| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593883 | 1453958 | 2012 | 8 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
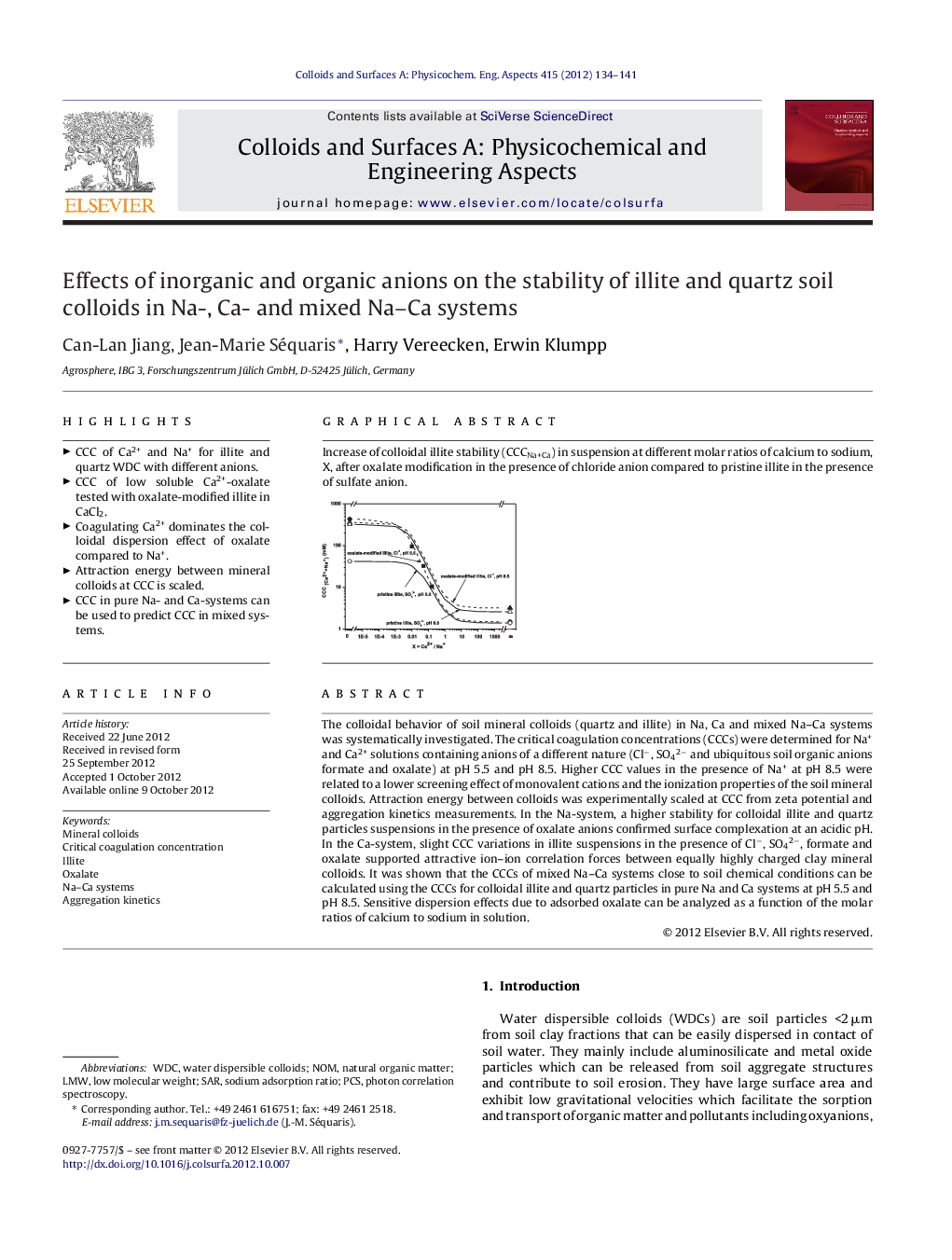
The colloidal behavior of soil mineral colloids (quartz and illite) in Na, Ca and mixed Na–Ca systems was systematically investigated. The critical coagulation concentrations (CCCs) were determined for Na+ and Ca2+ solutions containing anions of a different nature (Cl−, SO42− and ubiquitous soil organic anions formate and oxalate) at pH 5.5 and pH 8.5. Higher CCC values in the presence of Na+ at pH 8.5 were related to a lower screening effect of monovalent cations and the ionization properties of the soil mineral colloids. Attraction energy between colloids was experimentally scaled at CCC from zeta potential and aggregation kinetics measurements. In the Na-system, a higher stability for colloidal illite and quartz particles suspensions in the presence of oxalate anions confirmed surface complexation at an acidic pH. In the Ca-system, slight CCC variations in illite suspensions in the presence of Cl−, SO42−, formate and oxalate supported attractive ion–ion correlation forces between equally highly charged clay mineral colloids. It was shown that the CCCs of mixed Na–Ca systems close to soil chemical conditions can be calculated using the CCCs for colloidal illite and quartz particles in pure Na and Ca systems at pH 5.5 and pH 8.5. Sensitive dispersion effects due to adsorbed oxalate can be analyzed as a function of the molar ratios of calcium to sodium in solution.
Increase of colloidal illite stability (CCCNa+Ca) in suspension at different molar ratios of calcium to sodium, X, after oxalate modification in the presence of chloride anion compared to pristine illite in the presence of sulfate anion.Figure optionsDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights
► CCC of Ca2+ and Na+ for illite and quartz WDC with different anions.
► CCC of low soluble Ca2+-oxalate tested with oxalate-modified illite in CaCl2.
► Coagulating Ca2+ dominates the colloidal dispersion effect of oxalate compared to Na+.
► Attraction energy between mineral colloids at CCC is scaled.
► CCC in pure Na- and Ca-systems can be used to predict CCC in mixed systems.
Journal: Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects - Volume 415, 5 December 2012, Pages 134–141