| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6465020 | 1422951 | 2017 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
- NR could accelerate electron transfer efficiency in MEC for sulfate removal.
- Graphite felt triggered a better synergy with NR to facilitate electron transfer.
- GF morphology was conducive to biofilm formation and bioelectrocatalytic activity.
- Optimized MEC features higher sulfate removal and electron utilization efficiency.
- Improved MEC enhanced the population dominant of SRB and metabolic activity.
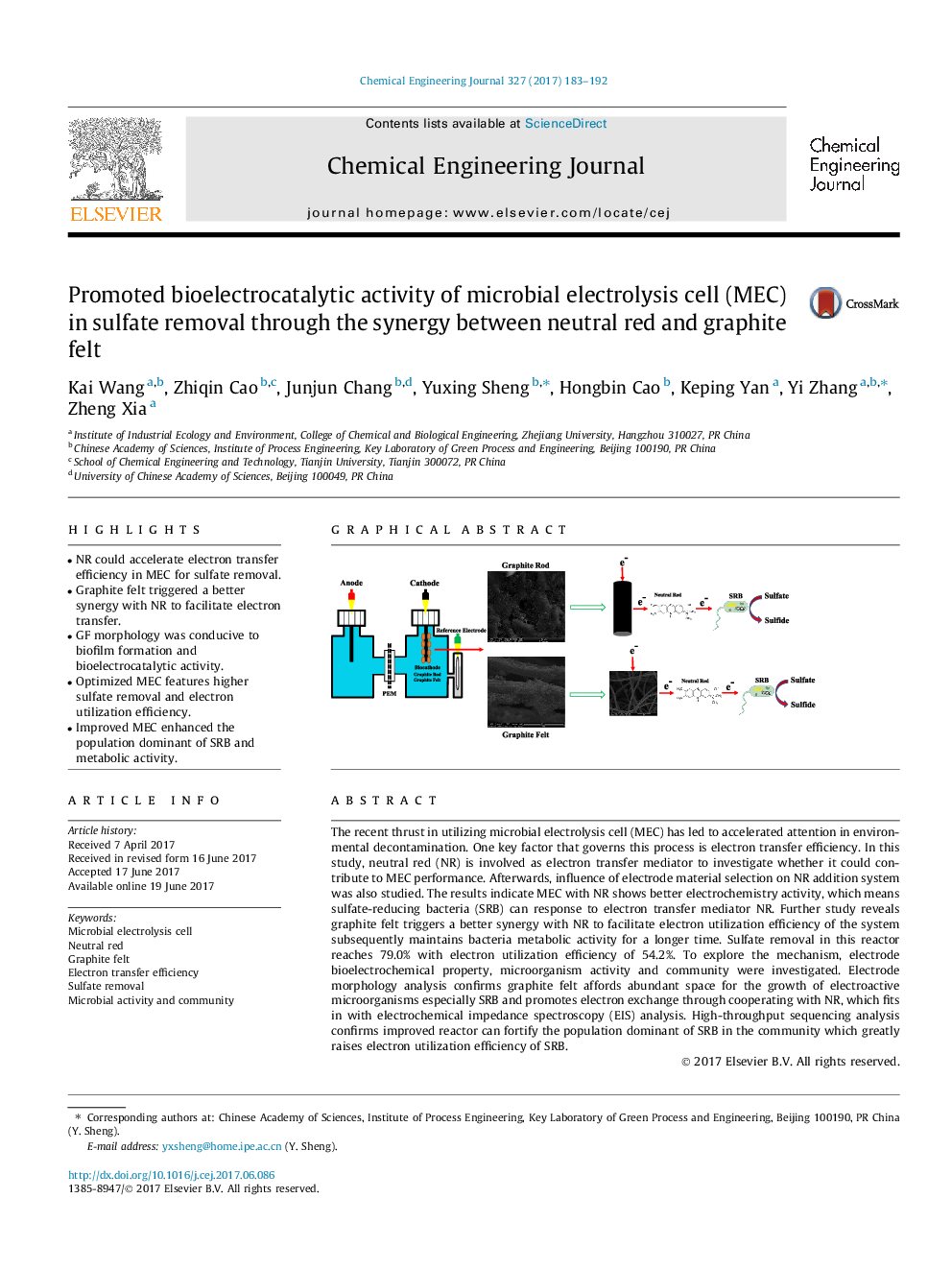
The recent thrust in utilizing microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) has led to accelerated attention in environmental decontamination. One key factor that governs this process is electron transfer efficiency. In this study, neutral red (NR) is involved as electron transfer mediator to investigate whether it could contribute to MEC performance. Afterwards, influence of electrode material selection on NR addition system was also studied. The results indicate MEC with NR shows better electrochemistry activity, which means sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) can response to electron transfer mediator NR. Further study reveals graphite felt triggers a better synergy with NR to facilitate electron utilization efficiency of the system subsequently maintains bacteria metabolic activity for a longer time. Sulfate removal in this reactor reaches 79.0% with electron utilization efficiency of 54.2%. To explore the mechanism, electrode bioelectrochemical property, microorganism activity and community were investigated. Electrode morphology analysis confirms graphite felt affords abundant space for the growth of electroactive microorganisms especially SRB and promotes electron exchange through cooperating with NR, which fits in with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) analysis. High-throughput sequencing analysis confirms improved reactor can fortify the population dominant of SRB in the community which greatly raises electron utilization efficiency of SRB.
156
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 327, 1 November 2017, Pages 183-192