| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593694 | 1453953 | 2013 | 6 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
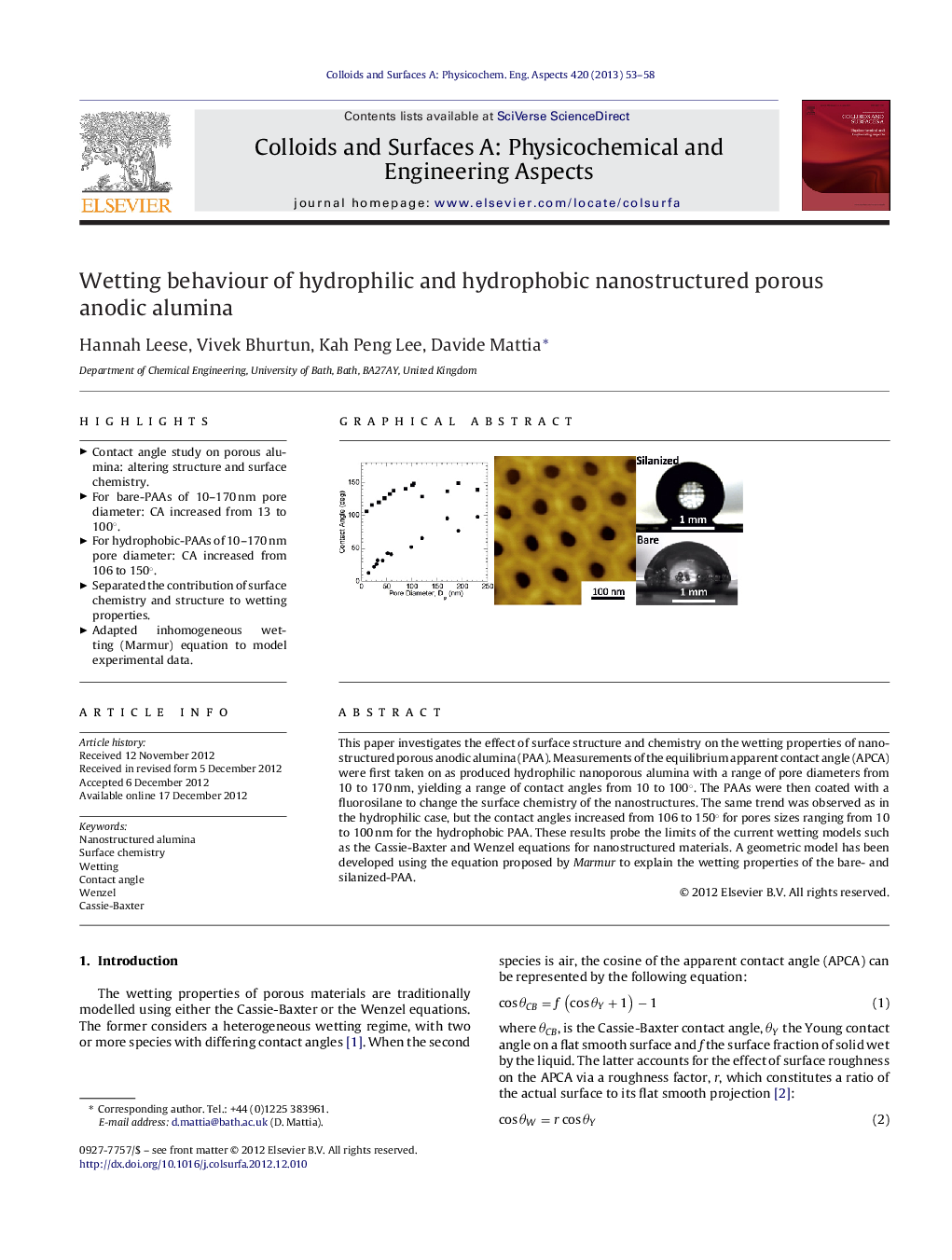
This paper investigates the effect of surface structure and chemistry on the wetting properties of nanostructured porous anodic alumina (PAA). Measurements of the equilibrium apparent contact angle (APCA) were first taken on as produced hydrophilic nanoporous alumina with a range of pore diameters from 10 to 170 nm, yielding a range of contact angles from 10 to 100°. The PAAs were then coated with a fluorosilane to change the surface chemistry of the nanostructures. The same trend was observed as in the hydrophilic case, but the contact angles increased from 106 to 150° for pores sizes ranging from 10 to 100 nm for the hydrophobic PAA. These results probe the limits of the current wetting models such as the Cassie-Baxter and Wenzel equations for nanostructured materials. A geometric model has been developed using the equation proposed by Marmur to explain the wetting properties of the bare- and silanized-PAA.
Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Contact angle study on porous alumina: altering structure and surface chemistry.
► For bare-PAAs of 10–170 nm pore diameter: CA increased from 13 to 100°.
► For hydrophobic-PAAs of 10–170 nm pore diameter: CA increased from 106 to 150°.
► Separated the contribution of surface chemistry and structure to wetting properties.
► Adapted inhomogeneous wetting (Marmur) equation to model experimental data.
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 420, 5 March 2013, Pages 53–58