| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6454180 | 1418811 | 2017 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
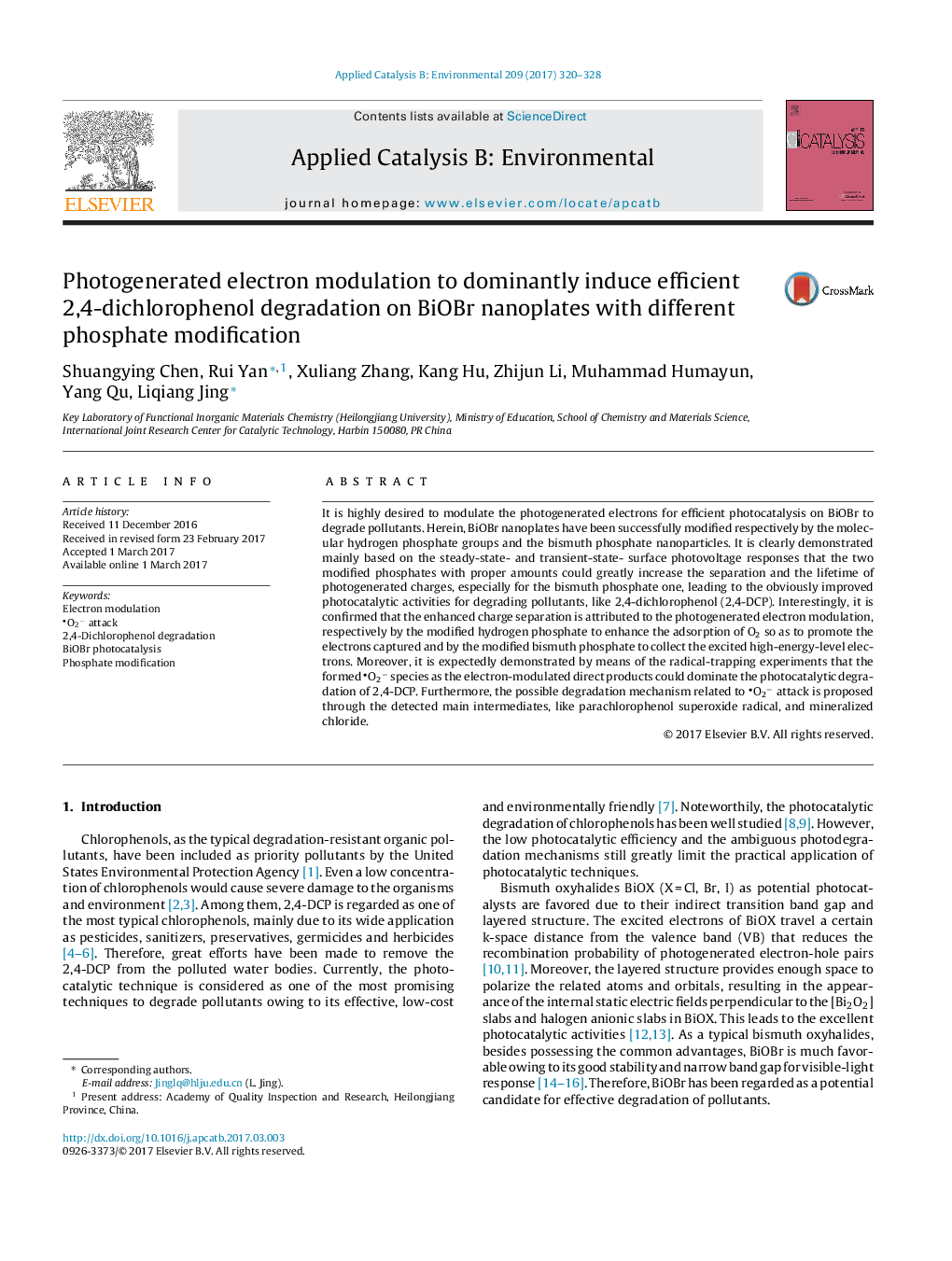
- BiOBr nanoplates are modified by hydrogen phosphate molecules and bismuth phosphate nanoparticles.
- The two modifications could increase separation and lifetime of photogenerated charges of BiOBr.
- This leads to obviously improved photocatalytic activities for degrading 2,4-DCP.
- Enhanced charge separation is attributed to the photogenerated electron modulation by modifiers.
- Formed O2â species dominates photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-DCP by inducing dechlorination.
It is highly desired to modulate the photogenerated electrons for efficient photocatalysis on BiOBr to degrade pollutants. Herein, BiOBr nanoplates have been successfully modified respectively by the molecular hydrogen phosphate groups and the bismuth phosphate nanoparticles. It is clearly demonstrated mainly based on the steady-state- and transient-state- surface photovoltage responses that the two modified phosphates with proper amounts could greatly increase the separation and the lifetime of photogenerated charges, especially for the bismuth phosphate one, leading to the obviously improved photocatalytic activities for degrading pollutants, like 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP). Interestingly, it is confirmed that the enhanced charge separation is attributed to the photogenerated electron modulation, respectively by the modified hydrogen phosphate to enhance the adsorption of O2 so as to promote the electrons captured and by the modified bismuth phosphate to collect the excited high-energy-level electrons. Moreover, it is expectedly demonstrated by means of the radical-trapping experiments that the formed O2â species as the electron-modulated direct products could dominate the photocatalytic degradation of 2,4-DCP. Furthermore, the possible degradation mechanism related to O2â attack is proposed through the detected main intermediates, like parachlorophenol superoxide radical, and mineralized chloride.
115Photogenerated electron modulation with different phosphate modification could dominantly induce efficient 2,4-DCP degradation on BiOBr nanoplates.
Journal: Applied Catalysis B: Environmental - Volume 209, 15 July 2017, Pages 320-328