| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5750646 | 1619695 | 2017 | 14 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
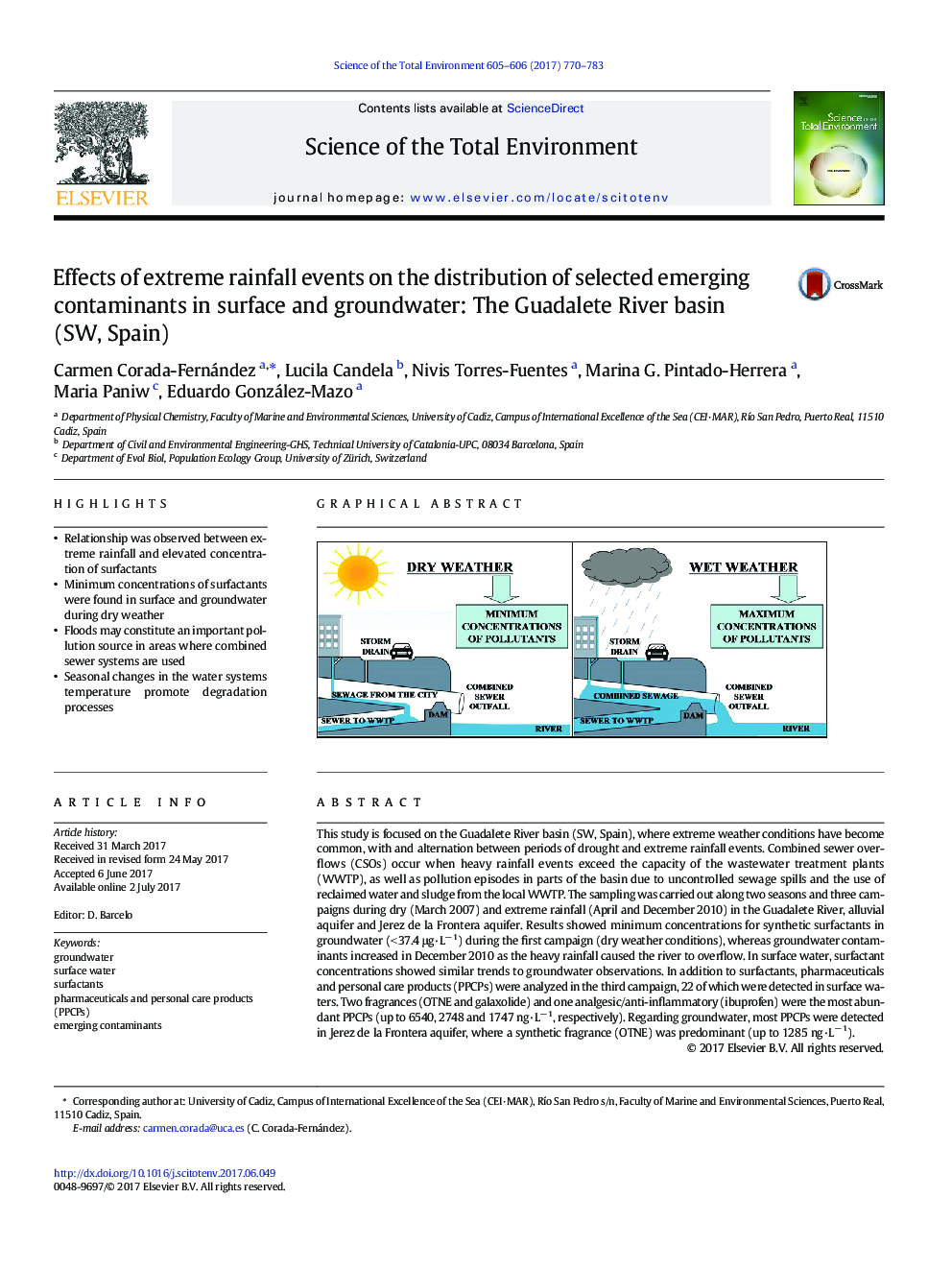
- Relationship was observed between extreme rainfall and elevated concentration of surfactants
- Minimum concentrations of surfactants were found in surface and groundwater during dry weather
- Floods may constitute an important pollution source in areas where combined sewer systems are used
- Seasonal changes in the water systems temperature promote degradation processes
This study is focused on the Guadalete River basin (SW, Spain), where extreme weather conditions have become common, with and alternation between periods of drought and extreme rainfall events. Combined sewer overflows (CSOs) occur when heavy rainfall events exceed the capacity of the wastewater treatment plants (WWTP), as well as pollution episodes in parts of the basin due to uncontrolled sewage spills and the use of reclaimed water and sludge from the local WWTP. The sampling was carried out along two seasons and three campaigns during dry (March 2007) and extreme rainfall (April and December 2010) in the Guadalete River, alluvial aquifer and Jerez de la Frontera aquifer. Results showed minimum concentrations for synthetic surfactants in groundwater (< 37.4 μg·Lâ 1) during the first campaign (dry weather conditions), whereas groundwater contaminants increased in December 2010 as the heavy rainfall caused the river to overflow. In surface water, surfactant concentrations showed similar trends to groundwater observations. In addition to surfactants, pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) were analyzed in the third campaign, 22 of which were detected in surface waters. Two fragrances (OTNE and galaxolide) and one analgesic/anti-inflammatory (ibuprofen) were the most abundant PPCPs (up to 6540, 2748 and 1747 ng·Lâ 1, respectively). Regarding groundwater, most PPCPs were detected in Jerez de la Frontera aquifer, where a synthetic fragrance (OTNE) was predominant (up to 1285 ng·Lâ 1).
257
Journal: Science of The Total Environment - Volumes 605â606, 15 December 2017, Pages 770-783