| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5746596 | 1618803 | 2017 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
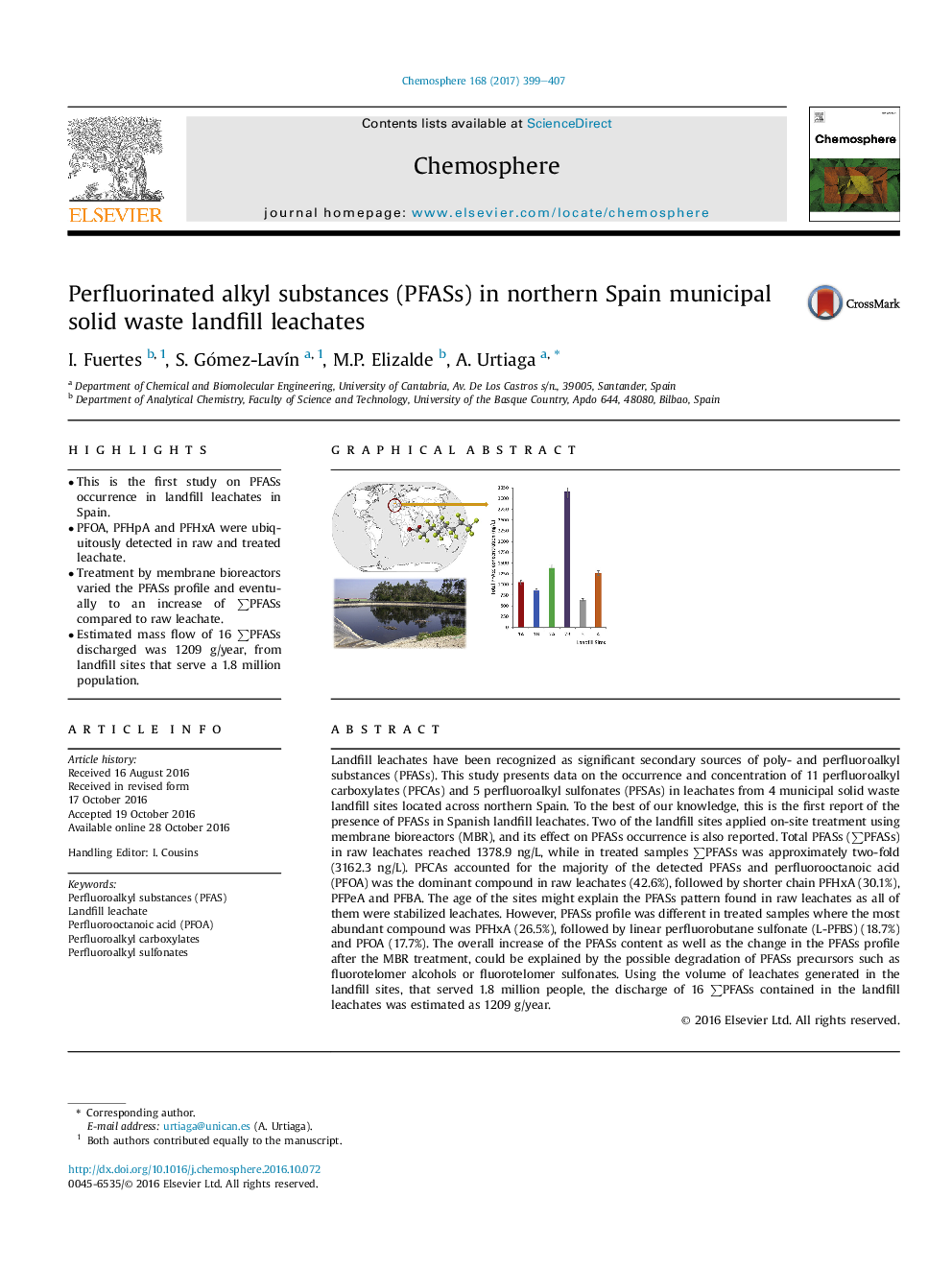
- This is the first study on PFASs occurrence in landfill leachates in Spain.
- PFOA, PFHpA and PFHxA were ubiquitously detected in raw and treated leachate.
- Treatment by membrane bioreactors varied the PFASs profile and eventually to an increase of âPFASs compared to raw leachate.
- Estimated mass flow of 16 âPFASs discharged was 1209 g/year, from landfill sites that serve a 1.8 million population.
Landfill leachates have been recognized as significant secondary sources of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). This study presents data on the occurrence and concentration of 11 perfluoroalkyl carboxylates (PFCAs) and 5 perfluoroalkyl sulfonates (PFSAs) in leachates from 4 municipal solid waste landfill sites located across northern Spain. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of the presence of PFASs in Spanish landfill leachates. Two of the landfill sites applied on-site treatment using membrane bioreactors (MBR), and its effect on PFASs occurrence is also reported. Total PFASs (âPFASs) in raw leachates reached 1378.9Â ng/L, while in treated samples âPFASs was approximately two-fold (3162.3Â ng/L). PFCAs accounted for the majority of the detected PFASs and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was the dominant compound in raw leachates (42.6%), followed by shorter chain PFHxA (30.1%), PFPeA and PFBA. The age of the sites might explain the PFASs pattern found in raw leachates as all of them were stabilized leachates. However, PFASs profile was different in treated samples where the most abundant compound was PFHxA (26.5%), followed by linear perfluorobutane sulfonate (L-PFBS) (18.7%) and PFOA (17.7%). The overall increase of the PFASs content as well as the change in the PFASs profile after the MBR treatment, could be explained by the possible degradation of PFASs precursors such as fluorotelomer alcohols or fluorotelomer sulfonates. Using the volume of leachates generated in the landfill sites, that served 1.8 million people, the discharge of 16 âPFASs contained in the landfill leachates was estimated as 1209Â g/year.
259
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 168, February 2017, Pages 399-407