| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3352878 | 1216804 | 2016 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
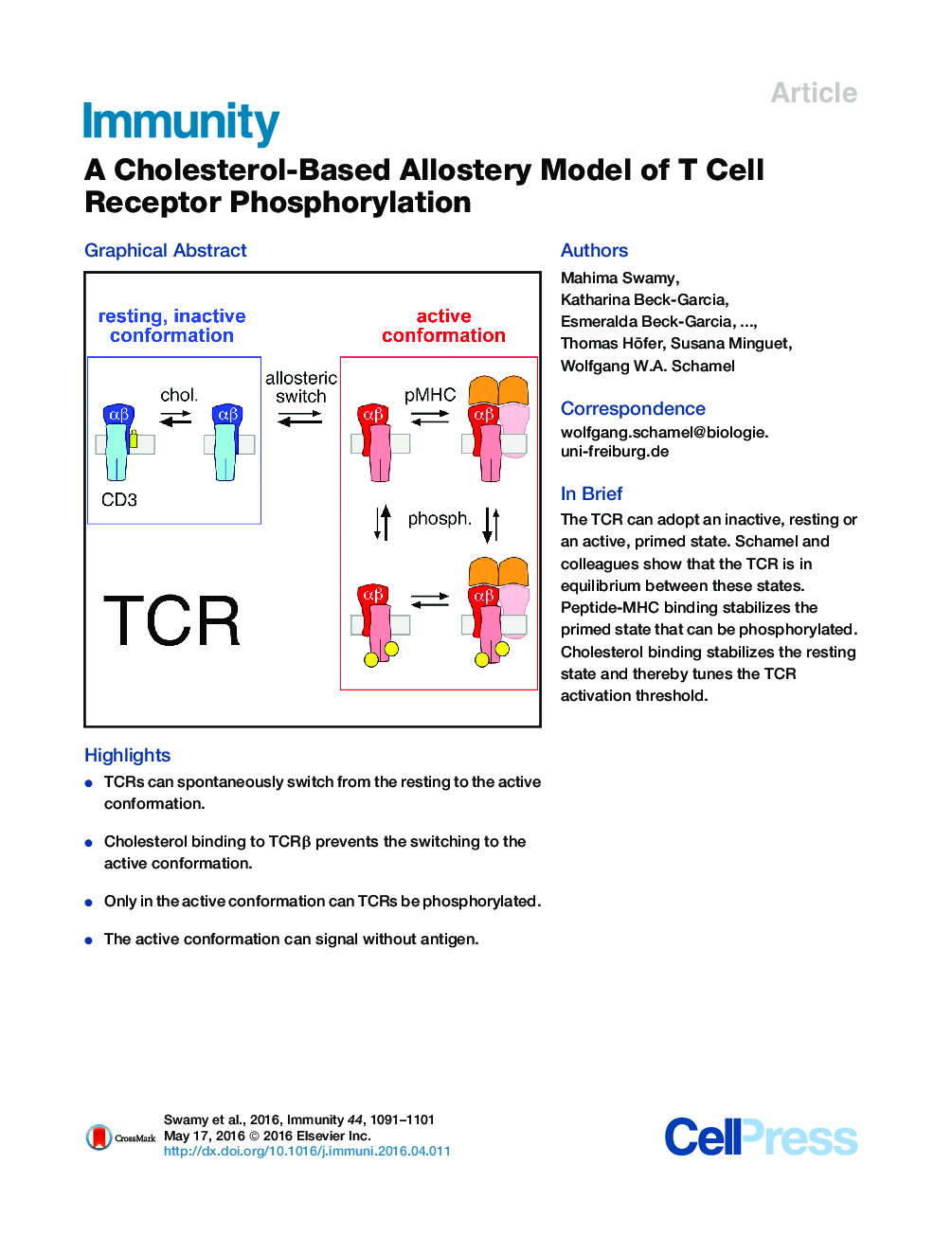
• TCRs can spontaneously switch from the resting to the active conformation.
• Cholesterol binding to TCRβ prevents the switching to the active conformation.
• Only in the active conformation can TCRs be phosphorylated.
• The active conformation can signal without antigen.
SummarySignaling through the T cell receptor (TCR) controls adaptive immune responses. Antigen binding to TCRαβ transmits signals through the plasma membrane to induce phosphorylation of the CD3 cytoplasmic tails by incompletely understood mechanisms. Here we show that cholesterol bound to the TCRβ transmembrane region keeps the TCR in a resting, inactive conformation that cannot be phosphorylated by active kinases. Only TCRs that spontaneously detached from cholesterol could switch to the active conformation (termed primed TCRs) and then be phosphorylated. Indeed, by modulating cholesterol binding genetically or enzymatically, we could switch the TCR between the resting and primed states. The active conformation was stabilized by binding to peptide-MHC, which thus controlled TCR signaling. These data are explained by a model of reciprocal allosteric regulation of TCR phosphorylation by cholesterol and ligand binding. Our results provide both a molecular mechanism and a conceptual framework for how lipid-receptor interactions regulate signal transduction.Video Abstract To view the video inline, enable JavaScript on your browser. However, you can download and view the video by clicking on the icon belowHelp with MP4 filesOptionsDownload video (7935 K)
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (166 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 44, Issue 5, 17 May 2016, Pages 1091–1101