| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145551 | 456343 | 2016 | 14 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
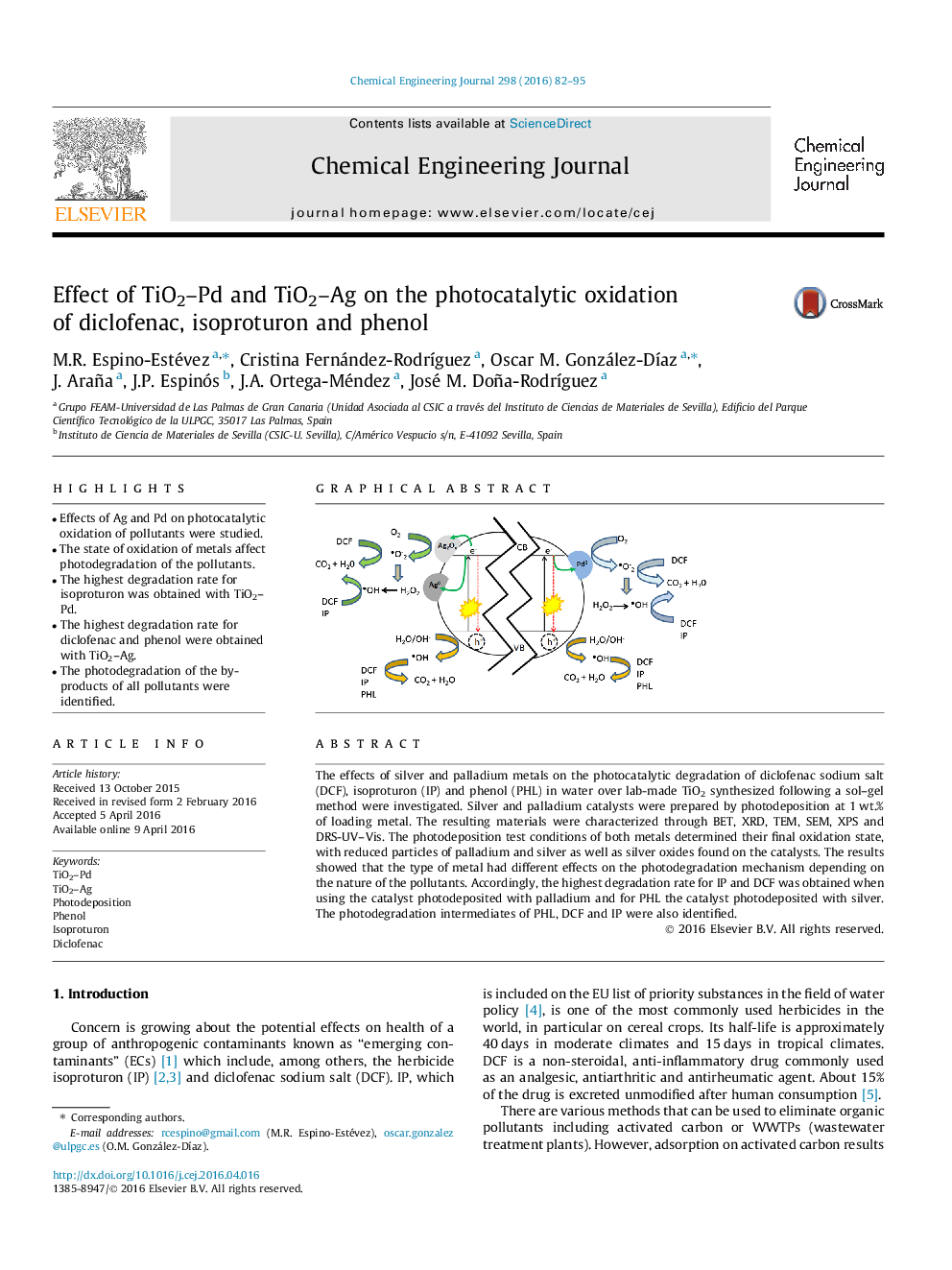
• Effects of Ag and Pd on photocatalytic oxidation of pollutants were studied.
• The state of oxidation of metals affect photodegradation of the pollutants.
• The highest degradation rate for isoproturon was obtained with TiO2–Pd.
• The highest degradation rate for diclofenac and phenol were obtained with TiO2–Ag.
• The photodegradation of the by-products of all pollutants were identified.
The effects of silver and palladium metals on the photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac sodium salt (DCF), isoproturon (IP) and phenol (PHL) in water over lab-made TiO2 synthesized following a sol–gel method were investigated. Silver and palladium catalysts were prepared by photodeposition at 1 wt.% of loading metal. The resulting materials were characterized through BET, XRD, TEM, SEM, XPS and DRS-UV–Vis. The photodeposition test conditions of both metals determined their final oxidation state, with reduced particles of palladium and silver as well as silver oxides found on the catalysts. The results showed that the type of metal had different effects on the photodegradation mechanism depending on the nature of the pollutants. Accordingly, the highest degradation rate for IP and DCF was obtained when using the catalyst photodeposited with palladium and for PHL the catalyst photodeposited with silver. The photodegradation intermediates of PHL, DCF and IP were also identified.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slide
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 298, 15 August 2016, Pages 82–95