| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593300 | 1453934 | 2013 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
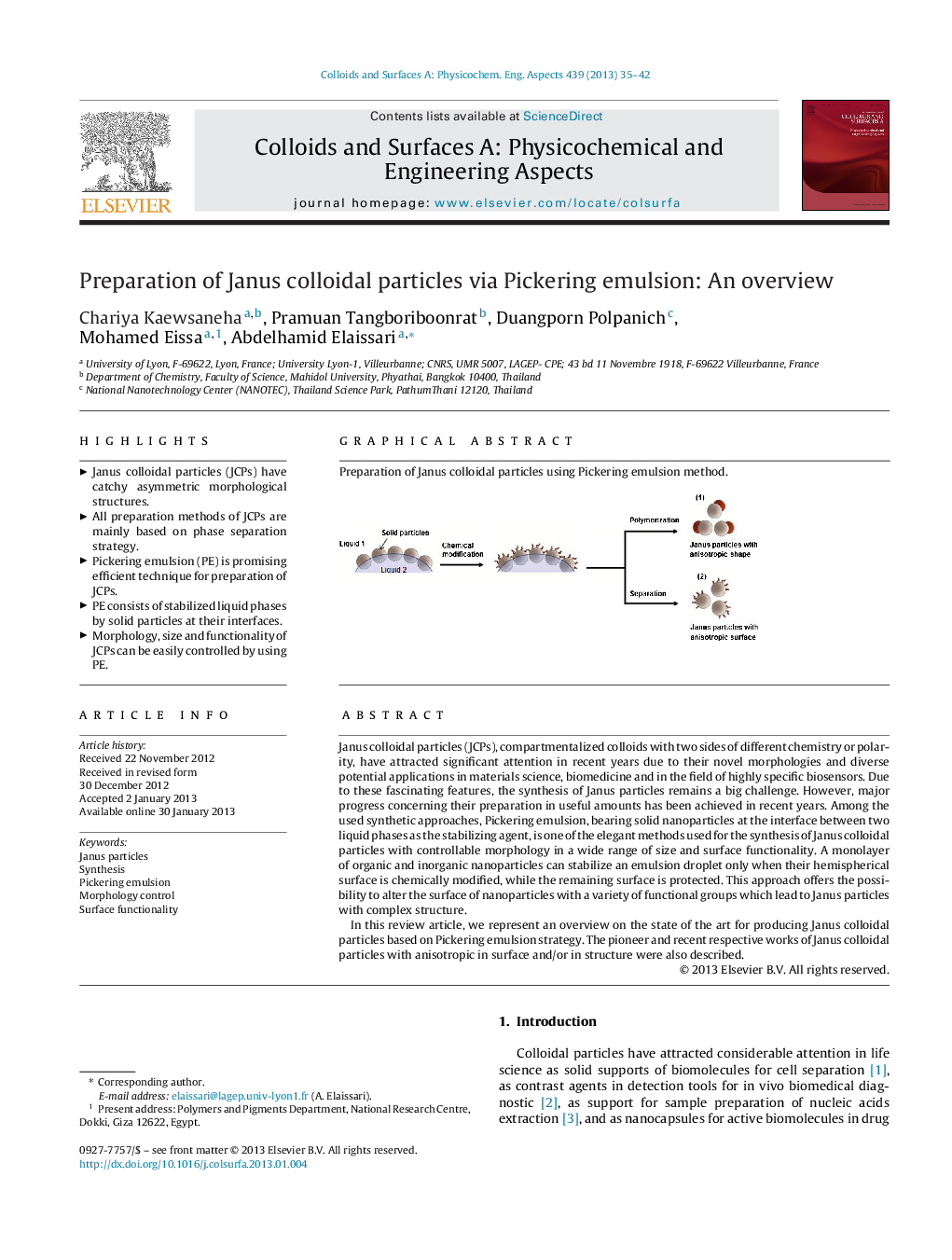
Janus colloidal particles (JCPs), compartmentalized colloids with two sides of different chemistry or polarity, have attracted significant attention in recent years due to their novel morphologies and diverse potential applications in materials science, biomedicine and in the field of highly specific biosensors. Due to these fascinating features, the synthesis of Janus particles remains a big challenge. However, major progress concerning their preparation in useful amounts has been achieved in recent years. Among the used synthetic approaches, Pickering emulsion, bearing solid nanoparticles at the interface between two liquid phases as the stabilizing agent, is one of the elegant methods used for the synthesis of Janus colloidal particles with controllable morphology in a wide range of size and surface functionality. A monolayer of organic and inorganic nanoparticles can stabilize an emulsion droplet only when their hemispherical surface is chemically modified, while the remaining surface is protected. This approach offers the possibility to alter the surface of nanoparticles with a variety of functional groups which lead to Janus particles with complex structure.In this review article, we represent an overview on the state of the art for producing Janus colloidal particles based on Pickering emulsion strategy. The pioneer and recent respective works of Janus colloidal particles with anisotropic in surface and/or in structure were also described.
Preparation of Janus colloidal particles using Pickering emulsion method.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Janus colloidal particles (JCPs) have catchy asymmetric morphological structures.
► All preparation methods of JCPs are mainly based on phase separation strategy.
► Pickering emulsion (PE) is promising efficient technique for preparation of JCPs.
► PE consists of stabilized liquid phases by solid particles at their interfaces.
► Morphology, size and functionality of JCPs can be easily controlled by using PE.
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 439, 20 December 2013, Pages 35–42