| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2792587 | 1155064 | 2016 | 14 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
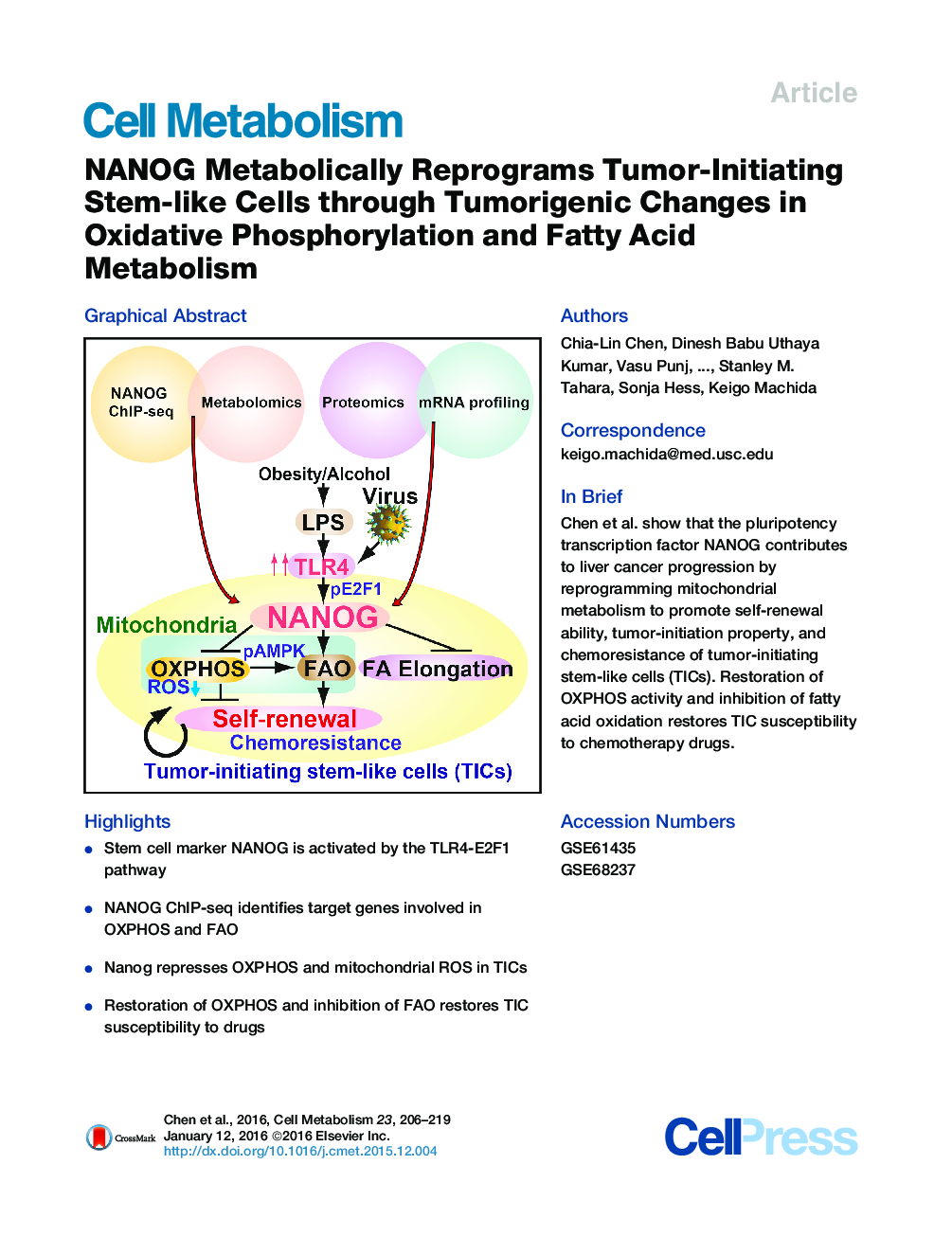
• Stem cell marker NANOG is activated by the TLR4-E2F1 pathway
• NANOG ChIP-seq identifies target genes involved in OXPHOS and FAO
• Nanog represses OXPHOS and mitochondrial ROS in TICs
• Restoration of OXPHOS and inhibition of FAO restores TIC susceptibility to drugs
SummaryStem cell markers, including NANOG, have been implicated in various cancers; however, the functional contribution of NANOG to cancer pathogenesis has remained unclear. Here, we show that NANOG is induced by Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling via phosphorylation of E2F1 and that downregulation of Nanog slows down hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression induced by alcohol western diet and hepatitis C virus protein in mice. NANOG ChIP-seq analyses reveal that NANOG regulates the expression of genes involved in mitochondrial metabolic pathways required to maintain tumor-initiating stem-like cells (TICs). NANOG represses mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) genes, as well as ROS generation, and activates fatty acid oxidation (FAO) to support TIC self-renewal and drug resistance. Restoration of OXPHOS activity and inhibition of FAO renders TICs susceptible to a standard care chemotherapy drug for HCC, sorafenib. This study provides insights into the mechanisms of NANOG-mediated generation of TICs, tumorigenesis, and chemoresistance through reprogramming of mitochondrial metabolism.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (254 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 23, Issue 1, 12 January 2016, Pages 206–219