| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5746199 | 1618787 | 2017 | 7 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
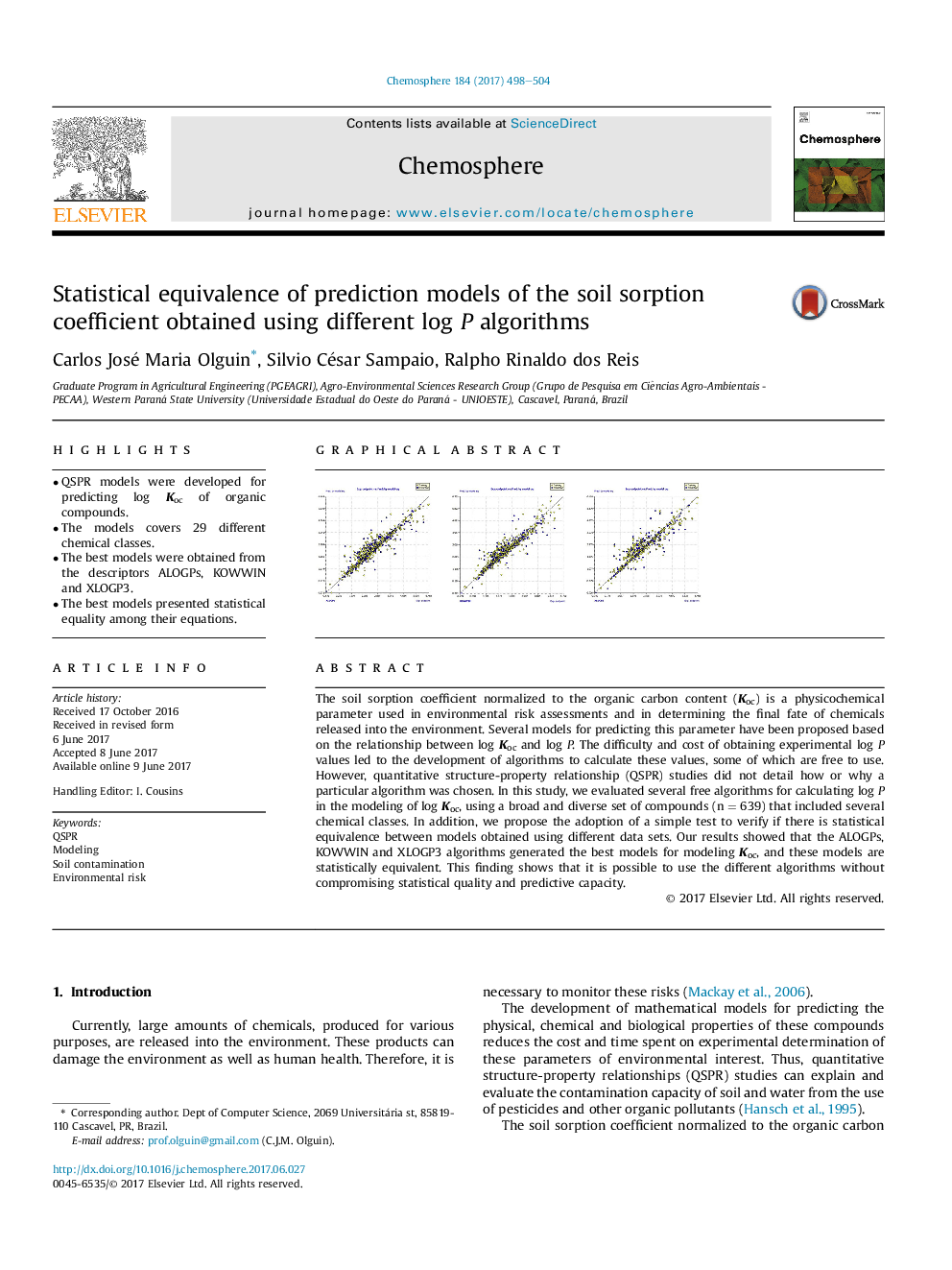
- QSPR models were developed for predicting log Koc of organic compounds.
- The models covers 29 different chemical classes.
- The best models were obtained from the descriptors ALOGPs, KOWWIN and XLOGP3.
- The best models presented statistical equality among their equations.
The soil sorption coefficient normalized to the organic carbon content (Koc) is a physicochemical parameter used in environmental risk assessments and in determining the final fate of chemicals released into the environment. Several models for predicting this parameter have been proposed based on the relationship between log Koc and log P. The difficulty and cost of obtaining experimental log P values led to the development of algorithms to calculate these values, some of which are free to use. However, quantitative structure-property relationship (QSPR) studies did not detail how or why a particular algorithm was chosen. In this study, we evaluated several free algorithms for calculating log P in the modeling of log Koc, using a broad and diverse set of compounds (n = 639) that included several chemical classes. In addition, we propose the adoption of a simple test to verify if there is statistical equivalence between models obtained using different data sets. Our results showed that the ALOGPs, KOWWIN and XLOGP3 algorithms generated the best models for modeling Koc, and these models are statistically equivalent. This finding shows that it is possible to use the different algorithms without compromising statistical quality and predictive capacity.
300
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 184, October 2017, Pages 498-504