| کد مقاله | کد نشریه | سال انتشار | مقاله انگلیسی | نسخه تمام متن |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6466072 | 1422953 | 2017 | 9 صفحه PDF | دانلود رایگان |
- A porous hexagonal boron nitride (p-BN) was facile prepared and characterized.
- p-BN had a superior adsorption capacity (322.16 mg gâ1) to tetracycline.
- Adsorption process was spontaneous and exothermic.
- The adsorption fitted the Freundlich and Tempkin model well.
- The adsorption mechanisms were mainly Ï-Ï interaction and electrostatic force.
The antibiotic contaminants from drug abuse, aquaculture wastewater and pharmaceutical industry effluent have enormous threat to microecology and human beings. In this paper, a porous hexagonal boron nitride (p-BN), which has high surface area up to 1062.88 m2 gâ1 and abundant pore structure, was prepared and characterized by XRD, SEM, FT-IR and physical-chemical isothermal adsorption. A systematical and comprehensive study of the adsorption kinetics, thermodynamics and isotherms of tetracycline (TC) on p-BN has been completed. Meanwhile, the effects of pH, temperature and salinity were also considered. It still had a rapidly adsorption rate and effective removal percentage (94.25%) to TC at high concentration. The maximum adsorption capacity can achieve to 322.16 mg gâ1 at the concentration of 160 mg Lâ1. Pseudo-second-order model and intra-particle diffusion model correlate with the experiment data better, the molecular diffusion of TC in the p-BN micropores is the rate-limiting step. Adsorption process was spontaneous and exothermic due to the thermodynamic calculation, lower temperatures is favorable to the adsorption process. Salting out effect made the adsorption capacity increases with the added Na+ ion. The adsorption isotherms were more accordant with the Freundlich and Tempkin model. The adsorption mechanisms were mainly Ï-Ï interaction and electrostatic force.
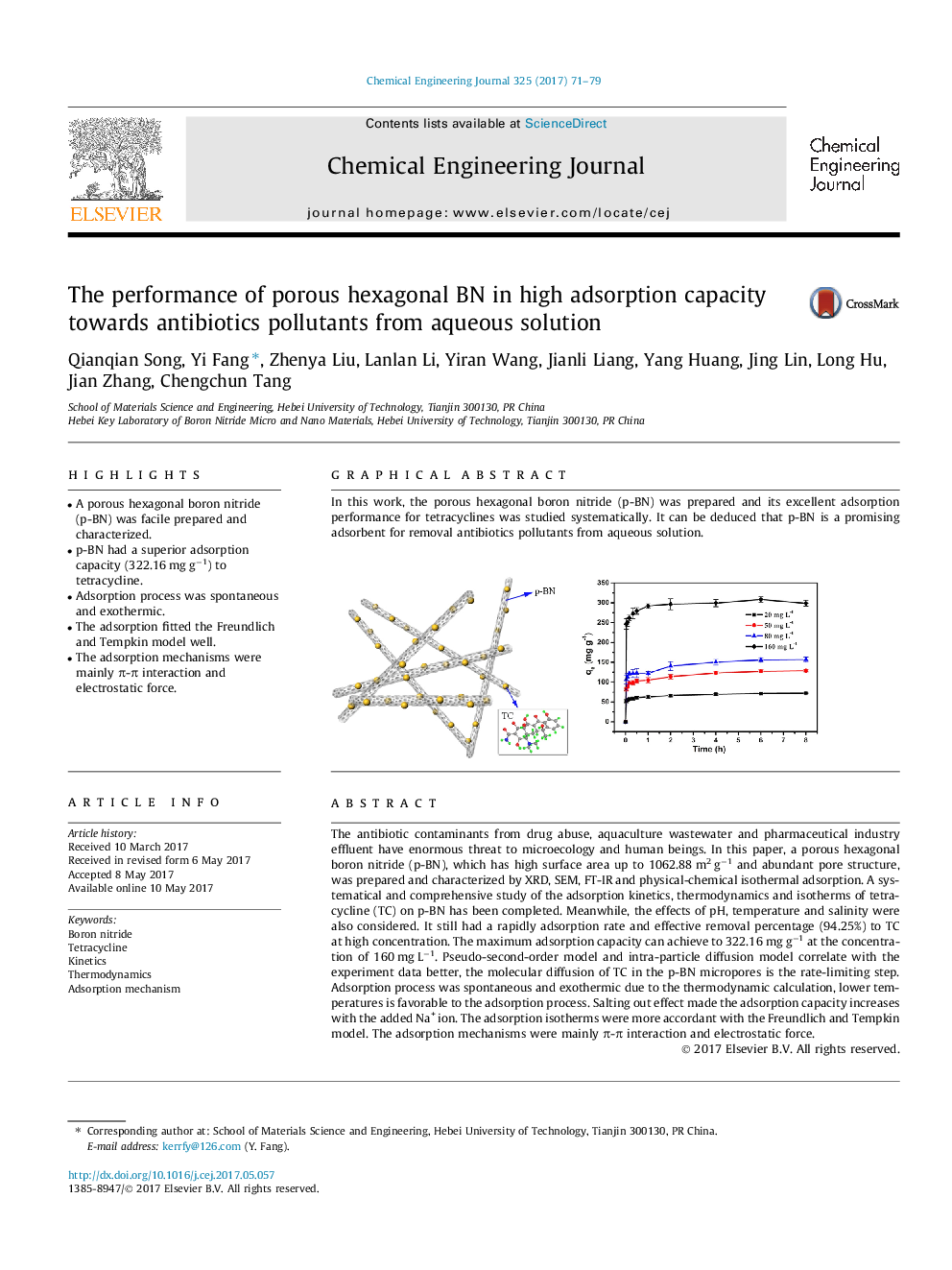
In this work, the porous hexagonal boron nitride (p-BN) was prepared and its excellent adsorption performance for tetracyclines was studied systematically. It can be deduced that p-BN is a promising adsorbent for removal antibiotics pollutants from aqueous solution.83
Journal: Chemical Engineering Journal - Volume 325, 1 October 2017, Pages 71-79