| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1308089 | 1499167 | 2014 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
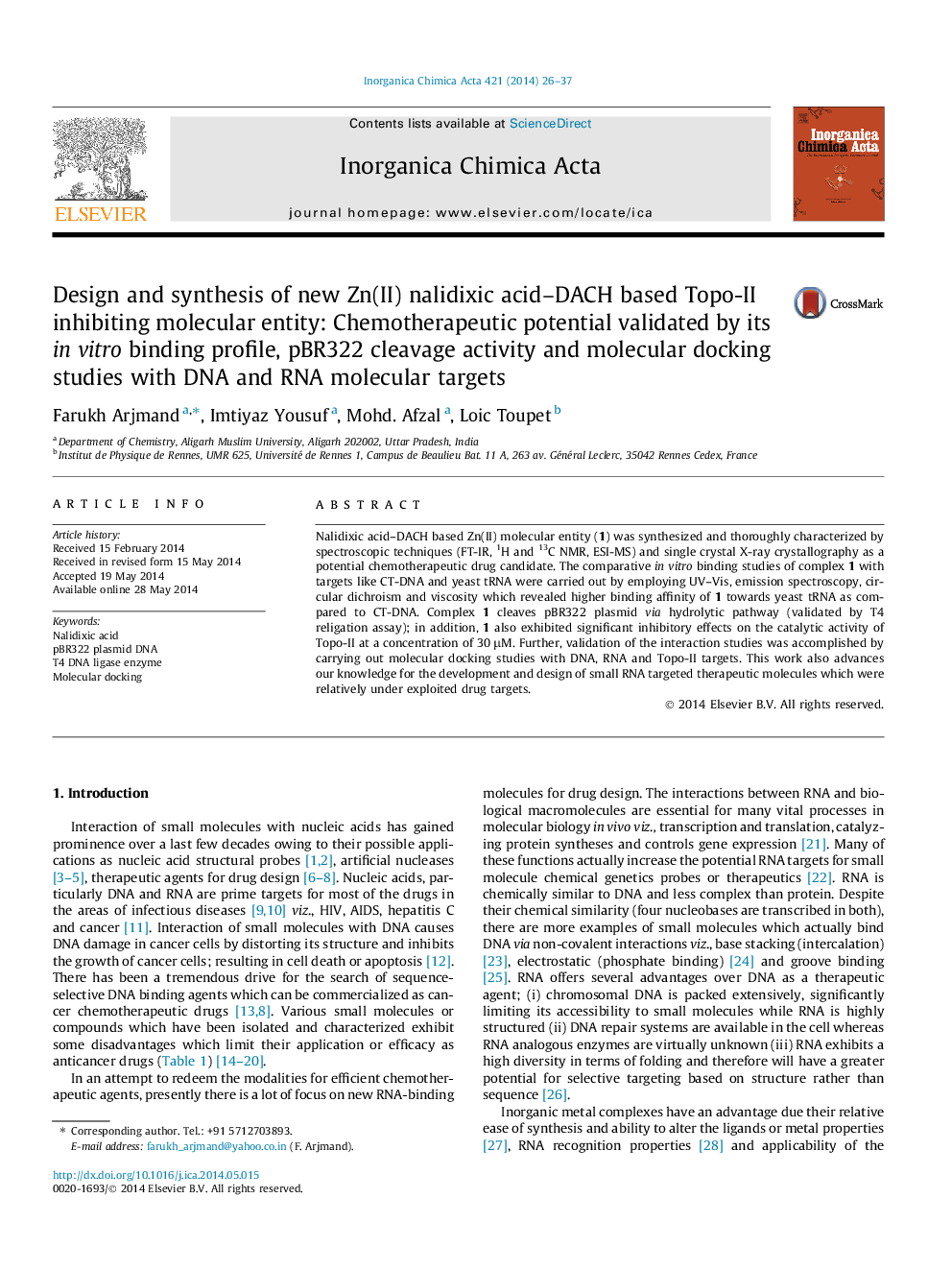
• Zinc(II) based drug entity, 1 was synthesized from nalidixic acid and DACH ligands.
• Complex 1 showed avid binding propensity for tRNA as compared to DNA.
• Complex 1 was found to be a catalytic inhibitor of human Topo-II.
• Hydrolytic cleavage of pBR322 DNA by complex 1 was validated by T4 DNA ligation assay.
• Molecular docking results corroborated well with other spectroscopic results.
Nalidixic acid–DACH based Zn(II) molecular entity (1) was synthesized and thoroughly characterized by spectroscopic techniques (FT-IR, 1H and 13C NMR, ESI-MS) and single crystal X-ray crystallography as a potential chemotherapeutic drug candidate. The comparative in vitro binding studies of complex 1 with targets like CT-DNA and yeast tRNA were carried out by employing UV–Vis, emission spectroscopy, circular dichroism and viscosity which revealed higher binding affinity of 1 towards yeast tRNA as compared to CT-DNA. Complex 1 cleaves pBR322 plasmid via hydrolytic pathway (validated by T4 religation assay); in addition, 1 also exhibited significant inhibitory effects on the catalytic activity of Topo-II at a concentration of 30 μM. Further, validation of the interaction studies was accomplished by carrying out molecular docking studies with DNA, RNA and Topo-II targets. This work also advances our knowledge for the development and design of small RNA targeted therapeutic molecules which were relatively under exploited drug targets.
Molecular docked model of Zn(II) nalidixic acid–DACH complex, 1 targeting TAR RNA.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Inorganica Chimica Acta - Volume 421, 1 September 2014, Pages 26–37