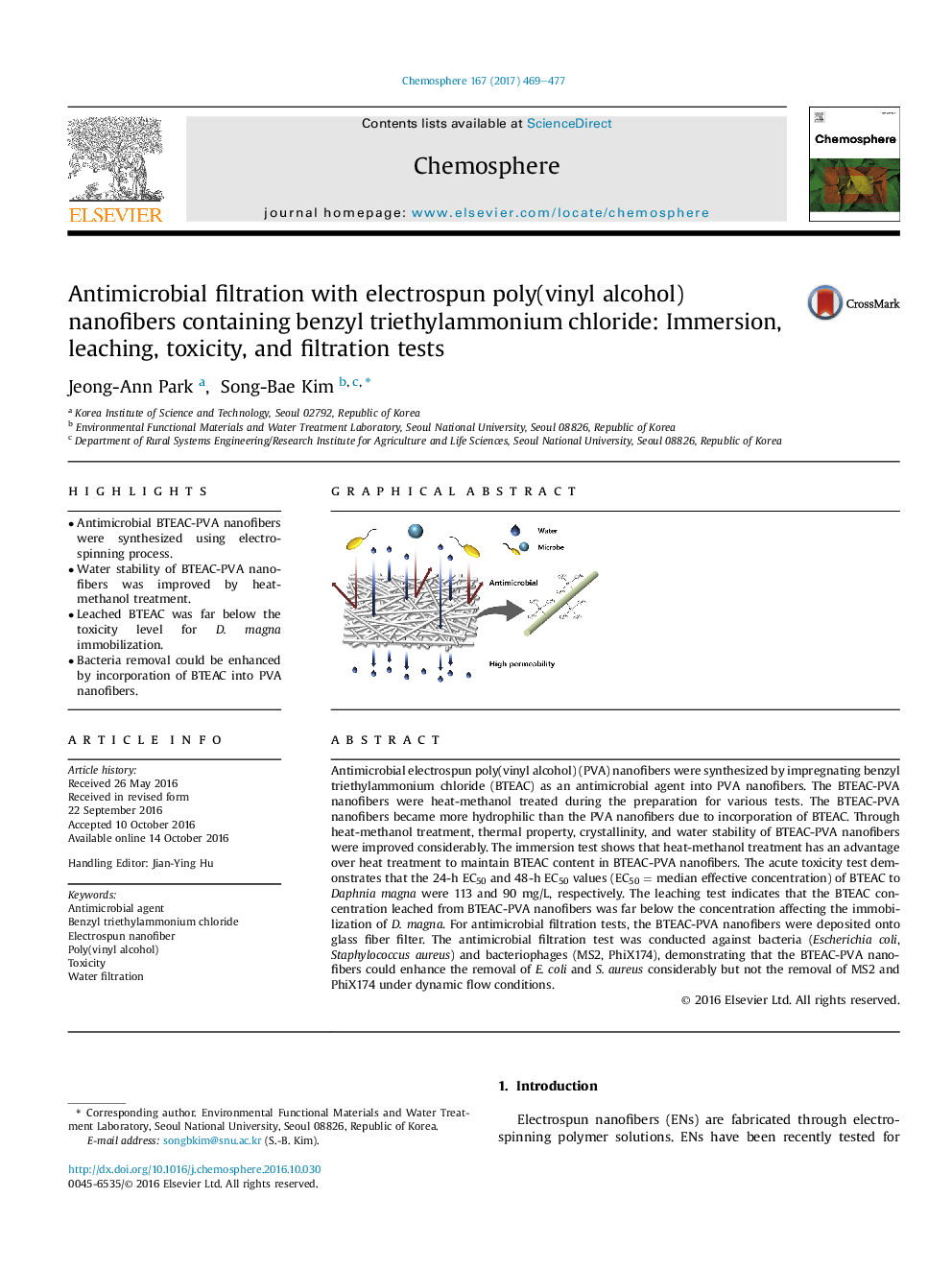
- Antimicrobial BTEAC-PVA nanofibers were synthesized using electrospinning process.
- Water stability of BTEAC-PVA nanofibers was improved by heat-methanol treatment.
- Leached BTEAC was far below the toxicity level for D. magna immobilization.
- Bacteria removal could be enhanced by incorporation of BTEAC into PVA nanofibers.
Antimicrobial electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) nanofibers were synthesized by impregnating benzyl triethylammonium chloride (BTEAC) as an antimicrobial agent into PVA nanofibers. The BTEAC-PVA nanofibers were heat-methanol treated during the preparation for various tests. The BTEAC-PVA nanofibers became more hydrophilic than the PVA nanofibers due to incorporation of BTEAC. Through heat-methanol treatment, thermal property, crystallinity, and water stability of BTEAC-PVA nanofibers were improved considerably. The immersion test shows that heat-methanol treatment has an advantage over heat treatment to maintain BTEAC content in BTEAC-PVA nanofibers. The acute toxicity test demonstrates that the 24-h EC50 and 48-h EC50 values (EC50 = median effective concentration) of BTEAC to Daphnia magna were 113 and 90 mg/L, respectively. The leaching test indicates that the BTEAC concentration leached from BTEAC-PVA nanofibers was far below the concentration affecting the immobilization of D. magna. For antimicrobial filtration tests, the BTEAC-PVA nanofibers were deposited onto glass fiber filter. The antimicrobial filtration test was conducted against bacteria (Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus) and bacteriophages (MS2, PhiX174), demonstrating that the BTEAC-PVA nanofibers could enhance the removal of E. coli and S. aureus considerably but not the removal of MS2 and PhiX174 under dynamic flow conditions.
209
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 167, January 2017, Pages 469-477