| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5747165 | 1618790 | 2017 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
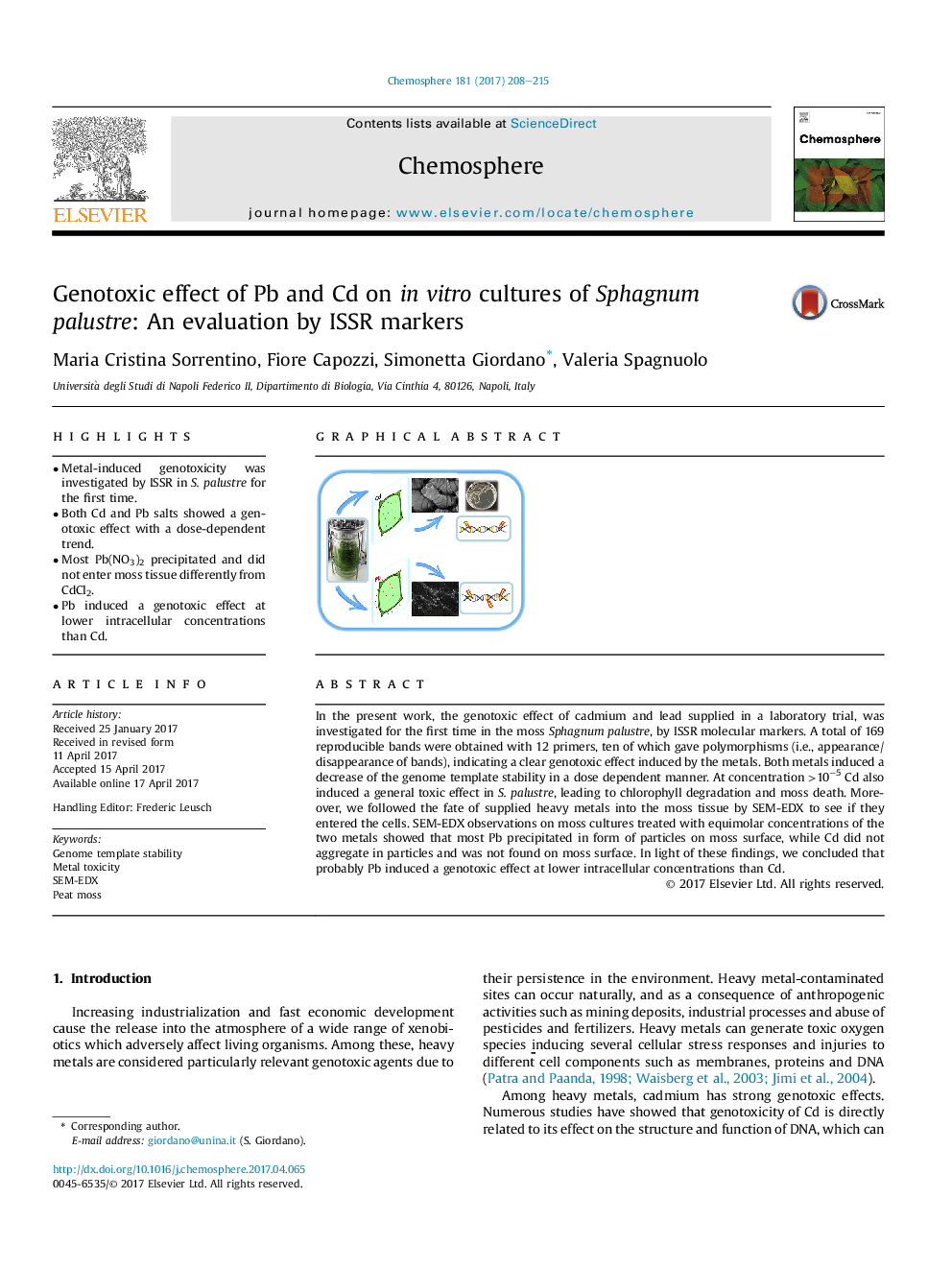
- Metal-induced genotoxicity was investigated by ISSR in S. palustre for the first time.
- Both Cd and Pb salts showed a genotoxic effect with a dose-dependent trend.
- Most Pb(NO3)2 precipitated and did not enter moss tissue differently from CdCl2.
- Pb induced a genotoxic effect at lower intracellular concentrations than Cd.
In the present work, the genotoxic effect of cadmium and lead supplied in a laboratory trial, was investigated for the first time in the moss Sphagnum palustre, by ISSR molecular markers. A total of 169 reproducible bands were obtained with 12 primers, ten of which gave polymorphisms (i.e., appearance/disappearance of bands), indicating a clear genotoxic effect induced by the metals. Both metals induced a decrease of the genome template stability in a dose dependent manner. At concentration >10â5 Cd also induced a general toxic effect in S. palustre, leading to chlorophyll degradation and moss death. Moreover, we followed the fate of supplied heavy metals into the moss tissue by SEM-EDX to see if they entered the cells. SEM-EDX observations on moss cultures treated with equimolar concentrations of the two metals showed that most Pb precipitated in form of particles on moss surface, while Cd did not aggregate in particles and was not found on moss surface. In light of these findings, we concluded that probably Pb induced a genotoxic effect at lower intracellular concentrations than Cd.
232
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 181, August 2017, Pages 208-215