| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6309140 | 1618864 | 2014 | 10 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
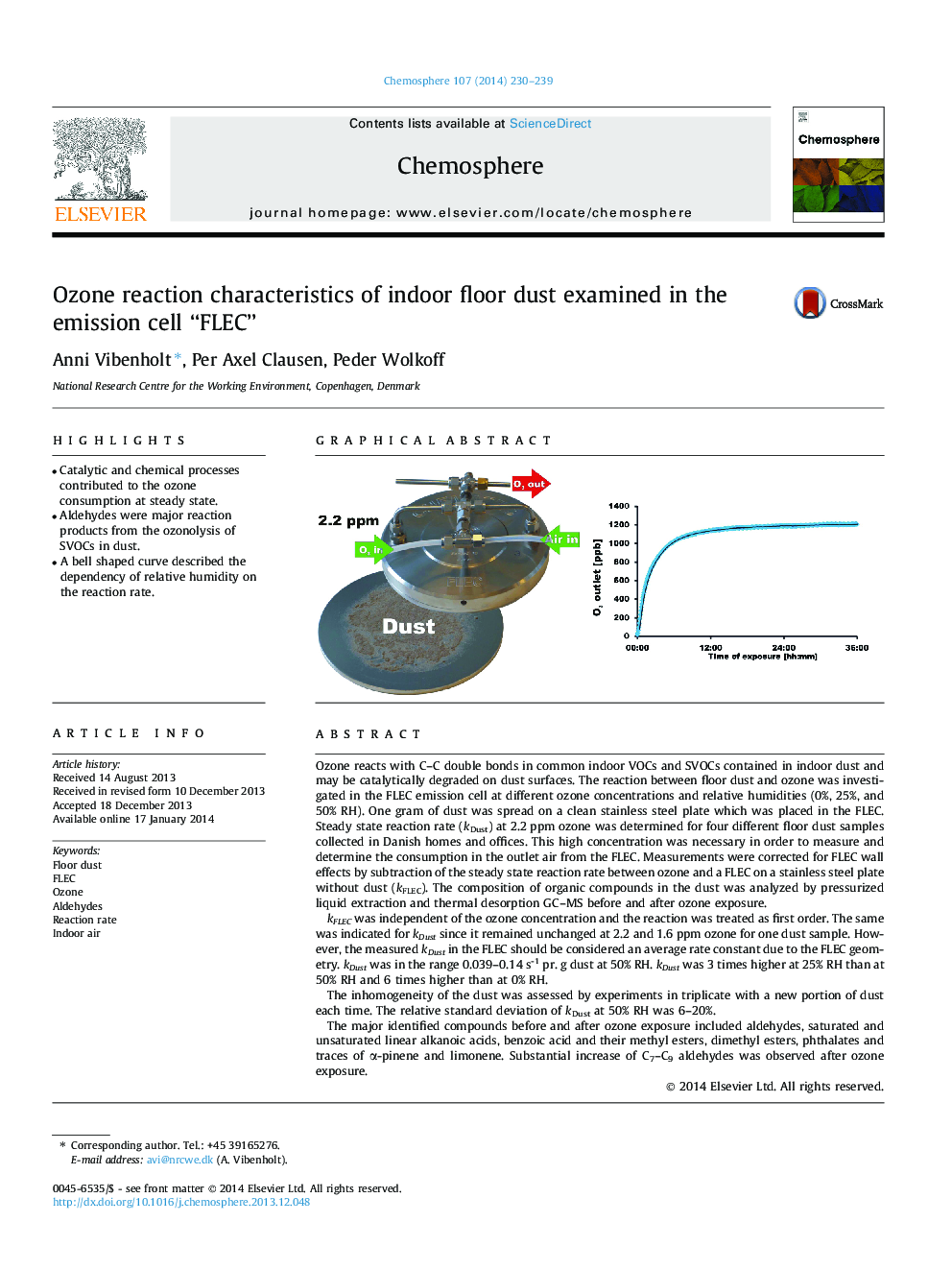
- Catalytic and chemical processes contributed to the ozone consumption at steady state.
- Aldehydes were major reaction products from the ozonolysis of SVOCs in dust.
- A bell shaped curve described the dependency of relative humidity on the reaction rate.
Ozone reacts with C-C double bonds in common indoor VOCs and SVOCs contained in indoor dust and may be catalytically degraded on dust surfaces. The reaction between floor dust and ozone was investigated in the FLEC emission cell at different ozone concentrations and relative humidities (0%, 25%, and 50% RH). One gram of dust was spread on a clean stainless steel plate which was placed in the FLEC. Steady state reaction rate (kDust) at 2.2 ppm ozone was determined for four different floor dust samples collected in Danish homes and offices. This high concentration was necessary in order to measure and determine the consumption in the outlet air from the FLEC. Measurements were corrected for FLEC wall effects by subtraction of the steady state reaction rate between ozone and a FLEC on a stainless steel plate without dust (kFLEC). The composition of organic compounds in the dust was analyzed by pressurized liquid extraction and thermal desorption GC-MS before and after ozone exposure.kFLEC was independent of the ozone concentration and the reaction was treated as first order. The same was indicated for kDust since it remained unchanged at 2.2 and 1.6 ppm ozone for one dust sample. However, the measured kDust in the FLEC should be considered an average rate constant due to the FLEC geometry. kDust was in the range 0.039-0.14 s-1 pr. g dust at 50% RH. kDust was 3 times higher at 25% RH than at 50% RH and 6 times higher than at 0% RH.The inhomogeneity of the dust was assessed by experiments in triplicate with a new portion of dust each time. The relative standard deviation of kDust at 50% RH was 6-20%.The major identified compounds before and after ozone exposure included aldehydes, saturated and unsaturated linear alkanoic acids, benzoic acid and their methyl esters, dimethyl esters, phthalates and traces of α-pinene and limonene. Substantial increase of C7-C9 aldehydes was observed after ozone exposure.
Journal: Chemosphere - Volume 107, July 2014, Pages 230-239