| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6309135 | 1618864 | 2014 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
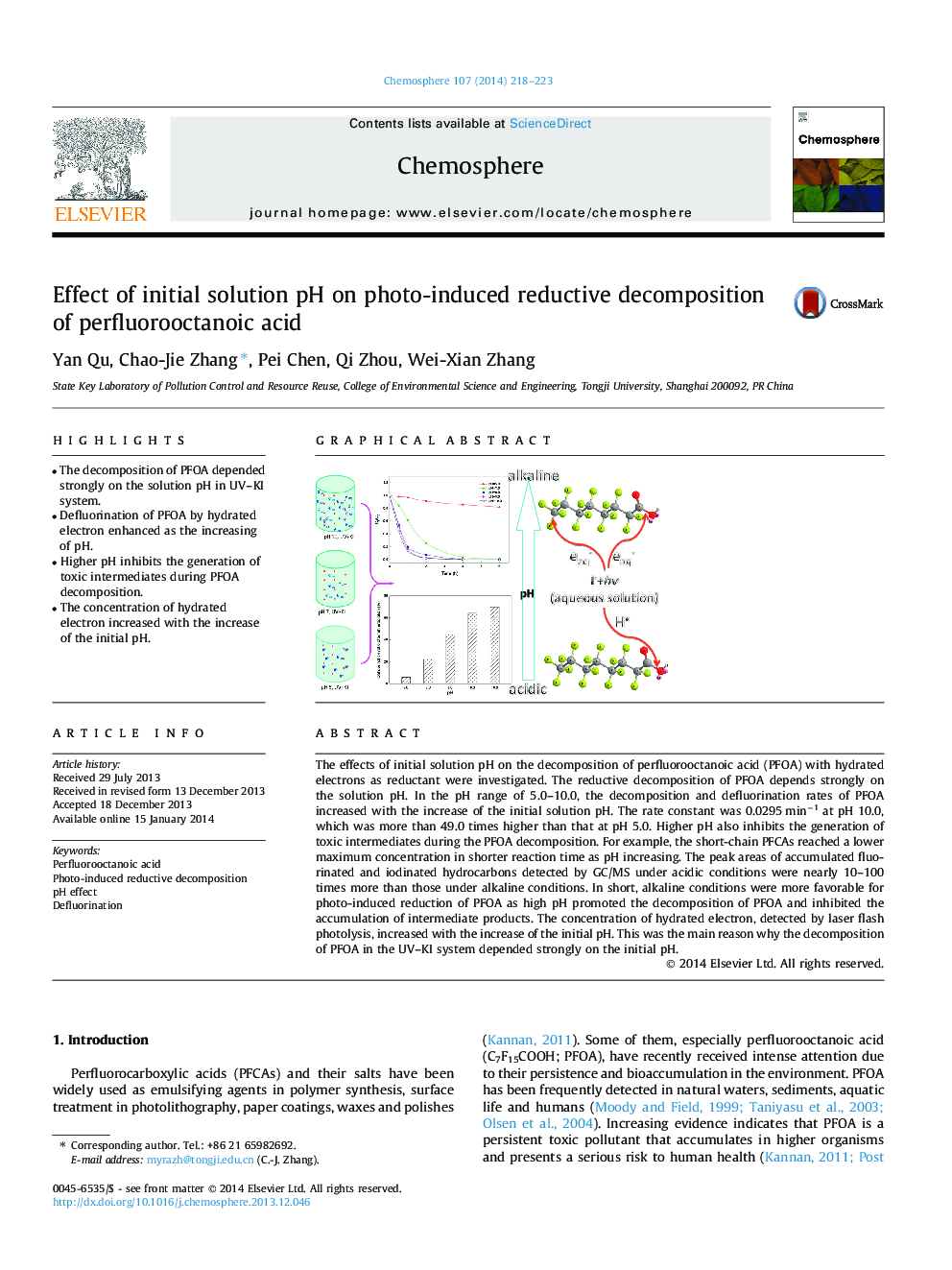
- The decomposition of PFOA depended strongly on the solution pH in UV-KI system.
- Defluorination of PFOA by hydrated electron enhanced as the increasing of pH.
- Higher pH inhibits the generation of toxic intermediates during PFOA decomposition.
- The concentration of hydrated electron increased with the increase of the initial pH.
The effects of initial solution pH on the decomposition of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) with hydrated electrons as reductant were investigated. The reductive decomposition of PFOA depends strongly on the solution pH. In the pH range of 5.0-10.0, the decomposition and defluorination rates of PFOA increased with the increase of the initial solution pH. The rate constant was 0.0295Â minâ1 at pH 10.0, which was more than 49.0 times higher than that at pH 5.0. Higher pH also inhibits the generation of toxic intermediates during the PFOA decomposition. For example, the short-chain PFCAs reached a lower maximum concentration in shorter reaction time as pH increasing. The peak areas of accumulated fluorinated and iodinated hydrocarbons detected by GC/MS under acidic conditions were nearly 10-100 times more than those under alkaline conditions. In short, alkaline conditions were more favorable for photo-induced reduction of PFOA as high pH promoted the decomposition of PFOA and inhibited the accumulation of intermediate products. The concentration of hydrated electron, detected by laser flash photolysis, increased with the increase of the initial pH. This was the main reason why the decomposition of PFOA in the UV-KI system depended strongly on the initial pH.
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 107, July 2014, Pages 218-223