| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145323 | 456338 | 2016 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
• EGCG/Fe3O4 showed notable catalytic ability for diuron degradation.
• Alcohols-scavenging experiments identified the presence of OH and SO4−.
• XPS demonstrated the variation of Fe and O in EGCG/Fe3O4 before and after use.
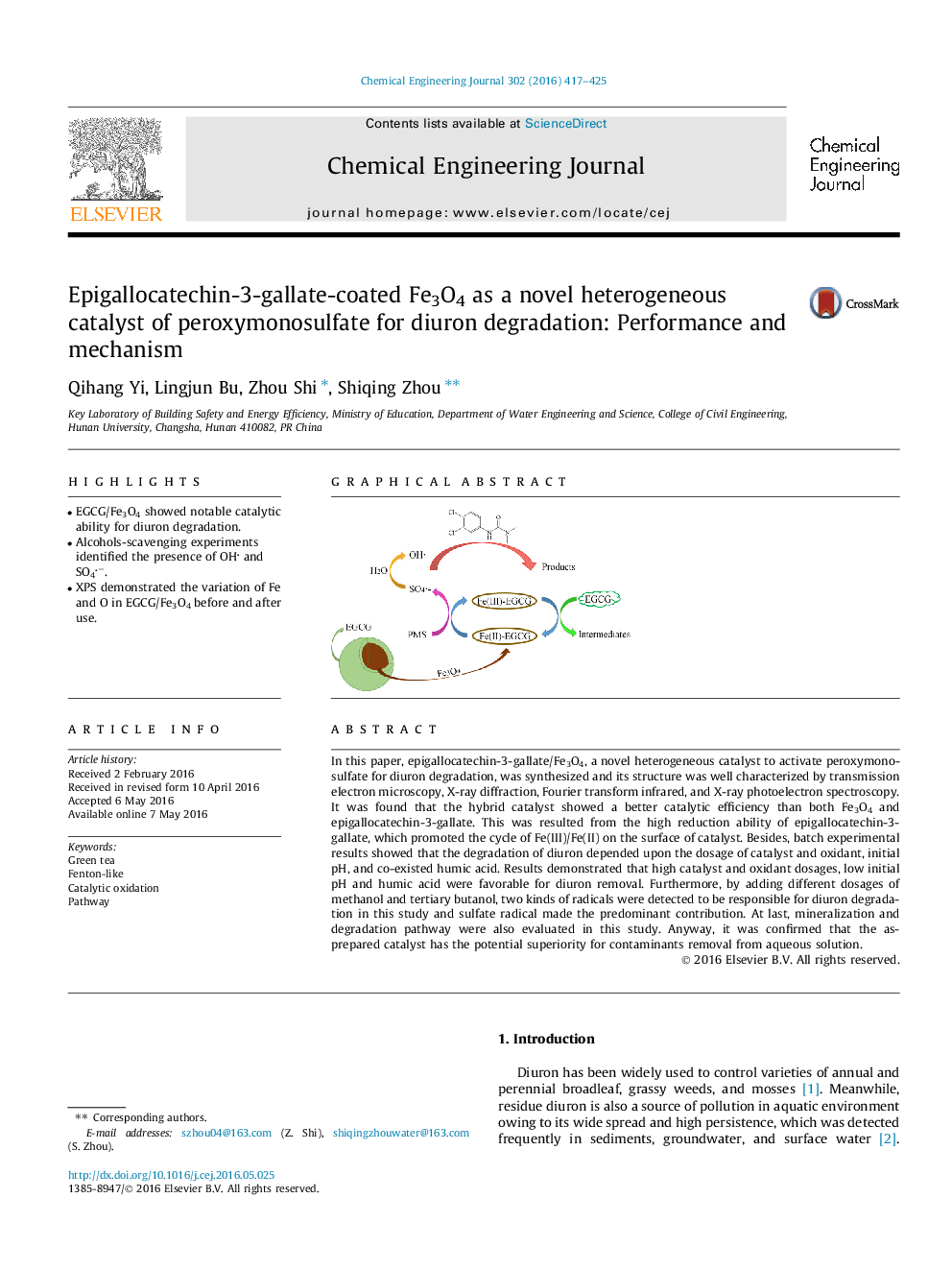
In this paper, epigallocatechin-3-gallate/Fe3O4, a novel heterogeneous catalyst to activate peroxymonosulfate for diuron degradation, was synthesized and its structure was well characterized by transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. It was found that the hybrid catalyst showed a better catalytic efficiency than both Fe3O4 and epigallocatechin-3-gallate. This was resulted from the high reduction ability of epigallocatechin-3-gallate, which promoted the cycle of Fe(III)/Fe(II) on the surface of catalyst. Besides, batch experimental results showed that the degradation of diuron depended upon the dosage of catalyst and oxidant, initial pH, and co-existed humic acid. Results demonstrated that high catalyst and oxidant dosages, low initial pH and humic acid were favorable for diuron removal. Furthermore, by adding different dosages of methanol and tertiary butanol, two kinds of radicals were detected to be responsible for diuron degradation in this study and sulfate radical made the predominant contribution. At last, mineralization and degradation pathway were also evaluated in this study. Anyway, it was confirmed that the as-prepared catalyst has the potential superiority for contaminants removal from aqueous solution.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 302, 15 October 2016, Pages 417–425