| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593740 | 1453952 | 2013 | 12 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
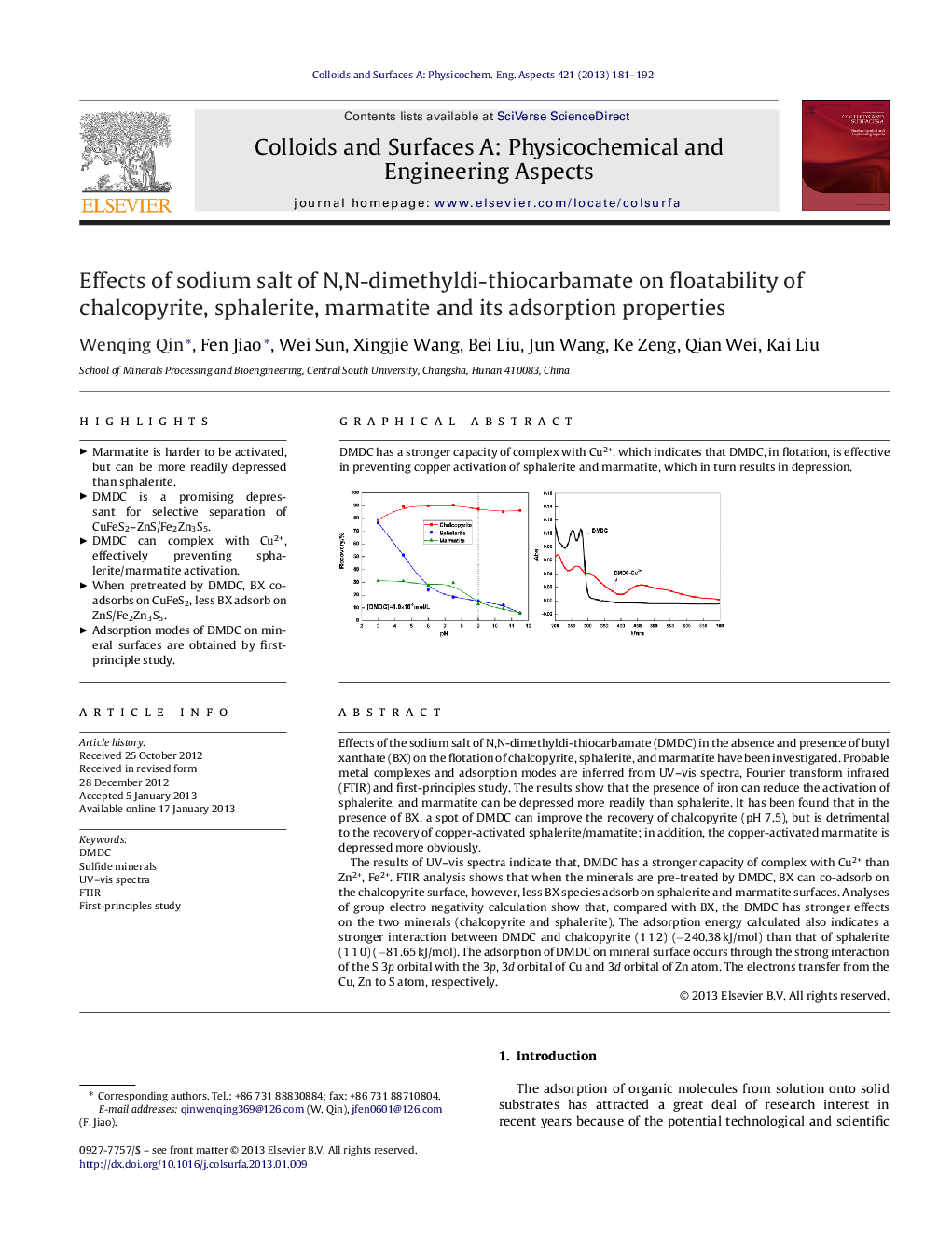
Effects of the sodium salt of N,N-dimethyldi-thiocarbamate (DMDC) in the absence and presence of butyl xanthate (BX) on the flotation of chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and marmatite have been investigated. Probable metal complexes and adsorption modes are inferred from UV–vis spectra, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and first-principles study. The results show that the presence of iron can reduce the activation of sphalerite, and marmatite can be depressed more readily than sphalerite. It has been found that in the presence of BX, a spot of DMDC can improve the recovery of chalcopyrite (pH 7.5), but is detrimental to the recovery of copper-activated sphalerite/mamatite; in addition, the copper-activated marmatite is depressed more obviously.The results of UV–vis spectra indicate that, DMDC has a stronger capacity of complex with Cu2+ than Zn2+, Fe2+. FTIR analysis shows that when the minerals are pre-treated by DMDC, BX can co-adsorb on the chalcopyrite surface, however, less BX species adsorb on sphalerite and marmatite surfaces. Analyses of group electro negativity calculation show that, compared with BX, the DMDC has stronger effects on the two minerals (chalcopyrite and sphalerite). The adsorption energy calculated also indicates a stronger interaction between DMDC and chalcopyrite (1 1 2) (−240.38 kJ/mol) than that of sphalerite (1 1 0) (−81.65 kJ/mol). The adsorption of DMDC on mineral surface occurs through the strong interaction of the S 3p orbital with the 3p, 3d orbital of Cu and 3d orbital of Zn atom. The electrons transfer from the Cu, Zn to S atom, respectively.
Graphical AbstractDMDC has a stronger capacity of complex with Cu2+, which indicates that DMDC, in flotation, is effective in preventing copper activation of sphalerite and marmatite, which in turn results in depression.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► Marmatite is harder to be activated, but can be more readily depressed than sphalerite.
► DMDC is a promising depressant for selective separation of CuFeS2–ZnS/Fe2Zn3S5.
► DMDC can complex with Cu2+, effectively preventing sphalerite/marmatite activation.
► When pretreated by DMDC, BX co-adsorbs on CuFeS2, less BX adsorb on ZnS/Fe2Zn3S5.
► Adsorption modes of DMDC on mineral surfaces are obtained by first-principle study.
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 421, 20 March 2013, Pages 181–192