| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4409501 | 1307487 | 2013 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
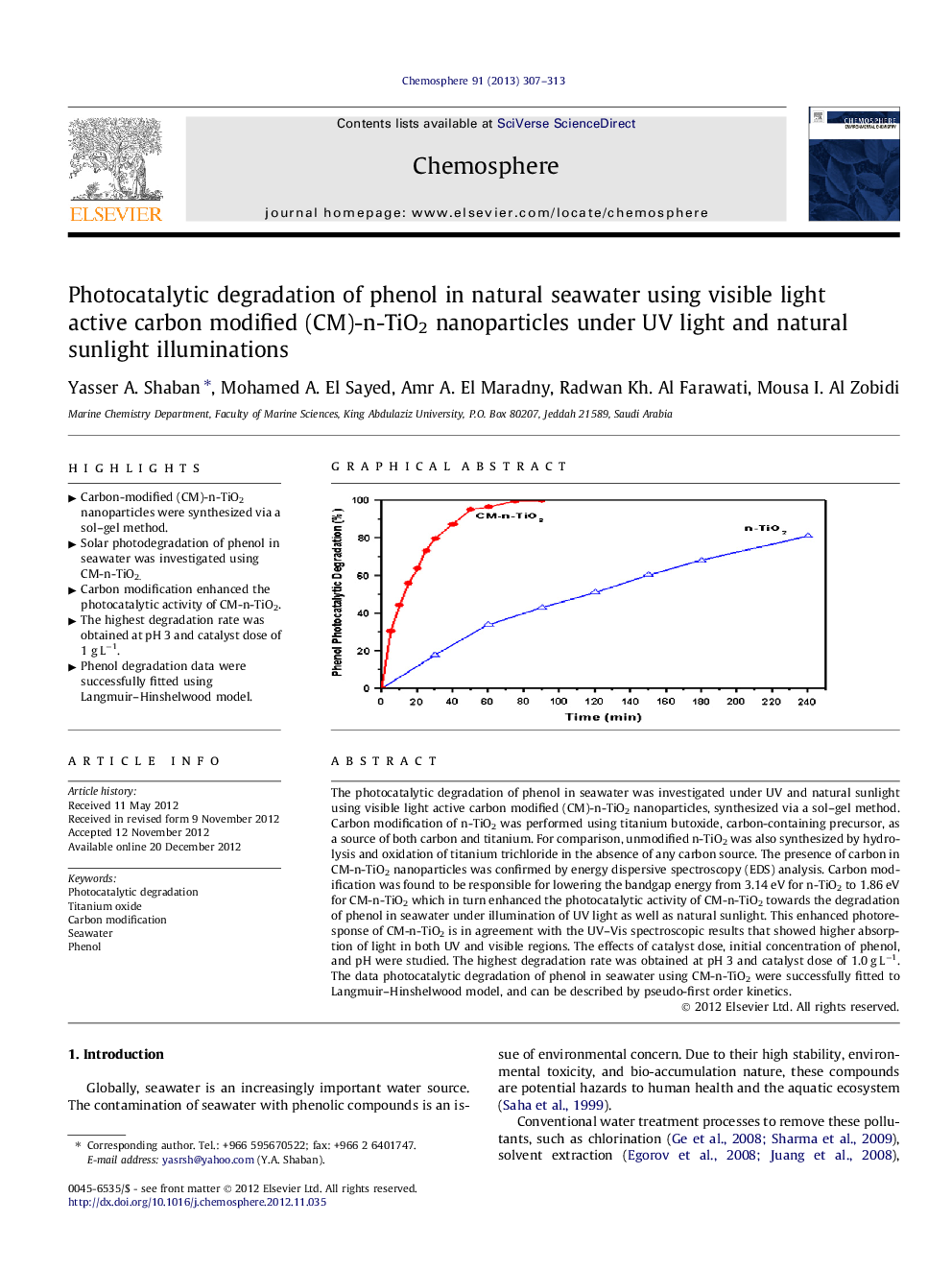
The photocatalytic degradation of phenol in seawater was investigated under UV and natural sunlight using visible light active carbon modified (CM)-n-TiO2 nanoparticles, synthesized via a sol–gel method. Carbon modification of n-TiO2 was performed using titanium butoxide, carbon-containing precursor, as a source of both carbon and titanium. For comparison, unmodified n-TiO2 was also synthesized by hydrolysis and oxidation of titanium trichloride in the absence of any carbon source. The presence of carbon in CM-n-TiO2 nanoparticles was confirmed by energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis. Carbon modification was found to be responsible for lowering the bandgap energy from 3.14 eV for n-TiO2 to 1.86 eV for CM-n-TiO2 which in turn enhanced the photocatalytic activity of CM-n-TiO2 towards the degradation of phenol in seawater under illumination of UV light as well as natural sunlight. This enhanced photoresponse of CM-n-TiO2 is in agreement with the UV–Vis spectroscopic results that showed higher absorption of light in both UV and visible regions. The effects of catalyst dose, initial concentration of phenol, and pH were studied. The highest degradation rate was obtained at pH 3 and catalyst dose of 1.0 g L−1. The data photocatalytic degradation of phenol in seawater using CM-n-TiO2 were successfully fitted to Langmuir–Hinshelwood model, and can be described by pseudo-first order kinetics.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Carbon-modified (CM)-n-TiO2 nanoparticles were synthesized via a sol–gel method.
► Solar photodegradation of phenol in seawater was investigated using CM-n-TiO2.
► Carbon modification enhanced the photocatalytic activity of CM-n-TiO2.
► The highest degradation rate was obtained at pH 3 and catalyst dose of 1 g L−1.
► Phenol degradation data were successfully fitted using Langmuir–Hinshelwood model.
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 91, Issue 3, April 2013, Pages 307–313