| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1164266 | 1490978 | 2015 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
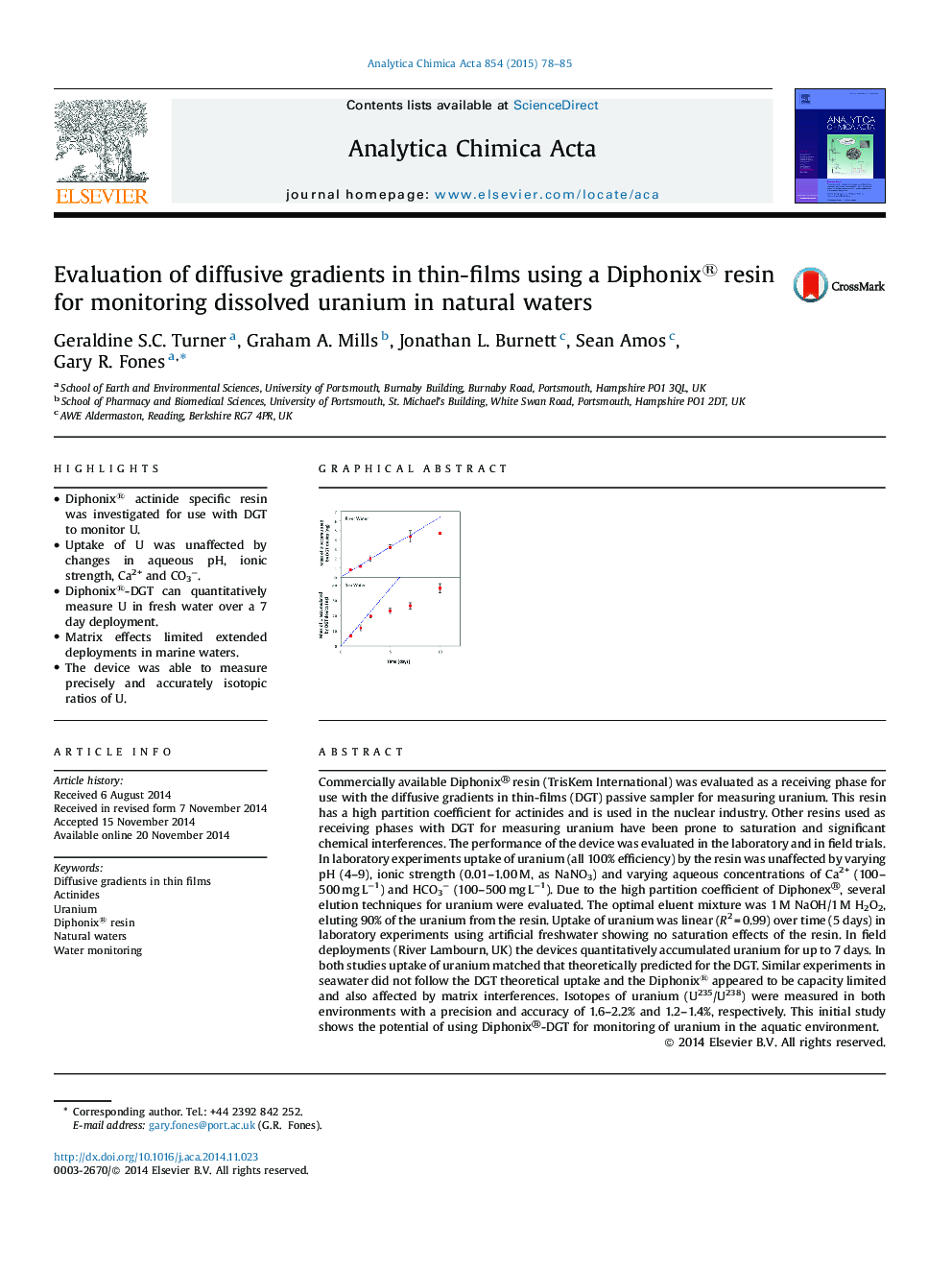
• Diphonix® actinide specific resin was investigated for use with DGT to monitor U.
• Uptake of U was unaffected by changes in aqueous pH, ionic strength, Ca2+ and CO3−.
• Diphonix®-DGT can quantitatively measure U in fresh water over a 7 day deployment.
• Matrix effects limited extended deployments in marine waters.
• The device was able to measure precisely and accurately isotopic ratios of U.
Commercially available Diphonix® resin (TrisKem International) was evaluated as a receiving phase for use with the diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) passive sampler for measuring uranium. This resin has a high partition coefficient for actinides and is used in the nuclear industry. Other resins used as receiving phases with DGT for measuring uranium have been prone to saturation and significant chemical interferences. The performance of the device was evaluated in the laboratory and in field trials. In laboratory experiments uptake of uranium (all 100% efficiency) by the resin was unaffected by varying pH (4–9), ionic strength (0.01–1.00 M, as NaNO3) and varying aqueous concentrations of Ca2+ (100–500 mg L−1) and HCO3− (100–500 mg L−1). Due to the high partition coefficient of Diphonex®, several elution techniques for uranium were evaluated. The optimal eluent mixture was 1 M NaOH/1 M H2O2, eluting 90% of the uranium from the resin. Uptake of uranium was linear (R2 = 0.99) over time (5 days) in laboratory experiments using artificial freshwater showing no saturation effects of the resin. In field deployments (River Lambourn, UK) the devices quantitatively accumulated uranium for up to 7 days. In both studies uptake of uranium matched that theoretically predicted for the DGT. Similar experiments in seawater did not follow the DGT theoretical uptake and the Diphonix® appeared to be capacity limited and also affected by matrix interferences. Isotopes of uranium (U235/U238) were measured in both environments with a precision and accuracy of 1.6–2.2% and 1.2–1.4%, respectively. This initial study shows the potential of using Diphonix®-DGT for monitoring of uranium in the aquatic environment.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 854, 7 January 2015, Pages 78–85