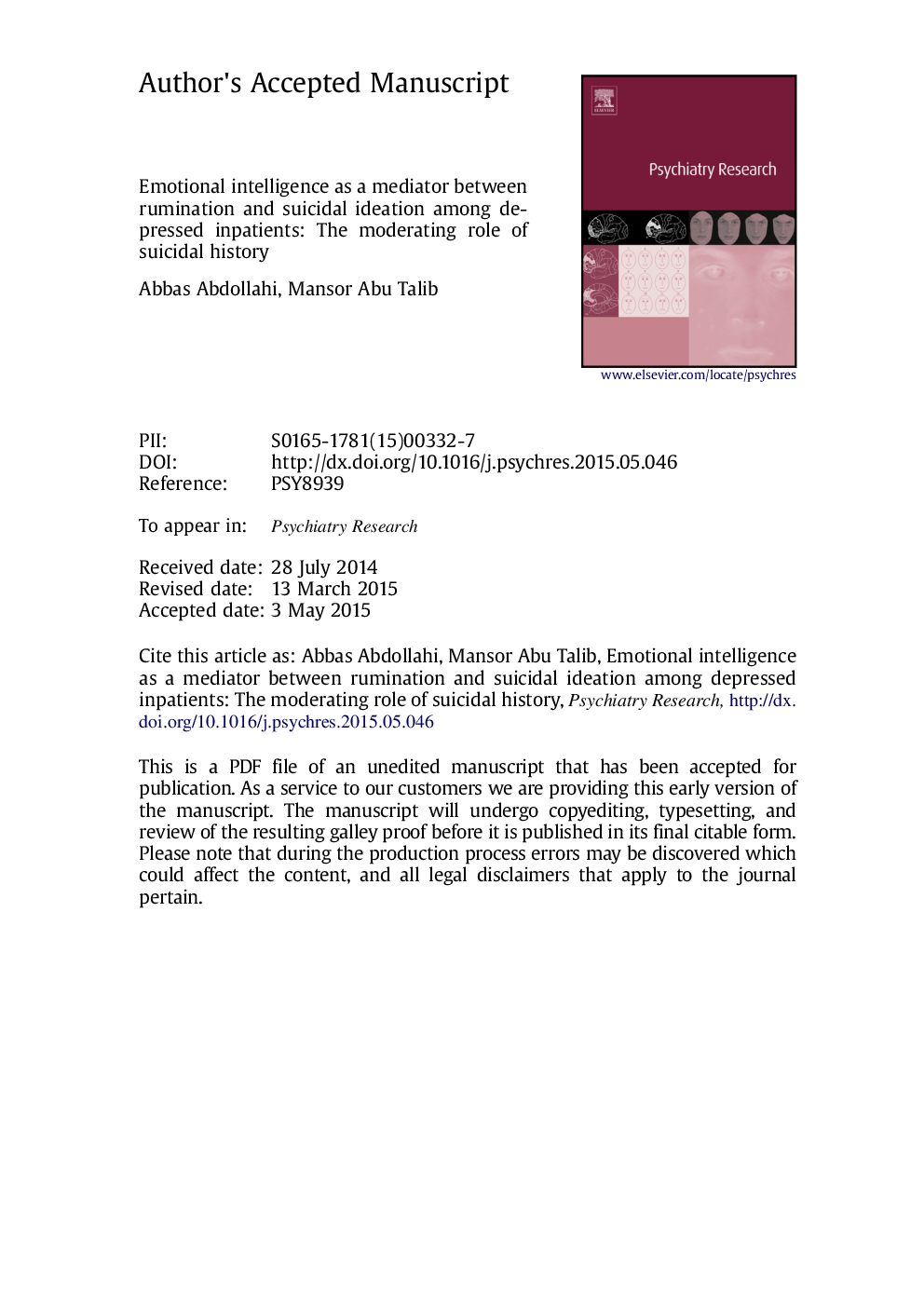
| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10303714 | 545613 | 2015 | 30 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
عنوان انگلیسی مقاله ISI
Emotional intelligence as a mediator between rumination and suicidal ideation among depressed inpatients: The moderating role of suicidal history
ترجمه فارسی عنوان
هوش هیجانی به عنوان یک واسطه بین نشستگی و عقاید خودکشی در میان بیماران افسرده: نقش مستمر سابقه خودکشی
دانلود مقاله + سفارش ترجمه
دانلود مقاله ISI انگلیسی
رایگان برای ایرانیان
کلمات کلیدی
شکنجه، هوش هیجانی، افکار خودکشی، بیماران افسرده،
ترجمه چکیده
خودکشی یک مسئله بهداشت عمومی محسوب می شود و در جهان به علت جدی مرگ است. بنابراین، این مطالعه به منظور بررسی روابط بین اخلاق، انعکاس، هوش هیجانی (ارزیابی شده با آزمون عملکردی) و ایده های خودکشی طراحی شده است. نقش میانجی گری هوش هیجانی بر روابط بین اخلاق و انعکاس با عقاید خودکشی؛ و نقش تعدیل کننده تاریخ خودکشی در روابط بین محرک، انعکاس و هوش هیجانی با افکار خودکشی در میان نوجوانان افسرده ایرانی. این مطالعه شامل یک نمونه مقطعی از 202 بیمار مبتلا به افسردگی نوجوانان از پنج بیمارستان دولتی شهر تهران بود که اقدامات افسردگی، نشستن، هوش هیجانی و سابقه خودکشی را به عنوان شاخص های افکار خودکشی انجام داد. مدل سازی معادلات ساختاری برآورد کرد که بیماران مبتلا به افسردگی با سطوح بالای نشخوار فکری و بازتابنده و سطح پایین هوش هیجانی بیشتر به افکار خودکشی گزارش داده می شود. علاوه بر این، هوش هیجانی بخشی از ارتباط روحیه بازدارندگی و انعکاسی با عقاید خودکشی است. تاریخ خودکشی روابط بین فرسودگی، انعکاس و هوش هیجانی با عقاید خودکشی را تعدیل کرد. این یافته ها، اهمیت هوش هیجانی را به عنوان عامل تأثیرگذار در مقابل اثرات زیانبار سبک های نشاط و عقاید خودکشی تقویت می کند. نتایج نشان می دهد که فرسودگی و انعکاس تأثیرات مضر روی افکار خودکشی در بیماران افسرده دارد.
موضوعات مرتبط
علوم زیستی و بیوفناوری
علم عصب شناسی
روانپزشکی بیولوژیکی
چکیده انگلیسی
Suicide is a substantial public health problem, and it remains a serious cause of death in the world. Therefore, this study was designed to examine the relationships between brooding, reflection, emotional intelligence (assessed by performance-based test), and suicidal ideation; the mediation role of emotional intelligence on the relationships between brooding and reflection with suicidal ideation; and the moderating role of suicidal history on the relationships between brooding, reflection, and emotional intelligence with suicidal ideation among Iranian depressed adolescents. The study consisted of a cross-sectional sample of 202 depressed adolescent inpatients from five public hospitals in Tehran, Iran completed measures of depression, rumination, emotional intelligence, and suicide attempt history as indices of suicidal ideation. Structural Equation Modelling estimated that depressed adolescent inpatients with high levels of brooding and reflective rumination, and low levels of emotional intelligence were more likely to report suicidal ideation. Moreover, emotional intelligence partially mediated the relationships between brooding and reflective rumination with suicidal ideation. Suicidal history moderated the relationships between brooding, reflection, and emotional intelligence with suicidal ideation. These findings reinforce the importance of emotional intelligence as an influencing factor against the deleterious effects of rumination styles and suicidal ideation. The results indicate that brooding and reflection have detrimental effects on suicidal ideation in depressed inpatients.
ناشر
Database: Elsevier - ScienceDirect (ساینس دایرکت)
Journal: Psychiatry Research - Volume 228, Issue 3, 30 August 2015, Pages 591-597
Journal: Psychiatry Research - Volume 228, Issue 3, 30 August 2015, Pages 591-597
نویسندگان
Abbas Abdollahi, Mansor Abu Talib,