| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5130685 | 1490845 | 2017 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
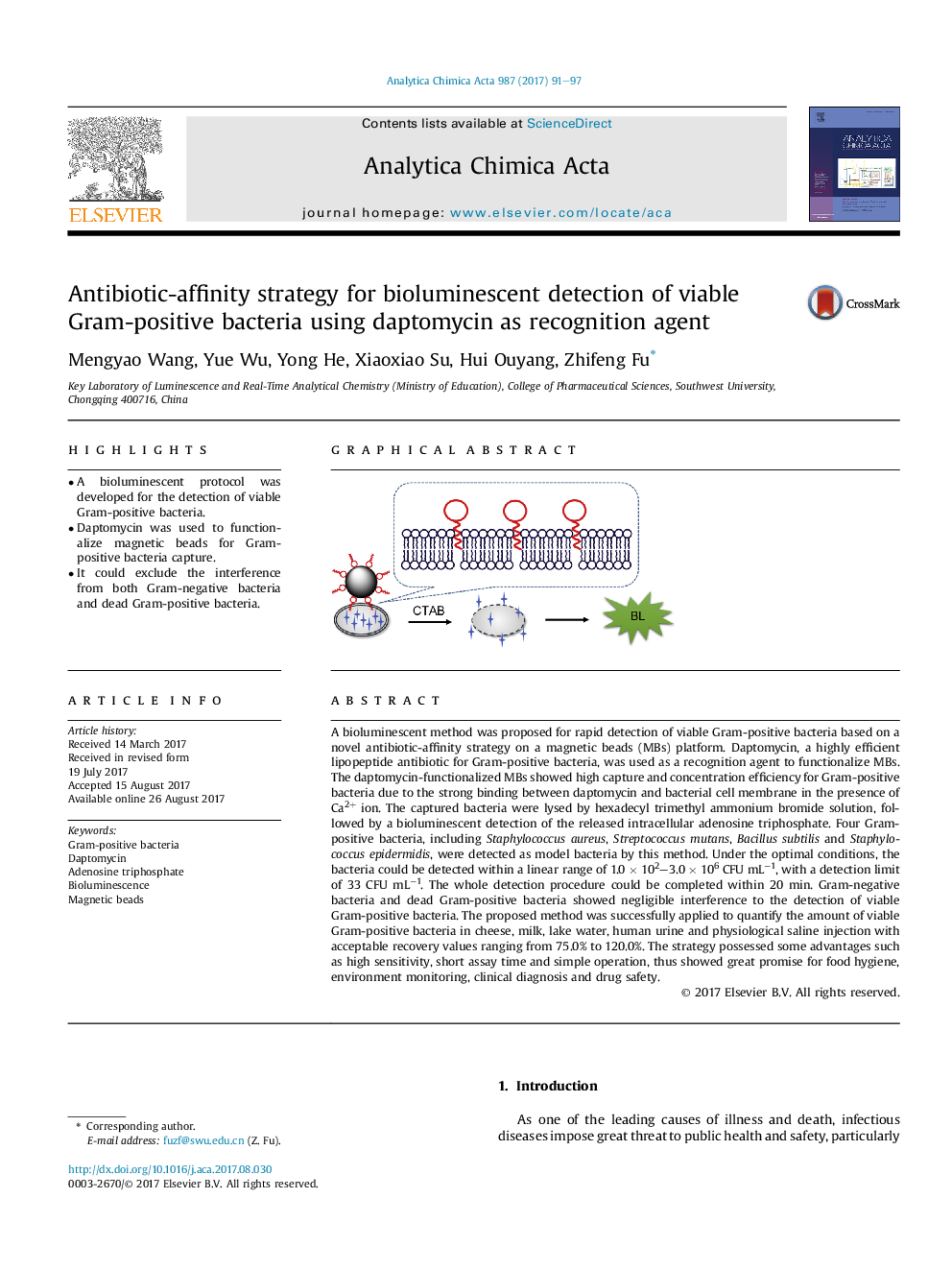
- A bioluminescent protocol was developed for the detection of viable Gram-positive bacteria.
- Daptomycin was used to functionalize magnetic beads for Gram-positive bacteria capture.
- It could exclude the interference from both Gram-negative bacteria and dead Gram-positive bacteria.
A bioluminescent method was proposed for rapid detection of viable Gram-positive bacteria based on a novel antibiotic-affinity strategy on a magnetic beads (MBs) platform. Daptomycin, a highly efficient lipopeptide antibiotic for Gram-positive bacteria, was used as a recognition agent to functionalize MBs. The daptomycin-functionalized MBs showed high capture and concentration efficiency for Gram-positive bacteria due to the strong binding between daptomycin and bacterial cell membrane in the presence of Ca2+ ion. The captured bacteria were lysed by hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide solution, followed by a bioluminescent detection of the released intracellular adenosine triphosphate. Four Gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus mutans, Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus epidermidis, were detected as model bacteria by this method. Under the optimal conditions, the bacteria could be detected within a linear range of 1.0Â ÃÂ 102-3.0Â ÃÂ 106Â CFUÂ mLâ1, with a detection limit of 33Â CFUÂ mLâ1. The whole detection procedure could be completed within 20Â min. Gram-negative bacteria and dead Gram-positive bacteria showed negligible interference to the detection of viable Gram-positive bacteria. The proposed method was successfully applied to quantify the amount of viable Gram-positive bacteria in cheese, milk, lake water, human urine and physiological saline injection with acceptable recovery values ranging from 75.0% to 120.0%. The strategy possessed some advantages such as high sensitivity, short assay time and simple operation, thus showed great promise for food hygiene, environment monitoring, clinical diagnosis and drug safety.
A bioluminescent method was developed for the detection of viable Gram-positive bacteria captured by daptomycin-functionalized magnetic beads.256
Journal: Analytica Chimica Acta - Volume 987, 22 September 2017, Pages 91-97