| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6306727 | 1618817 | 2016 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
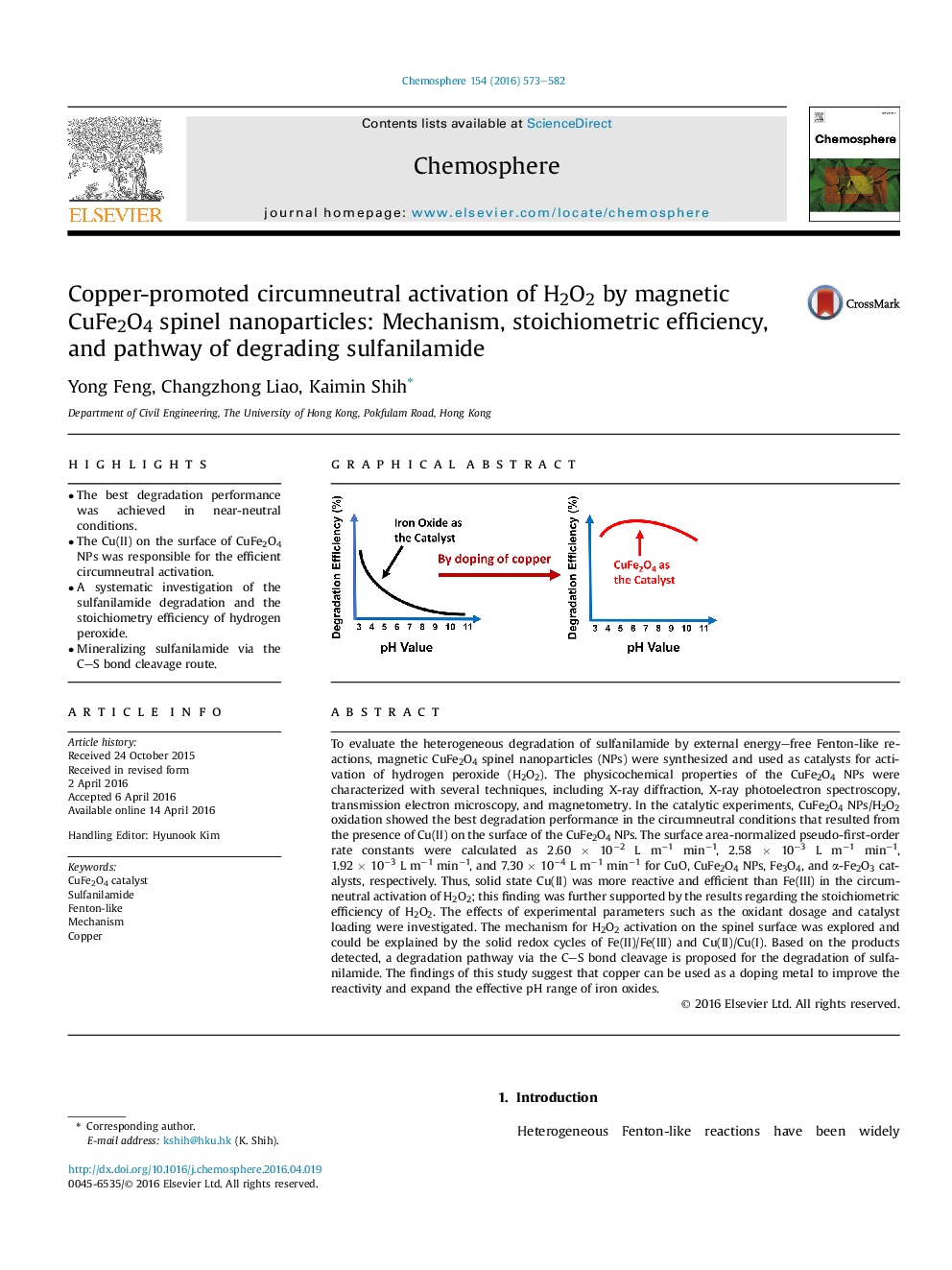
- The best degradation performance was achieved in near-neutral conditions.
- The Cu(II) on the surface of CuFe2O4 NPs was responsible for the efficient circumneutral activation.
- A systematic investigation of the sulfanilamide degradation and the stoichiometry efficiency of hydrogen peroxide.
- Mineralizing sulfanilamide via the CS bond cleavage route.
To evaluate the heterogeneous degradation of sulfanilamide by external energy-free Fenton-like reactions, magnetic CuFe2O4 spinel nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized and used as catalysts for activation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The physicochemical properties of the CuFe2O4 NPs were characterized with several techniques, including X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and magnetometry. In the catalytic experiments, CuFe2O4 NPs/H2O2 oxidation showed the best degradation performance in the circumneutral conditions that resulted from the presence of Cu(II) on the surface of the CuFe2O4 NPs. The surface area-normalized pseudo-first-order rate constants were calculated as 2.60 Ã 10â2 L mâ1 minâ1, 2.58 Ã 10â3 L mâ1 minâ1, 1.92 Ã 10â3 L mâ1 minâ1, and 7.30 Ã 10â4 L mâ1 minâ1 for CuO, CuFe2O4 NPs, Fe3O4, and α-Fe2O3 catalysts, respectively. Thus, solid state Cu(II) was more reactive and efficient than Fe(III) in the circumneutral activation of H2O2; this finding was further supported by the results regarding the stoichiometric efficiency of H2O2. The effects of experimental parameters such as the oxidant dosage and catalyst loading were investigated. The mechanism for H2O2 activation on the spinel surface was explored and could be explained by the solid redox cycles of Fe(II)/Fe(III) and Cu(II)/Cu(I). Based on the products detected, a degradation pathway via the CS bond cleavage is proposed for the degradation of sulfanilamide. The findings of this study suggest that copper can be used as a doping metal to improve the reactivity and expand the effective pH range of iron oxides.
215
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 154, July 2016, Pages 573-582