| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1166327 | 1491099 | 2012 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
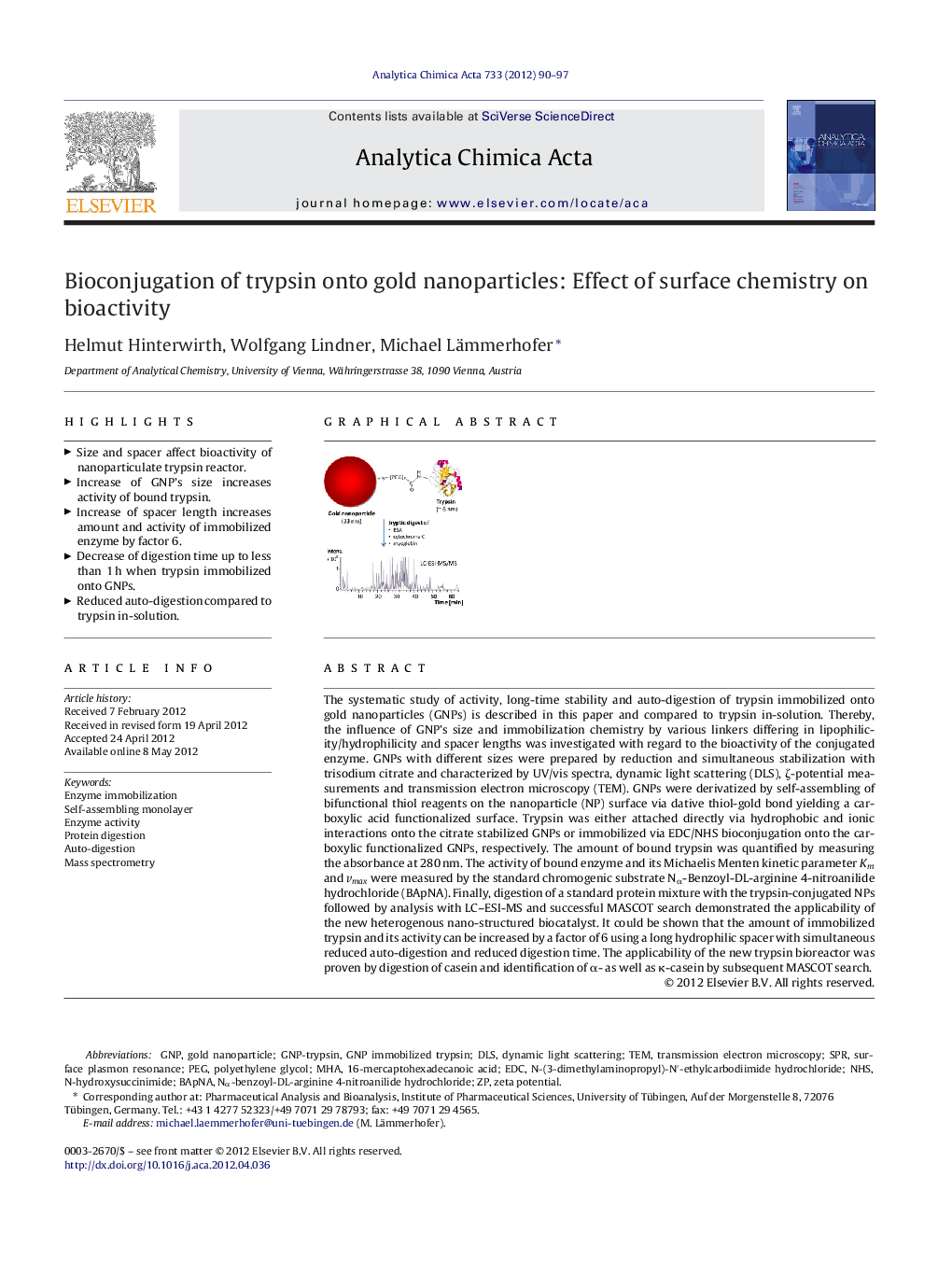
The systematic study of activity, long-time stability and auto-digestion of trypsin immobilized onto gold nanoparticles (GNPs) is described in this paper and compared to trypsin in-solution. Thereby, the influence of GNP's size and immobilization chemistry by various linkers differing in lipophilicity/hydrophilicity and spacer lengths was investigated with regard to the bioactivity of the conjugated enzyme. GNPs with different sizes were prepared by reduction and simultaneous stabilization with trisodium citrate and characterized by UV/vis spectra, dynamic light scattering (DLS), ζ-potential measurements and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). GNPs were derivatized by self-assembling of bifunctional thiol reagents on the nanoparticle (NP) surface via dative thiol-gold bond yielding a carboxylic acid functionalized surface. Trypsin was either attached directly via hydrophobic and ionic interactions onto the citrate stabilized GNPs or immobilized via EDC/NHS bioconjugation onto the carboxylic functionalized GNPs, respectively. The amount of bound trypsin was quantified by measuring the absorbance at 280 nm. The activity of bound enzyme and its Michaelis Menten kinetic parameter Km and vmax were measured by the standard chromogenic substrate Nα-Benzoyl-DL-arginine 4-nitroanilide hydrochloride (BApNA). Finally, digestion of a standard protein mixture with the trypsin-conjugated NPs followed by analysis with LC–ESI-MS and successful MASCOT search demonstrated the applicability of the new heterogenous nano-structured biocatalyst. It could be shown that the amount of immobilized trypsin and its activity can be increased by a factor of 6 using a long hydrophilic spacer with simultaneous reduced auto-digestion and reduced digestion time. The applicability of the new trypsin bioreactor was proven by digestion of casein and identification of α- as well as κ-casein by subsequent MASCOT search.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Size and spacer affect bioactivity of nanoparticulate trypsin reactor.
► Increase of GNP's size increases activity of bound trypsin.
► Increase of spacer length increases amount and activity of immobilized enzyme by factor 6.
► Decrease of digestion time up to less than 1 h when trypsin immobilized onto GNPs.
► Reduced auto-digestion compared to trypsin in-solution.
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 733, 6 July 2012, Pages 90–97