| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3352959 | 1216814 | 2015 | 11 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
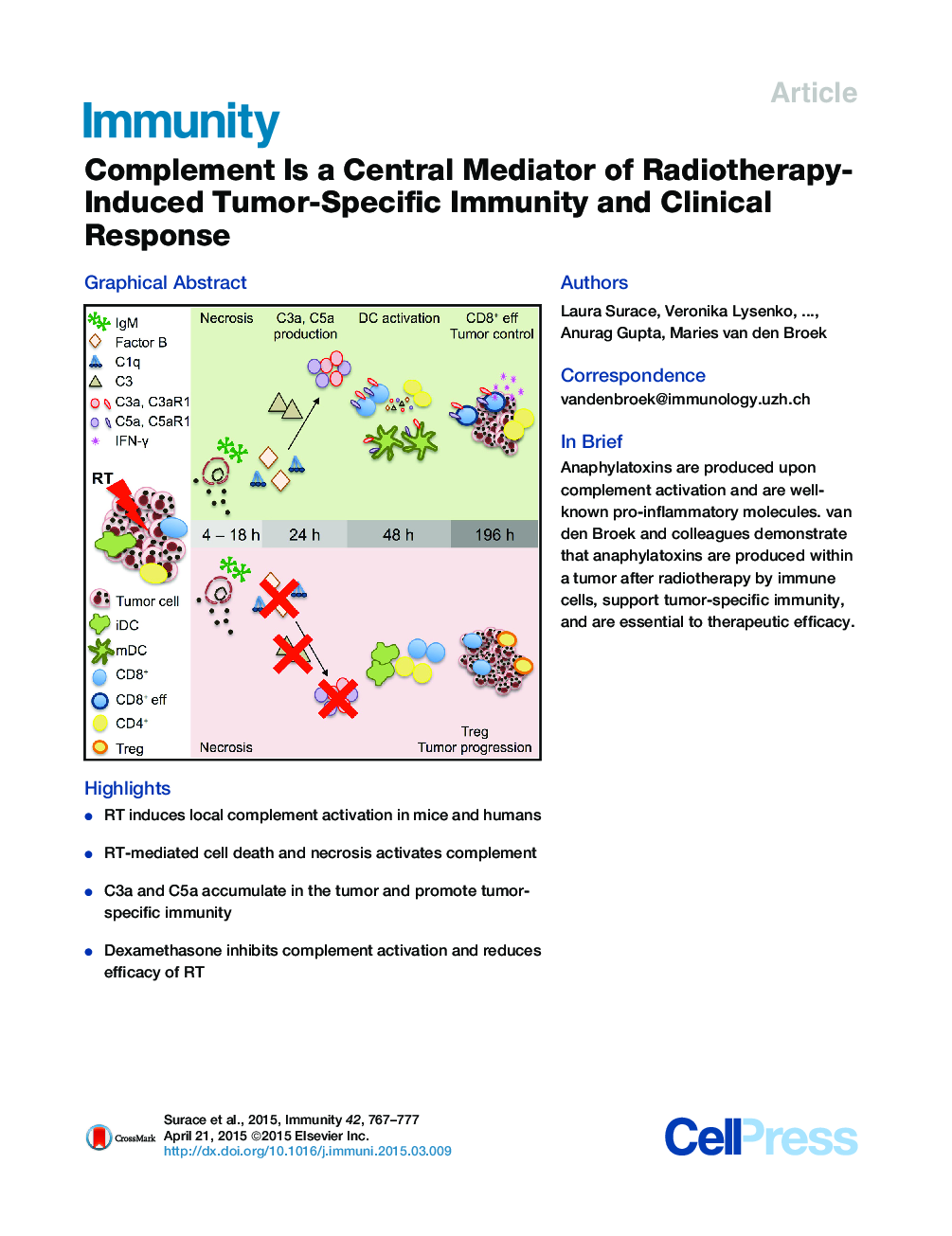
• RT induces local complement activation in mice and humans
• RT-mediated cell death and necrosis activates complement
• C3a and C5a accumulate in the tumor and promote tumor-specific immunity
• Dexamethasone inhibits complement activation and reduces efficacy of RT
SummaryRadiotherapy induces DNA damage and cell death, but recent data suggest that concomitant immune stimulation is an integral part of the therapeutic action of ionizing radiation. It is poorly understood how radiotherapy supports tumor-specific immunity. Here we report that radiotherapy induced tumor cell death and transiently activated complement both in murine and human tumors. The local production of pro-inflammatory anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a was crucial to the tumor response to radiotherapy and concomitant stimulation of tumor-specific immunity. Dexamethasone, a drug frequently given during radiotherapy, limited complement activation and the anti-tumor effects of the immune system. Overall, our findings indicate that anaphylatoxins are key players in radiotherapy-induced tumor-specific immunity and the ensuing clinical responses.
Graphical AbstractFigure optionsDownload high-quality image (204 K)Download as PowerPoint slide
Journal: - Volume 42, Issue 4, 21 April 2015, Pages 767–777